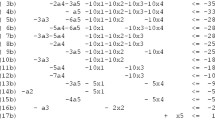Abstract
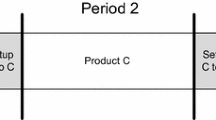
The economic lot scheduling problem schedules the production of several different products on a single machine over an infinite planning horizon. In this paper, a nonlinear integer programming model is used to determine the optimal solution under the extended basic period and power-of-two policy. A small-step search algorithm is presented to find a solution which approaches optimal when the step size approaches zero, where a divide-and-conquer procedure is introduced to speed up the search. Further a faster heuristic algorithm is proposed which finds the same solutions in almost all the randomly generated sample cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boctor F.F.: The g-group heuristic for single machine lot scheduling. Int. J. Prod. Res. 25, 363–379 (1987)
Bomberger E.: A dynamic programming approach to a lot size scheduling problem. Manage. Sci. 12, 778–784 (1966)
Chatfield D.: The economic lot scheduling problem: a pure genetic search approach. Comput. Oper. Res. 34, 2865–2881 (1987)
Dobson G.: The economic lot scheduling problem: achieving feasibility using time-varying lot sizes. Oper. Res. 35, 764–771 (1987)
Doll C.L., Whybark D.C.: An interactive procedure for the single-machine multi-product lot scheduling problem. Manage. Sci. 20, 50–55 (1973)
Elmaghraby S.E.: The economic lot scheduling problem (ELSP): review and extensions. Manage. Sci. 24, 587–598 (1978)
Geng P.C., Vickson R.G.: Two heuristics for the economic lot scheduling problem: an experimental study. Nav. Res. Logist. 35, 605–617 (1988)
Grznar J., Riggle C.: An optimal algorithm for the basic period approach to the economic lot scheduling problem. Omega 25, 355–364 (1997)
Haessler R.: An improved extended basic period procedure for solving the economic lot scheduling problem. AIIE Trans. 11, 355–364 (1979)
Hanssmann F.: Operations Research in Production and Inventory Control. Wiley, New York (1962)
Lopez M.A., Kingsman B.G.: The economic lot scheduling problem: theory and practice. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 23, 147–164 (1991)
Madigan J.C.: Scheduling a multi-product single machine system for an infinite planning period. Manage. Sci. 14, 713–719 (1968)
Roundy R.: Rounding off to powers of two in continuous relaxations of capacitated lot sizing problems. Manage. Sci. 35, 1433–1442 (1989)
Yao M., Elmaghraby S.: The economic lot scheduling problem under power-of-two policy. Comput. Math. Appl. 41, 1379–1393 (2001)
Zipkin P.: Computing optimal lot sizes in the economic lot scheduling problem. Oper. Res. 39, 56–63 (1991)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, H., Huang, HC. & Jaruphongsa, W. The economic lot scheduling problem under extended basic period and power-of-two policy. Optim Lett 4, 157–172 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-009-0154-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-009-0154-5