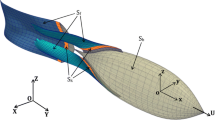
Abstract
Many fishes use undulatory fin to propel themselves in the underwater environment. These locomotor mechanisms have a popular interest to many researchers. In the present study, we perform a three-dimensional unsteady computation of an undulatory mechanical fin that is driven by Shape Memory Alloy (SMA). The objective of the computation is to investigate the fluid dynamics of force production associated with the undulatory mechanical fin. An unstructured, grid-based, unsteady Navier-Stokes solver with automatic adaptive remeshing is used to compute the unsteady flow around the fin through five complete cycles. The pressure distribution on fin surface is computed and integrated to provide fin forces which are decomposed into lift and thrust. The velocity field is also computed throughout the swimming cycle. Finally, a comparison is conducted to reveal the dynamics of force generation according to the kinematic parameters of the undulatory fin (amplitude, frequency and wavelength).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. B. C. Davies, B. Deacon, D. M. Lane, M. Sfakiotakis. Fish Swimming Gaits. [Online], Available: http://www.ece.eps.hw.ac.uk/Research/oceans/projects/flaps/mpfmodes.htm, August, 2006.
J. A. Walker, M. W. Westneat. Performance Limits of Labriform Propulsion and Correlates with Fin Shape and Motion. The Journal of Experimental Biology, vol. 205, no. 2, pp. 177–187, 2002.
L. J. Rosenberger. Pectoral Fin Locomotion in Batoid Fishes: Undulation Versus Oscillation. The Journal of Experimental Biology, vol. 204, no. 22, pp. 379–394, 2001.
P. R. Bandyopadhyay. Maneuvering Hydrodynamics of Fish and Small Underwater Vehicles. Integrative and Comparative Biology, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 102–117, 2002.
N. Kato, M. Furushima. Pectoral Fin Model for Maneuver of Underwater Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 1996 Symposium on Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Technology. Monterrey, CA, pp. 49–56, 1996.
K. H. Low, A. Willy. Development and Initial Investigation of NTU Robotic Fish with Modular Flexible Fins. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics & Automation (ICMA2005), Niagara Falls, Canada, pp. 958–963, 2005.
S. Guo, Y. Okuda. Characteristic Evaluation of an Underwater Micro Biped Robot with Multi DOF. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Conference on Intelligent Mechatronics and Automation, Chengdu, China, pp. 95–100, 2004.
S. Guo, Y. Okuda, K. Asaka. A Novel Type of Underwater Micro Biped Robot with Multi DOF. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 4881–4886, 2004.
H. Liu, K. Kawachi. A Numerical Study of Undulatory Swimming. Journal of Computational Physics, vol. 155, no. 2, pp. 223–247, 1999.
H. Liu, K. Kawachi. The Three-dimensional Hydrodynamics of Tadpole Locomotion. The Journal of Experimental Biology, vol. 200, no. 4, pp. 2807–2819, 1997.
R. Ramamurtil, W. C. Sandberg, R. Lohner, J. A. Walker, M.W. Westneat. Fluid Dynamics of Flapping Aquatic Flight in the Bird Wrasse: Three-dimensional Unsteady Computations with Fin Deformation. The Journal of Experimental Biology, vol. 205, no. 19, pp. 2997–3008, 2002.
Hiroyoshi Suzuki, Naomi Kato. A Numerical Study on Unsteady Flow Around a Mechanical Pectoral Fin. International Journal of Offshore and Polar Engineering, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 161–167, 2005.
Y. Zhang, J. He, J. Yang. Design and investigation of shape memory alloy dce on robotics and biomimetics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO2006), Kunming, China, to be published.
Y. Yang, X. Yin, X. Lu. Flow visualization over a 2D traveling wave wall. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 84–90, 2005.
G. J. Dong, X. Y. Lu. Numerical Analysis on the Propulsive Performance and Vortex Shedding of Fish-like Travelling Wavy Plate. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, vol. 48, no. 12, pp. 1351–1373, 2005.
K. H. Low, A. Willy. Biomimetic motion planning of an undulating robotic fish fin. Journal of Vibration and Control, to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yong-Hua Zhang received his B.Sc. degree in precision instrumentation and precision machinery from University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, in 2003. He is now pursuing his Ph.D. degree in University of Science and Technology of China.
He has published over 10 refereed journal and conference papers. His current research is about biomimetic robotic fish fin using smart material (SMA). His research interest also includes underwater microrobots utilizing artificial muscles.
Jian-Hui He received her B.Sc. degree in computer science from China Agriculture University, Beijing, China, in 2003. She is now pursuing her M.Sc degree in Department of Precision Machinery and Precision Instrumentation, University of Science and Technology of China. Currently, she is working on the influence of electric field’s strength on the fabrication of micro droplet lens.
She has published 5 refereed journal and conference papers in recent two years. Her research interests include micro-optics and underwater robots.
Jie Yang graduated from the Department of Physical Chemistry at the Beijing University of Science and Technology, in 1969. He is currently a professor in the Department of Precision Machinery and Precision Instrumentation of University of Science and Technology of China. He leads several research groups focusing on intelligent robots supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and 863 Project.
His research interests include intelligent robots, precision machinery materials, and high speed photography.
Shi-Wu Zhang received his B.Sc. degree in mechanical and electrical engineering and the Ph.D. degree in precision instrumentation and precision machinery from University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China. He is currently a research assistant in the Department of Precision Machinery and Precision Instrumentation, University of Science and Technology of China. He has been a research assistant in the Department of Computer Science, Hong Kong Baptist University for one and a half years.
His current interests include web intelligence, autonomy oriented computation, complex systems, and intelligent robots.
Kin Huat Low received his M.Sc and Ph.D. degrees in mechanical engineering from the University of Waterloo, Canada, in 1983 and 1986, respectively. After spending two years as a post-doctoral fellow at the University of Waterloo, he joined the School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering of the Nanyang Technological University.
He is the author of five books and more than 90 journal papers in the areas of biomimetics, robotics, rehabilitation, impacts, power transmission systems, structural dynamics and vibrations. His research interests include robotics, vibrations, impacts, machines, mechanisms, exoskeleton systems, and mechatronics design.
Dr. Low is a member of IEEE, IASTED, SIAA and SiC-ToMM. He is also a member of several technical, conference committees, and journal editorial boards. He has won awards at the two IEEE conferences on the research work on robotics fish and powered exoskeleton, respectively.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YH., He, JH., Yang, J. et al. A Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis of an undulatory mechanical fin driven by shape memory alloy. Int J Automat Comput 3, 374–381 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-006-0374-4
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-006-0374-4