Abstract
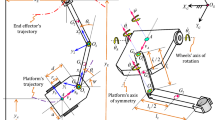
This paper addresses the trajectory tracking control of a nonholonomic wheeled mobile manipulator with parameter uncertainties and disturbances. The proposed algorithm adopts a robust adaptive control strategy where parametric uncertainties are compensated by adaptive update techniques and the disturbances are suppressed. A kinematic controller is first designed to make the robot follow a desired end-effector and platform trajectories in task space coordinates simultaneously. Then, an adaptive control scheme is proposed, which ensures that the trajectories are accurately tracked even in the presence of external disturbances and uncertainties. The system stability and the convergence of tracking errors to zero are rigorously proven using Lyapunov theory. Simulations results are given to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed robust adaptive control law in comparison with a sliding mode controller.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
V. Pavlov, A. Timofeyev. Construction and stabilization of programmed movements of a mobile robot-manipulator. Engineering Cybernetics, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 70–79, 1976.
J. H. Chung, S. A. Velinsky. Modeling and control of a mobile manipulator. Robotica, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 607–613, 1998.
[3] K.Watanabe, K. Sato, K. Izumi, Y. Kunitake. Analysis and control for an omnidirectional mobile manipulator. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, vol. 27, no. 1–2, pp. 3–20, 2000.
Y. Yamamoto, X. P. Yun. Effect of the dynamic interaction on coordinated control of mobile manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 816–824, 1996.
O. Khatib. Mobile manipulation: The robotic assistant. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, vol. 26, no. 2–3, pp. 157–183, 1999.
N. Hootsmanns, S. Dubowsky. The motion control of manipulators on mobile vehicles. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automatics, IEEE, Sacramento, USA, vol. 3, pp. 2336–2341, 1991.
E. Padopoulos, J. Poulakakis. Planning and modelbased control for mobile manipulators. In Proceedings of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IEEE, Takamatsu, Japan, 2000.
S. Lin, A. A. Goldenberg. Neural-network control of mobile manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 1121–1133, 2001.
C. Y. Lee, I. K. Jeong, I. H. Lee, J. J. Lee. Motion control of mobile manipulator based on neural networks and error compensation. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, IEEE, New Orleans, USA, pp. 4627–4632, 2004.
X. M. Tan, D. B. Zhao, J. Q. Yi, D. Xu. Adaptive hybrid control for omnidirectional mobile manipulators using neural-network. In Proceedings of American Control Conference, IEEE, Seattle, Washington, USA, pp. 5174–5179, 2008.
X. M. Tan, D. B. Zhao, J. Q. Yi, Z. G. Hou, D. Xu. Unified model and robust neural-network control of omnidirectional mobile manipulators. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Informatics, IEEE, California, USA, pp. 411–418, 2007.
T. T. Arif. Adaptive control of rigid body satellite. International Journal of Automation and Computing, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 296–306, 2008.
M. B. Cheng, C. C. Tsai. Hybrid sliding-mode fuzzy neural network tracking control for a wheeled mobile manipulator. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, IEEE, Hong Kong, PRC, pp. 944–949, 2005.
M. Z. Hou, A. G. Wu, G. R. Duan. Robust output feedback control for a class of nonlinear systems with input unmodeled dynamics. International Journal of Automation and Computing, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 307–312, 2008.
N. D, F. N. Hu, X. Y. An improved control algorithm for high-order nonlinear systems with unmodelled dynamics. International Journal of Automation and Computing, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 234–239, 2009.
G. White. Simultaneous Motion and Interaction Force Control of a Nonholonomic Mobile Manipulator, Ph. D. dissertation, University of New York at Buffalo, USA, 2006.
Y. Guo, P. Y. Woo. Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control for robotic manipulators. In Proceedings of the 42nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, IEEE, Maui, USA, vol. 3, pp. 2174–2179, 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mohamed Boukattaya received the electromechanical engineering diploma from the National School of Engineers, University of Sfax, Tunisia in 2002. From the same school, he received the master degree in automatic and industrial informatics in 2006. He is currently a researcher in the Control of Industrial Process Unit at the same school.
His research interests include robot control and simulation, especially in mobile manipulators, mobile robotics, and redundant systems.
Tarak Damak received the electrical engineering diploma from the National School of Engineers, University of Sfax, Tunisia in 1989, the D.E.A degree in automatic control from the Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Toulouse-France in 1990, the Ph.D. degree from the University Paul Sabatier de Toulouse-France in 1994. In 2006, he obtained the University Habilitation from the National School of Engineers, University of Sfax. He is currently a professor at the same school.
His research interests include distributed parameter systems, sliding mode control and observers, and adaptive nonlinear control.
Mohamed Jallouli received the D.E.A degree from University of Valenciennes, France in 1986 in automatics and the Ph.D. degree from University Paris XII, France in 1991, in robotics engineering. He is currently an assistant professor of electric and computer engineering at National School of Engineers, University of Sfax, Tunisia.
His research interests include the implementation of intelligent methods (neural network, fuzzy logic, and genetic algorithm) in robotic and vision system as well as in multisensory data fusion mobile bases.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boukattaya, M., Damak, T. & Jallouli, M. Robust adaptive control for mobile manipulators. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 8, 8–13 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-010-0548-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-010-0548-y