Abstract
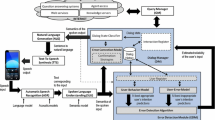
This work presents a spoken dialog summarization system with HAPPINESS/SUFFERING factor recognition. The semantic content is compressed and classified by factor categories from spoken dialog. The transcription of automatic speech recognition is then processed through Chinese Knowledge and Information Processing segmentation system. The proposed system also adopts the part-of-speech tags to effectively select and rank the keywords. Finally, the HAPPINESS/SUFFERING factor recognition is done by the proposed point-wise mutual information. Compared with the original method, the performance is improved by applying the significant scores of keywords. The experimental results show that the average precision rate for factor recognition in outside test can reach 73.5% which demonstrates the possibility and potential of the proposed system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee H, Shiang S R, Yeh C F, Chen Y N, Huang Y, Kong S Y, Lee L S. Spoken knowledge organization by semantic structuring and a prototype course lecture system for personalized learning. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP), 2014, 22(5), 883–898
Huang C L, Wu C H. Spoken document retrieval using multilevel knowledge and semantic verification. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2007, 15(8): 2551–2560
Wang J F, Chen BW, Fan WK, Li C H. Emotion-aware assistive system for humanistic care based on the orange computing concept. Applied Computational Intelligence and Soft Computing, 2012
Koolagudi S G, Kumar N, Rao K S. Speech emotion recognition using segmental level prosodic analysis. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Devices and Communication. 2011, 1–5
Ahmed T, Islam M, Ahmad M. Human emotion modeling based on salient global features of EEG signal. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering. 2013, 246–251
Tsai H C, Fan W K, Chen B W, Wang J F, Lin P C. A real-time awareness system for happiness expression based on the multilayer histogram of oriented gradients. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Awareness Science and Technology. 2012, 289–293
Park J S, Jang G J, Kim J H. Multistage utterance verification for keyword recognition-based online spoken content retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2012, 58(3), 1000–1005
Liu F, Liu F F, Liu Y. A supervised framework for keyword extraction from meeting transcripts. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2011, 19(3), 538–548
Liu F, Liu Y. Towards abstractive speech summarization: exploring unsupervised and supervised approaches for spoken utterance compression. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2013, 21(7), 1469–1480
Qin Y. Applying frequency and location information to keyword extraction in single document. In: Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligent Systems. 2012, 1398–1402
Wartena C, Brussee R, Slakhorst W. Keyword extraction using word co-occurrence. In: Proceedings of IEEE Workshops on Database and Expert Systems Applications. 2010, 54–58
Jiao H, Liu Q, Jia H B. Chinese keyword extraction based on n-gram and word co-occurrence In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security Workshops. 2007, 152–155
Gupta A, Dixit A, Sharma A K. A novel statistical and linguistic features based technique for keyword extraction. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks. 2014, 55–59
Hu X H, Wu B. Automatic keyword extraction using linguistic features. In: Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops. 2006, 19–23
Chen B W, Rho S, Guizani M, Fan W K. Cognitive sensors based on kernel ridge phase-smoothing localization and multiregional histograms of oriented gradients. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2016
Troyka L Q, Thweatt J W. Structured Reading. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2003
Huang C L, Hsieh C H, Wu C H. Spoken document summarization using acoustic, prosodic and semantic information. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Multimedia. 2005
Kurmi R, Jain P. Text summarization using enhanced MMR technique. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics. 2014, 1–5
Li Y B, Merialdo B. Multi-video summarization based on Video- MMR. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Image Analysis for Multimedia Interactive Services, 2010, 1–4
Ferreira R, Freitas F, Cabral L S, Lins R D, Lima R, França G, Simskez S J, Favaro L. A four dimension graph model for automatic text summarization. In: Proceedings of IEEE/WIC/ACM International Joint Conferences on Web Intelligence (WI) and Intelligent Agent Technologies. 2013, 389–396
Cambria E, Schuller B, Xia Y Q, Havasi C. New avenues in opinion mining and sentiment analysis. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 2013, 15–21
Ortony A, Clore G L, Collins A. The Cognitive Structure of Emotions. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1990
Stevenson R A, Mikels J A, James T W. Characterization of the affective norms for English words by discrete emotional categories. Behavior Research Methods, 2007, 39(4): 1020–1024
Grassi M, Cambria E, Hussain A, Piazza F. Sentic web: a new paradigm for managing social media affective information. Cognitive Computation, 2011, 3(3), 480–489
Chen B W, He X Y, Ji W, Rho S, Kung S Y. Support vector analysis of large-scale data based on kernels with iteratively increasing order. Journal of Supercomputing, 2016, 72(9): 3297–3311
Olsher D J. Full spectrum opinion mining: integrating domain, syntactic and lexical knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops. 2012, 693–700
Wu C H, Liang WB. Emotion recognition of affective speech based on multiple classifiers using acoustic-prosodic information and semantic labels. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2011, 2(1): 10–21
Xie S S, Liu Y. Using n-best lists and confusion networks for meeting summarization. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2011, 19(5), 1160–1169
Chen B W, Ji W. Intelligent marketing in smart cities: crowdsourced data for geo-conquesting. IT Professional, 2016, 18(4): 18–24
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yang-Yen Ou received the BS and MS degrees from the Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Da- Yeh University, China in 2009 and 2011, respectively. He is currently pursuing the PhD in the Department of Electrical Engineering, Cheng Kung University, China. His current research interests include psychology analysis, speech and image signal processing, and pattern recognition.
Ta-Wen Kuan received the PhD degree in electrical engineering from Cheng Kung University (NCKU), China in 2012. He is currently an assistant research fellow in the Department of Electrical Engineering, NCKU. Dr. Kuan is also a member of the Association for Computing Machinery. His research interests include spoken language processing, VLSI architecture design, pattern recognition, and machine learning.
Anand Paul received the PhD degree in electrical engineering from Cheng Kung University, China in 2010. He is currently working as an associate professor with the School of Computer Science and Engineering, Kyungpook National University, South Korea. He is a delegate representing South Korea for M2M focus group and for MPEG. Prof. Paul has guest edited various international journals and he is also part of Editorial Team for Journal of Platform Technology, ACM Applied Computing review and Cyber Physical Systems. He is the track chair for Smart human computer interaction in ACM SAC 2016, 2015, and 2014. He is an IEEE Senior Member. His research interests include algorithm and architecture reconfigurable embedded computing, IoT and big data.
Jhing-Fa Wang is currently a chair and a distinguished professor with the Department of Electrical Engineering, Cheng Kung University, China. He has published about 135 journal papers on IEEE, SIAM, IEICE, and IEE and about 220 conference papers. He developed a Mandarin speech recognition system called Venus-Dictate, known as a pioneering system in Taiwan. He also served as an editor-in-chief on International Journal of Chinese Engineering from 1995 to 2000. He was elected as a fellow of the IEEE in 1999 for his contribution on “Hardware and Software Co-Design on Speech Signal Processing”. His research interests including speech signal processing, image processing, biomedical signal processing, and VLSI system design.
An-Chao Tsai received the PhD degree in electrical engineering from Cheng Kung University, China in 2010. He is currently working as an assistant professor in the Department of Digital Multimedia Design, Tajen University, China. Prof. Tsai also served as the track chair for International Conference on Orange technologies 2016 and program chair in 2015. His research interests include image processing, happiness application development, unity 3D game design, virtual reality, and augmented reality.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ou, YY., Kuan, TW., Paul, A. et al. Spoken dialog summarization system with HAPPINESS/SUFFERING factor recognition. Front. Comput. Sci. 11, 429–443 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-016-6190-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-016-6190-2