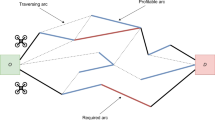
Abstract
Traditional route planners commonly focus on finding the shortest path between two points in terms of travel distance or time over road networks. However, in real cases, especially in the era of smart cities where many kinds of transportation-related data become easily available, recent years have witnessed an increasing demand of route planners that need to optimize for multiple criteria, e.g., finding the route with the highest accumulated scenic score along (utility) while not exceeding the given travel time budget (cost). Such problem can be viewed as a variant of arc orienteering problem (AOP), which is well-known as an NP-hard problem. In this paper, targeting a more realistic AOP, we allow both scenic score (utility) and travel time (cost) values on each arc of the road network are time-dependent (2TD-AOP), and propose a memetic algorithm to solve it. To be more specific, within the given travel time budget, in the phase of initiation, for each population, we iteratively add suitable arcs with high scenic score and build a path fromthe origin to the destination via a complicate procedure consisting of search region narrowing, chromosome encoding and decoding. In the phase of the local search, each path is improved via chromosome selection, local-improvement-based mutation and crossoveroperations. Finally, we evaluate the proposed memetic algorithm in both synthetic and real-life datasets extensively, and the experimental results demonstrate that it outperforms the baselines.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Chen C, Zhang D, Ma X, Guo B, Wang L, Wang Y, Sha E. Crowddeliver: planning city-wide package delivery paths leveraging the crowd of taxis. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 18(6): 1478–1496
Delling D, Goldberg A V, Pajor T, Werneck R F. Customizable route planning in road networks. Transportation Science, 2015, 51(2): 566–591
Funke S, Storandt S. Personalized route planning in road networks. In. Proceedings of the 23rd SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems. 2015, 45
Wang Z, Guo B, Yu Z, Zhou X. Wi-Fi CSI-based behavior recognition: from signals and actions to activities. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(5): 109–115
Guo B, Zhang D, Yu Z, Liang Y, Wang Z, Zhou X. From the internet of things to embedded intelligence. World Wide Web, 2013, 16(4): 399–420
Castro P S, Zhang D, Chen C, Li S, Pan G. From taxi GPS traces to social and community dynamics: a survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2013, 46(2): 17
Li X, Pan G, Wu Z, Qi G, Li S, Zhang D, Zhang W, Wang Z. Prediction of urban human mobility using large-scale taxi traces and its applications. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2012, 6(1): 111–121
Zhang D, Guo B, Yu Z. The emergence of social and community intelligence. Computer, 2011, 44(7): 21–28
Zhang D, Sun L, Li B, Chen C, Pan G, Li S, Wu Z. Understanding taxi service strategies from taxi GPS traces. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(1): 123–135
Wang L, Guo B, Yang Q. Smart city development with urban transfer learning. Computer, 2018, 51(12): 32–41
Quercia D, Schifanella R, Aiello L M. The shortest path to happiness: recommending beautiful, quiet, and happy routes in the city. In. Proceedings of the 25th ACM conference on Hypertext and Social Media. 2014, 116-125
Galbrun E, Pelechrinis K, Terzi E. Urban navigation beyond shortest route: the case of safe paths. Information Systems, 2016, 57: 160–171
Chen C, Chen X, Wang L, Ma X, Wang Z, Liu K, Guo B, Zhou Z. MASSR: a memetic algorithm for skyline scenic routes planning leveraging heterogeneous user-generated digital footprints. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(7): 5723–5736
Runge N, Samsonov P, Degraen D, Schöning J. No more autobahn!: scenic route generation using googles street view. In. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces. 2016, 147-151
Zheng Y T, Yan S, Zha Z J, Li Y, Zhou X, Chua T S, Jain R. GPSView: a scenic driving route planner. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 2013, 9(1): 3
Lu Y, Jossé G, Emrich T, Demiryurek U, Renz M, Shahabi C, Schubert M. Scenic routes now: effciently solving the time-dependent arc orienteering problem. In. Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. 2017, 487-496
Liang H, Wang K. Top-k route search through submodularity modeling of recurrent poi features. In. Proceedings of the 41st International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research & Development in Information Retrieval. 2018, 545-554
Taylor K, Lim K H, Chan J. Travel itinerary recommendations with must-see points-of-interest. In. Proceedings of the International World Wide Web Conference. 2018, 1198-1205
Hsueh Y L, Huang H M. Personalized itinerary recommendation with time constraints using GPS datasets. Knowledge & Information Systems, 2018, 6: 1–22
Chen C, Jiao S, Zhang S, Liu W, Feng L, Wang Y. TripImputor: real-time imputing taxi trip purpose leveraging multi-sourced urban data. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(10): 3292–3304
Wang L, Yu Z, Guo B, Yi F, Xiong F. Mobile crowd sensing task optimal allocation: a mobility pattern matching perspective. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2018, 12(2): 231–244
Wang L, Zhang D, Wang Y, Chen C, Han X, M’hamed A. Sparse mobile crowdsensing: challenges and opportunities. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(7): 161–167
Demiryurek U, Banaei-Kashani F, Shahabi C, Ranganathan A. Online computation of fastest path in time-dependent spatial networks. In. Proceedings of International Symposium on Spatial and Temporal Databases. 2011, 92-111
Mei Y, Salim FD, Li X. Effcient meta-heuristics for the multi-objective time-dependent orienteering problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016, 254(2): 443–457
Chen C, Chen X, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhang D. ScenicPlanner: planning scenic travel routes leveraging heterogeneous user-generated digital footprints. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2017, 11(1): 61–74
Golberg D E. Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning. Addion Wesley, 1989
Li Y, Yiu M L. Route-saver: leveraging route apis for accurate and efficient query processing at location-based services. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2015, 27(1): 235–249
Seresinhe C I, Moat H S, Preis T. Quantifying scenic areas using crowdsourced data. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 2017, 45(3): 567–582
Wang W, Xiao L, Zhang J, Yang Y, Tian P, Wang H, He X. Potential of Internet street-view images for measuring tree sizes in roadside forests. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2018, 35: 211–220
Gunawan A, Lau H C, Vansteenwegen P. Orienteering problem: a survey of recent variants, solution approaches and applications. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016, 255(2): 315–332
Gavalas D, Konstantopoulos C, Mastakas K, Pantziou G, Vathis N. Approximation algorithms for the arc orienteering problem. Information Processing Letters, 2015, 115(2): 313–315
Feillet D, Dejax P, Gendreau M. The profitable arc tour problem: solution with a branch-and-price algorithm. Transportation Science, 2005, 39(4): 539–552
Verbeeck C, Vansteenwegen P, Aghezzaf E H. An extension of the arc orienteering problem and its application to cycle trip planning. Transportation Research Part E Logistics & Transportation Review, 2014, 68(4): 64–78
Hsieh H P, Li C T. Mining and planning time-aware routes from checkin data. In. Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. 2014, 481-490
Vansteenwegen P, Souffriau W, Van Oudheusden D. The orienteering problem: a survey. European Journal of Operational Research, 2011, 209(1): 1–10
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2017YFB1002000), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61602067 and 61872050), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2018cdqyjsj0024), the Chongqing Basic and Frontier Research Program (cstc2018jcyjAX0551), and the Frontier Interdisciplinary Research Funds for the Central Universities (106112017cdjqj188828). Chao Chen and Liping Gao contributed equally on this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chao Chen is a full professor at College of Computer Science, Chongqing University, China. He obtained his PhD degree from Pierre and Marie Curie University and Institut Mines-Télécom/Télécom SudParis, France in 2014. He received the BSc and MSc degrees in control science and control engineering from Northwestern Polytechnical University, China in 2007 and 2010, respectively. Dr. Chen got published over 80 papers including 20 ACM/IEEE Transactions. His work on taxi trajectory data mining was featured by IEEE Spectrum in 2011 and 2016 respectively. He was also the recipient of the Best Paper Runner-Up Award at MobiQuitous 2011.
In 2009, he worked as a research assistant with Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China. His research interests include pervasive computing, mobile computing, urban logistics, data mining from large-scale GPS trajectory data, and big data analytics for smart cities.
Liping Gao is currently a master student at College of Computer Science, Chongqing University, China. She obtained her bachelor degree from the College of Software Engineering of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China in 2016. Her research interests include travel route planning, crowdsourced data mining for smart services.
Xuefeng Xie is a research assistant at the College of Computer Science, Chongqing University, China. She obtained her Master of Arts degree with the highest honor from the School of Media and Communication, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK. She received the Bachelor of Arts degree in film art from Sichuan Fine Art Institute, China in 2012. Her research interests include data visualization, aesthetic beauty, and quantitative analysis.
Zhu Wang is an associate professor of computer science at Northwestern Polytechnical University, China. He obtained his PhD degree in computer science from Northwestern Polytechnical University, China in 2013. His research interests include pervasive computing, mobile social network analysis, and mobile healthcare.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Gao, L., Xie, X. et al. Enjoy the most beautiful scene now: a memetic algorithm to solve two-fold time-dependent arc orienteering problem. Front. Comput. Sci. 14, 364–377 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-019-8364-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-019-8364-1