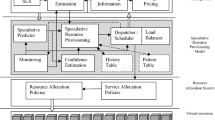
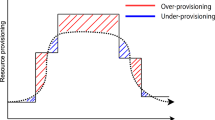
Abstract
Dynamic resource provisioning is a challenging technique to meet the service level agreement (SLA) requirements of multi-tier applications in virtualization-based cloud computing. Prior efforts have addressed this challenge based on either a cost-oblivious approach or a cost-aware approach. However, both approaches may suffer frequent SLA violations under flash crowd conditions. Because they ignore the benefit gained that a multi-tier application continuously guarantees the SLA in the new configuration. In this paper, we propose a benefit-aware approach with feedback control theory to solve this problem. Experimental results based on live workload traces show that our approach can reduce resource provisioning cost by as much as 30% compared with a costoblivious approach, and can effectively reduce SLA violations compared with a cost-aware approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaquero L M, Rodero-Merino L, Caceres J, Lindner M. A break in the clouds: towards a cloud definition. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2008, 39(1): 50–55
Armbrust M, Fox RA. a, Joseph A D, Katz R H, Konwinski A, Lee G, Patterson D A, Rabkin A, Zaharia M. Above the clouds: a berkeley view of cloud computing. Technical Report, Dept. Electrical Eng. and Comput. Sciences, University of California, Berkeley, 2009
Pettey C, Stevens H. Gartner maps out the rapidly evolving market for cloud infrastructure as a service. http://www.gartner.com/it/page.jsp?id=1622514,2011
Amazon ec2. http://aws.amazon.com/ec2/, 2013
Ibm smartcloud. http://www.ibm.com/cloud-computing/social/us/en/, 2013
Opsource cloud. http://cloud-vpn.net/, 2013
Bennani M N, Menasce D A. Resource allocation for autonomic data centers using analytic performance models. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Autonomic Computing. 2005, 229–240
Zhang Q, Cherkasova L, Smirni E. A regression-based analytic model for dynamic resource provisioning of multi-tier applications. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Autonomic Computing, ICAC’07. 2007, 17–26
Urgaonkar B, Shenoy P, Chandra A, Goyal P, Wood T. Agile dynamic provisioning of multi-tier internet applications. ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems (TAAS), 2008, 3(1): 1
Sharma U, Shenoy P, Sahu S, Shaikh A. A cost-aware elasticity provisioning system for the cloud. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS). 2011, 559–570
Jung G, Joshi K, Hiltunen M, Schlichting R, Pu C. A cost-sensitive adaptation engine for server consolidation of multitier applications. Middleware, 2009, 163–183
Bubis benchmark. http://rubis.ow2.org/, 2005
Pettey C, Stevens H. Gartner maps out the rapidly evolving market for cloud infrastructure as a service. http://www.gartner.com/it/page.jsp?id=1622514, 2011
Clifton C, Leavens G T, Chambers C, Millstein T. Multijava: modular open classes and symmetric multiple dispatch for java. In: ACM Sigplan Notices. 2000, 130–145
The powerful open source industry standard for virtualization. http://www.xen.org
Clark C, Fraser K, Hand S, Hansen J G, Jul E, Limpach C, Pratt I, Warfield A. Live migration of virtual machines. In: Proceedings of the 2nd conference on Networked Systems Design & Implementation-Volume 2. 2005, 273–286
Xu J, Zhao M, Fortes J, Carpenter R, Yousif M. On the use of fuzzy modeling in virtualized data center management. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Autonomic Computing, 2007. ICAC’07. 2007
Bennani M N, Menasce D A. Resource allocation for autonomic data centers using analytic performance models. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Autonomic Computing, 2005. ICAC 2005. 2005, 229–240
Hoff T. Friendster lost lead because of a failure to scale. http://highscalability.com/blog/2007/11/13/friendster-lost-lead-because-ofa-failure-to-scale.html, 2007
Hepric hq. http://www.hyperic.com/, 2013
Apache commons math. http://commons.apache.org/proper/commonsmath/, 2013
Zhang Q, Cherkasova L, Mi N F, Smirni E. A regression-based analytic model for capacity planning of multi-tier applications. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing. 2008, 197–211
Krishnamurthy D, Rolia J A, Majumdar S. A synthetic workload generation technique for stress testing session-based systems. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2006, 32(11): 868–882
Cherkasova L, Phaal P. Session-based admission control: a mechanism for peak load management of commercial web sites. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2002, 51(6): 669–685
Ming Z, Yin J, Yang W, Wang H, Xiao Z. A web performance testing framework and its mixed performance modeling process. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2010, 47(7): 1192–1200
Xiong P, Chi Y, Zhu S, Moon H J, Pu C, Hacigumus H. Intelligent management of virtualized resources for database systems in cloud environment. In: Proceedings of the 27th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE). 2011, 87–98
Bagnall A, Janacek G. Clustering time series from arma models with clipped data. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. 2004, 49–58
Arlitt M, Jin T. A workload characterization study of the 1998 world cup web site. IEEE Network, 2000, 14(3): 30–37
Dilley J A. Web server workload characterization. Hewlett-Packard Laboratories, Technical Publications Department, 1996
Rolia J, Cherkasova L, McCarthy C. Configuring workload manager control parameters for resource pools. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium. 2006, 127–137
Cecchet E, Singh R, Sharma U, Shenoy P. Dolly: virtualization-driven database provisioning for the cloud. In: ACM SIGPLAN Notices. 2011, 51–62
Tao H, Ningjiang C, Jun W, Wen-bo Z, Yong Z. OnceAS/Q: a QoSenabled web application server. Journal of Software, 2004, 15(12): 1787–1799
Norris J, Coleman K, Fox A, Candea G. Oncall: defeating spikes with a free-market application cluster. In: Proceedings of the 2004 Interna tional Conference on Autonomic Computing. 2004, 198–205
Liu X, Zhu X, Singhal S, Arlitt M. Adaptive entitlement control of resource containers on shared servers. In: Proceedings of the 9th IFIP/IEEE International Symposium onIntegrated Network Management. 2005, 163–176
Zhu X, Wang Z, Singhal S. Utility-driven workload management using nested control design. In: Proceedings of the 2006 American Control Conference. 2006, 6033–6038
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Heng Wu is a PhD candidate in the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China. His research interests include cloud computing, and middleware. He received his MS from the National University of Defense Technology in 2007, and his BS from the Changsha University of Science and Technology in 2005.
Wenbo Zhang is an associate professor in the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China. His research interests include cloud computing, and middleware. He received his PhD from the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China in 2007, and his MS in Computer Science and Technology from the Shandong University in 2002, and his BS in Computer Science and Technology from the Shandong Polytechnic University in 1999. He has published over 30 papers in international journals and conferences.
Jianhua Zhang received his BS from the Xidian University in 2006, and is now a PhD candidate in the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China. His research interests include service oriented computing, cloud computing, and middleware.
Jun Wei is a professor in the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China. His research interests include service oriented computing, middleware, and software engineering. He received his BS and PhD in Computer Science from the Wuhan University, China in 1992 and 1997, respectively. He was a postdoctoral researcher at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, China. He has published over 80 papers in international journals and conferences.
Tao Huang is a professor in the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China. His research interests include cloud computing, middleware, and software engineering. He received his BS, MS, and PhD in computer science from the University of Science and Technology of China, China in 1988, 1991, and 1994, respectively. He has published over 100 papers in international journals and conferences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Zhang, W., Zhang, J. et al. A benefit-aware on-demand provisioning approach for multi-tier applications in cloud computing. Front. Comput. Sci. 7, 459–474 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-013-2201-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-013-2201-8