Abstract
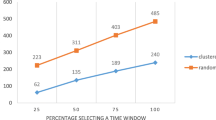
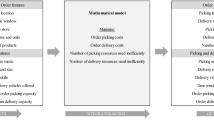
In this paper we address a real industrial application involving a company that manages an e-marketplace for logistics services in the Italian territory. For the carriers, the main service offered by the company consists in the design of the optimal routes integrating additional delivery requests with those already in charge. The aim is to increase the profit exploiting the residual capacity of the vehicles. We model the problem as a multi-vehicle pick-up and delivery problem with mandatory customers. We test the proposed approach on some real instances provided by the company. The computational results confirm the efficacy of the approach in providing more profitable solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, R., Ergun, O.: Network design and allocation mechanisms for carrier alliances in liner shipping. Oper. Res. 58, 1726–1742 (2010)
Nandiraju, S., Regan, A.: Freight transportation electronic marketplaces: a survey of the industry and exploration of important research issues. In: Earlier Faculty Research. University of California Transportation Center (2008)
Berbeglia, G., Cordeau, J.-F., Gribkovskaia, I., Laporte, G.: Static pickup and delivery problems: a classification scheme and survey. TOP 15(1), 1–31 (2007)
Chu, C.-W.: A heuristic algorithm for the truckload and less-than-truckload problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 165(3), 657–667 (2005)
Bolduc, M., Renaud, J., Boctor, F., Laporte, G.: A perturbation metaheuristic for the vehicle routing problem with private fleet and common carriers. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 59(6), 776–787 (2008)
Stenger, A., Vigo, D., Enz, S., Schwind, M.: An adaptive variable neighborhood search algorithm for a vehicle routing problem arising in small package shipping. Transp. Sci. 47(1), 64–80 (2013)
Archetti, C., Speranza, M.G., Vigo, D.: Vehicle routing problems with profits. In: Toth, P., Vigo, D. (eds.) Vehicle Routing: Problems, Methods, and Applications, pp. 273–297. MOS-SIAM series on optimization, Philadelphia (2014)
Gansterer, M., Küçüktepe, M., Hartl, R.F.: The multi-vehicle profitable pickup and delivery problem. OR Spectr. 39(1), 303–319 (2017)
De Maio, A., Violi, A., Laganá, D., Beraldi, P.: A freight adviser for a delivery logistics service e-marketplace. In: Daniele, P., Scrimali, L. (eds.) New Trends in Emerging Complex Real Life Problems. AIRO Springer Series, vol. 1. Springer, Cham (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work has been partially supported by POR Calabria FESR-FSE 2014-2020, with the grant for research project “Smart Macingo”, CUP J18C17000580006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beraldi, P., De Maio, A., Laganà, D. et al. A pick-up and delivery problem for logistics e-marketplace services. Optim Lett 15, 1565–1577 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-019-01472-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-019-01472-3