Abstract
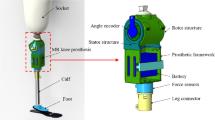
The above-knee intelligent bionic leg is very helpful to amputees in the area of rehabilitation medicine. This paper first introduces the functional demand of the above-knee prosthesis design. Then, the advantages of the four-bar link mechanism and the magneto-rheological (MR) damper are analyzed in detail. The fixed position of the MR damper is optimized and a virtual prototype of knee joint is given. In the end, the system model of kinematics, dynamics, and controller are given and a control experiment is performed. The control experiment indicates that the intelligent bionic leg with multi-axis knee is able to realize gait tracking of the amputee’s healthy leg based on semi-active control of the MR damper.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
R. C. Wang, D. W. Jin. Research and development of bionic and intelligent limb prosthesis. China Medical Devices Information, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 3–5, 2009. (in Chinese)
J. H. Kim, J. H. Oh. Development of an above knee prosthesis using MR damper. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, IEEE, Seoul, Korea, pp. 3686–3691, 2001.
B. X. Lu, W. Z. Han. Research on the above-knee prosthesis with a pneumatic swing control knee joint. Journal of North China Institute of Astronautic Engineer, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 1–5, 2003. (in Chinese)
G. Z. Tan, L. M. Wu. Progress and development trend towards study of artificial legs (prosthesis) in foreign countries and China. Robot, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 91–96, 2001. (in Chinese)
J. W. Breakey. Theory of integrated balance: The lower limb amputee. Journal of Prosthetics and Orthotics, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 42–44, 1998.
D. W. Jin, R. C. Wang, C. Q. Bai, C. H. Huang, J. C. Zhang. Swing phase control of intelligent lower limb prosthesis using electrorheological fluid. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 40–43, 1998. (in Chinese)
C. Gao, B. R. Wang, H. L. Xie, X. H. Xu. Design and control of bionic limb of biped robot with heterogeneous legs. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), vol. 25, no. 11, pp. 1030–1033, 2004. (in Chinese)
H. L. Xie, B. R. Wang, D. H. Cong, X. H. Xu. Structure modeling and iterative learning control simulation of biped robot with heterogeneous legs. Journal of System Simulation, vol. 18, no. 11, pp. 3234–3262, 2006. (in Chinese)
H. N. Li, H. Yang, X. L. Li. Advance of research on parameterized dynamic models of magnetorheological dampers. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 616–624, 2004. (in Chinese)
Z. D. Xu, Y. P. Shen. Calculating models and simulation analysis about magnetorheological damper. Building Structure, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 68–69, 2003. (in Chinese)
H. L. Xie, F. Li, F. Wang, Y. X. LIU. Intelligent control of BRHL based on MR damper. Applied Mechanics and Materials, vol. 10, no. 12, pp. 466–470, 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 20080441093), Key Laboratory Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 2008S088) and Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Northeastern University (No. 20080411).
Hua-Long Xie received the bachelor degree in mechatronic engineering, master degree in mechanical design and theory, and Ph.D. degree in control theory and control engineering from Northeastern University, PRC in 2000, 2003, and 2006, respectively. Since 2006, he has been a postdoctoral research fellow and lecturer at Northeastern University.
His research interests include robotics, intelligent control, intelligent bionic leg, and biomechanics.
Ze-Zhong Liang received the B.Eng. degree in mechanical engineering from Shenyang University of Chemical Technology, PRC in 2009. Currently, he is a postgraduate in School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation at Northeastern University, PRC.
His research interests include mechanical manufacturing and automation.
Fei Li received the bachelor degree in measurement and control technology and instrumentation, master degree in control theory and control engineering from Shenyang Institute of Chemical Technology, PRC in 2001 and 2004, respectively, and the Ph.D. degree in pattern recognition and intelligent system from Northeastern University, PRC in 2007. Currently, she is a lecturer in the School of Information Science and Engineering at Shenyang University of Technology, PRC.
Her research interests include robotics, control theory, and computer vision.
Li-Xin Guo received the Ph.D. degree from Northeastern University, PRC in 2000. Currently, he is a professor at Northeastern University.
His research interests include robot motion planning and control, mechanical vibration analysis, finite element analysis, and biomechanics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, HL., Liang, ZZ., Li, F. et al. The knee joint design and control of above-knee intelligent bionic leg based on magneto-rheological damper. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 7, 277–282 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-010-0503-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-010-0503-y