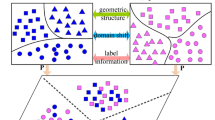
Abstract
Unsupervised transfer subspace learning is one of the challenging and important topics in domain adaptation, which aims to classify unlabeled target data by using source domain information. The traditional transfer subspace learning methods often impose low-rank constraints, i.e., trace norm, to preserve data structural information of different domains. However, trace norm is only the convex surrogate to approximate the ideal low-rank constraints and may make their solutions seriously deviate from the original optimums. In addition, the traditional methods directly use the strict labels of source domain, which is difficult to deal with label noise. To solve these problems, we propose a novel nonconvex and discriminative transfer subspace learning method named NDTSL by incorporating Schatten-p norm and soft label matrix. Specifically, Schatten-p norm can be imposed to approximate the low-rank constraints and obtain a better low-rank representation. Then, we design and adopt soft label matrix in source domain to learn a more flexible classifier and enhance the discriminative ability of target data. Besides, due to the nonconvexity of Schatten-p norm, we design an efficient alternative algorithm IALM to solve it. Finally, experimental results on several public transfer tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of NDTSL compared with several state-of-the-art methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Margolis A. A literature review of domain adaptation with unlabeled data. Washington: University of Washington, 2011, 1–42
You K, Long M, Cao Z, Wang J, Jordan M I. Universal domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019, 2715–2724
Kouw W M, Loog M. A review of domain adaptation without target labels. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(3): 766–785
Farahani A, Voghoei S, Rasheed K, Arabnia H R. A brief review of domain adaptation. In: Stahlbock R, Weiss G M, Abou-Nasr M, Yang C Y, Arabnia H R, Deligiannidis L, eds. Advances in Data Science and Information Engineering. Cham: Springer, 2021, 877–894
Patel V M, Gopalan R, Li R, Chellappa R. Visual domain adaptation: a survey of recent advances. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2015, 32(3): 53–69
Csurka G. Domain Adaptation in Computer Vision Applications. Cham: Springer, 2017
Jiang J. Domain adaptation in natural language processing. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Dissertation, 2008
Perone C S, Ballester P, Barros R C, Cohen-Adad J. Unsupervised domain adaptation for medical imaging segmentation with self-ensembling. NeuroImage, 2019, 194: 1–11
Zhang Y, Wei Y, Wu Q, Zhao P, Niu S, Huang J, Tan M. Collaborative unsupervised domain adaptation for medical image diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7834–7844
Guan H, Liu M. Domain adaptation for medical image analysis: a survey. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 69(3): 1173–1185
Pan S J, Tsang I W, Kwok J T, Yang Q. Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(2): 199–210
Long M, Wang J, Ding G, Sun J, Yu P S. Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2013, 2200–2207
Wang J, Chen Y, Hao S, Feng W, Shen Z. Balanced distribution adaptation for transfer learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. 2017, 1129–1134
Zhang W, Wu D. Discriminative joint probability maximum mean discrepancy (DJP-MMD) for domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. 2020, 1–8
Wang W, Li H, Ding Z, Nie F, Chen J, Dong X, Wang Z. Rethinking maximum mean discrepancy for visual domain adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(1): 264–277
Gretton A, Borgwardt K M, Rasch M J, Schölkopf B, Smola A. A kernel two-sample test. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2012, 13: 723–773
Fernando B, Habrard A, Sebban M, Tuytelaars T. Unsupervised visual domain adaptation using subspace alignment. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2013, 2960–2967
Sun B, Saenko K. Subspace distribution alignment for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. 2015, 24.1–24.10
Sun B, Feng J, Saenko K. Return of frustratingly easy domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 30th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2016, 2058–2065
Gopalan R, Li R, Chellappa R. Domain adaptation for object recognition: an unsupervised approach. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2011, 999–1006
Gong B, Shi Y, Sha F, Grauman K. Geodesic flow kernel for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2012, 2066–2073
Shao M, Kit D, Fu Y. Generalized transfer subspace learning through low-rank constraint. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2014, 109(1–2): 74–93
Xu Y, Fang X, Wu J, Li X, Zhang D. Discriminative transfer subspace learning via low-rank and sparse representation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(2): 850–863
Li J, Zhao J, Lu K. Joint feature selection and structure preservation for domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2016, 1697–1703
Lin Z, Zhao Z, Luo T, Yang W, Zhang Y, Tang Y. Non-convex transfer subspace learning for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. 2019, 1468–1473
Yang L, Zhou Q. Transfer subspace learning joint low-rank representation and feature selection. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(27): 38353–38373
Li W, Chen S. Unsupervised domain adaptation with progressive adaptation of subspaces. Pattern Recognition, 2022, 132: 108918
Razzaghi P, Razzaghi P, Abbasi K. Transfer subspace learning via low-rank and discriminative reconstruction matrix. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 163: 174–185
Xiao T, Liu P, Zhao W, Liu H, Tang X. Structure preservation and distribution alignment in discriminative transfer subspace learning. Neurocomputing, 2019, 337: 218–234
Xia H, Jing T, Ding Z. Maximum structural generation discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(3): 3434–3445
Madadi Y, Seydi V, Hosseini R. Multi-source domain adaptation-based low-rank representation and correlation alignment. International Journal of Computers and Applications, 2022, 44(7): 670–677
Yang L, Lu B, Zhou Q, Su P. Unsupervised domain adaptation via re-weighted transfer subspace learning with inter-class sparsity. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023, 263: 110277
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y. Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1): 171–184
Fazel M, Hindi H, Boyd S P. A rank minimization heuristic with application to minimum order system approximation. In: Proceedings of IEEE American Control Conference. 2001, 4734–4739
Fang X, Xu Y, Li X, Lai Z, Wong W K, Fang B. Regularized label relaxation linear regression. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(4): 1006–1018
Wang Y, Yin W, Zeng J. Global convergence of ADMM in nonconvex nonsmooth optimization. Journal of Scientific Computing, 2019, 78(1): 29–63
Nie F, Wang H, Cai X, Huang H, Ding C. Robust matrix completion via joint schatten p-Norm and lp-norm minimization. In: Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. 2012, 566–574
Lin Z, Chen M, Wu L, Ma Y. The augmented Lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices. Urbana: Coordinated Science Laboratory, 2009
Saenko K, Kulis B, Fritz M, Darrell T. Adapting visual category models to new domains. In: Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision. 2010, 213–226
Griffin G, Holub A, Perona P. Caltech-256 object category dataset. Pasadena: California Institute of Technology, 2007
Everingham M, Van Gool L, Williams C K I, Winn J, Zisserman A. The PASCAL visual object classes (VOC) challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303–338
Russell B C, Torralba A, Murphy K P, Freeman W T. LabelMe: a database and web-based tool for image annotation. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2008, 77(1–3): 157–173
Choi M J, Lim J J, Torralba A, Willsky A S. Exploiting hierarchical context on a large database of object categories. In: Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2010, 129–136
Bay H, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L. SURF: speeded up robust features. In: Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision. 2006, 404–417
Donahue J, Jia Y, Vinyals O, Hoffman J, Zhang N, Tzeng E, Darrell T. DeCAF: a deep convolutional activation feature for generic visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning. 2014, I–647–I–655
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61922087), and the Huxiang Young Talents Program of Hunan Province (2021RC3070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests or financial conflicts to discloe.
Additional information
Yueying Liu received the BS degree in Information and Computing Science from Shanxi University, China in 2021. She is working toward the master degree in System Theory at National University of Defense Technology, China. Her current research interests include machine learning, optimization, and computer vision.
Tingjin Luo received his PhD degrees from National University of Defense Technology, China. He is currently an associate professor with the College of Science of the same university. He was a visiting PhD student with the University of Michigan, USA from 2015 to 2017. He has authored more than 40 papers in journals and conferences, such as the IEEE TKDE, IEEE TCYB, ACM KDD, and ICME. He has been a Program Committee member of several conferences including IJCAI, AAAI, ICPR, etc. His research interests include machine learning, optimization, data mining, and computer vision.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Luo, T. Nonconvex and discriminative transfer subspace learning for unsupervised domain adaptation. Front. Comput. Sci. 19, 192307 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-023-3228-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-023-3228-0