Abstract
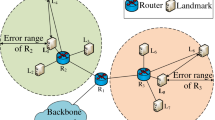
Location based services (LBS) are widely utilized, and determining the location of users’ IP is the foundation for LBS. Constrained by unstable delay and insufficient landmarks, the existing geolocation algorithms have problems such as low geolocation accuracy and uncertain geolocation error, difficult to meet the requirements of LBS for accuracy and reliability. A new IP geolocation algorithm based on router error training is proposed in this manuscript to improve the accuracy of geolocation results and obtain the current geolocation error range. Firstly, bootstrapping is utilized to divide the landmark data into training set and verification set, and /24 subnet distribution is utilized to extend the training set. Secondly, the path detection is performed on nodes in the three data sets respectively to extract the metropolitan area network (MAN) of the target city, and the geolocation result and error of each router in MAN are obtained by training the detection results. Finally, the MAN is utilized to get the target’s location. Based on China’s 24,254 IP geolocation experiments, the proposed algorithm has higher geolocation accuracy and lower median error than existing typical geolocation algorithms LBG, SLG, NNG and RNBG, and in most cases the difference is less than 10km between estimated error and actual error.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Hara T, Suzuki A, Iwata M, Arase Y, Xie X. Dummy-based user location anonymization under real-world constraints. IEEE Access, 2016, 4: 673–687
Chen L, Thombre S, Järvinen K, Lohan E S, Alén-Savikko A K, Leppäkoski H. Robustness, security and privacy in location-based services for future IoT: a survey. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 8956–8977
Niu B, Li Q, Zhu X, Cao G, Li H. Enhancing privacy through caching in location-based services. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. 2015, 1017–1025
Zheng X, Cai Z, Li J, Gao H. Location-privacy-aware review publication mechanism for local business service systems. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. 2017, 1–9
Chen J, Liu F, Zhao F, Zhu G, Ding S. A sc-vivaldi network coordinate system based method for IP geolocation. Journal of Internet Technology, 2016, 17(1): 119–127
Komosny D, Vozňák M, Rehman S U. Location accuracy of commercial IP address geolocation databases. Information Technology and Control, 2017, 46(3): 333–344
Poese I, Uhlig S, Kaafar M A, Donnet B, Gueye B. IP geolocation databases: unreliable?. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2011, 41(2): 53–56
Shavitt Y, Zilberman N. A geolocation databases study. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2011, 29(10): 2044–2056
Zhao F, Song Y, Liu F, Ke K, Chen J, Luo X. City-level geolocation based on routing feature. In: Proceedings of the 29th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications. 2015, 414–419
Guo C, Liu Y, Shen W, Wang H, Yu Q, Zhang Y. Mining the web and the Internet for accurate IP address geolocations. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. 2009, 2841–2845
Liu H, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Zhang D, Fu X, Ramakrishnan K K. Mining checkins from location-sharing services for client-independent IP geolocation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. 2014, 619–627
Dan O, Parikh V, Davison B D. Distributed reverse DNS geolocation. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Big Data. 2018, 1581–1586
Scheitle Q, Gasser O, Sattler P, Carle G. HLOC: hints-based geolocation leveraging multiple measurement frameworks. In: Proceedings of Network Traffic Measurement and Analysis Conference. 2017, 1–9
Gueye B, Ziviani A, Crovella M, Fdida S. Constraint-based geolocation of Internet hosts. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2006, 14(6): 1219–1232
Eriksson B, Barford P, Sommers J, Nowak R. A learning-based approach for IP geolocation. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Passive and Active Network Measurement. 2010, 171–180
Wang Y, Burgener D, Flores M, Kuzmanovic A, Huang C. Towards street-level client independent IP geolocation. In: Proceedings of the 8th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation. 2011, 365–379
Jiang H, Liu Y, Matthews J. IP geolocation estimation using neural networks with stable landmarks. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops. 2016, 170–175
Liu C, Luo X, Yuan F, Liu F. RNBG: a ranking nodes based IP geolocation method. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops. 2020, 80–84
IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks — port 16: air interface for fixed broadband wireless access systems. IEEE Std 802.16〈TM〉-2004, 2004
Mukne N, Paffenroth R. Probabilistic inference of internet node geolocation with anomaly detection. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Technologies for Homeland Security. 2017, 1–6
Zu S, Luo X, Liu S, Liu Y, Liu F. City-level IP geolocation algorithm based on PoP network topology. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 64867–64875
Li D, Chen J, Guo C, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Zhang Y. IP-geolocation mapping for moderately connected Internet regions. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2012, 24(2): 381–391
Augustin B, Cuvellier X, Orgogozo B, Viger F, Friedman T, Latapy M, Magnien C, Teixeira R. Avoiding traceroute anomalies with paris traceroute. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement. 2006, 153–158
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1804263, U1636219), the Science and Technology Innovation Talent Project of Henan Province (184200510018) and Zhongyuan Science and Technology Innovation Leading Talent Project (214200510019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shuodi Zu received his BS and MS from the State Key Laboratory of Mathematical Engineering and Advanced Computing, China in 2016. He has been with the State Key Laboratory of Mathematical Engineering and Advanced Computing since July 2012. His research interest includes network security and network geolocation. He received the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Basic and Frontier Technology Research Program of Henan Province.
Xiangyang Luo received his BS, MS and PhD from the State Key Laboratory of Mathematical Engineering and Advanced Computing, China in 2001, 2004, and 2010, respectively. He has been with the State Key Laboratory of Mathematical Engineering and Advanced Computing, China since July 2004. From 2011, he is a postdoctoral of Institute of China Electronic System Equipment Engineering Co., Ltd, China. He is the author or co-author of more than 100 refereed international journal and conference papers. His research interest includes network topology, network security and network geolocation. He obtained the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China and the Basic and Frontier Technology Research Program of Henan Province.
Fan Zhang received the BS degree from the Xiangtan University, China in 2017 and the MS degree from the State Key Laboratory of Mathematical Engineering and Advanced Computing, China in 2020. His research interests include network topology analysis and IP geolocation. He received the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Basic and Frontier Technology Research Program of Henan Province.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zu, S., Luo, X. & Zhang, F. IP-geolocater: a more reliable IP geolocation algorithm based on router error training. Front. Comput. Sci. 16, 161504 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-021-0427-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-021-0427-4