Abstract
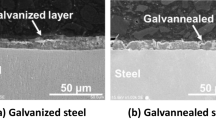
Laser welding of zinc-coated steels in an overlap setup is prone to weld defects and seam expulsion reducing in particular the properties in mechanical loading and in general the deployability of such weldments in industry. Several laser welding process technologies failed to created defect-free welds in zinc-coated steels. This paper renders the welding of zinc-coated steels by the novel technology of bifocal hybrid laser welding. The zinc-coated steels under consideration are DX56D + Z, DC04 + ZE, and HXT700D. The bifocal hybrid laser system is realised by combining an Nd:YAG laser with a high power diode laser, both of 3 kW maximum output power. The beam parameter product (BPP) of the employed Nd:YAG laser of 25 mm mrad translates with an optical system of focal length f = 150 mm into a circular focus of diameter 0.45 mm, whereas the BPP of the HPDL of 85 mm × 200 mm mrad can achieve a rectangular focus of 0.9 mm × 3.7 mm. The optical system allows the respective focal plane and relative position of the foci to be independently vertically and horizontally positioned. This paper presents research into the causes of instabilities in laser welding of zinc-coated steels. Experimental evidence is considered and presented to establish the need for an empirical process model for stable laser welding of zinc-coated steels. The increase of process robustness is discussed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roeren S, Trautmann A, Zaeh MF (2005) Modelling of transient clamping conditions during laser beam welding. In: Proceedings of 3rd international WLT-conference on lasers in manufacturing (LIM), Munich, vol 13, pp 95–100
Glumann C (1996) Verbesserte Prozeßsicherheit und Qualität durch Strahlkombination beim Laserschweißen. In: Hügel H (ed) Laser in der Materialbearbeitung. Forschungsberichte des IFSW, Stuttgart
Hohenberger B (2003) Laserstrahlschweißen mit der Nd:YAG-Doppelfokustechnik - Steigerung von Prozeßstabilität, Flexibilität und verfügbarer Strahlleistung. In: Hügel H (ed) Laser in der Materialbearbeitung. Forschungsberichte des IFSW, Muenchen, Herbert Utz
Gref W (2005) Laserstrahlschweißen von Aluminiumwerkstoffen mit der Fokusmatrixtechnik. In: Hügel H (ed) Laser in der Materialbearbeitung. Forschungsberichte des IFSW, Muenchen, Herbert Utz
Allmen M, Blatter A (1995) Laser–beam interactions with materials, physical principles and applications. Springer, Heidelberg
Coste F, Fabbro R, Sabatier L (1997) Applications of visions to laser welding: increase of operating tolerances using beam-oscillation and filler. In: Proceedings of 17th international congress on application of lasers and electro-optics, ICALEO 1997, LIA, Orlando, FL, USA, pp 21–29
Rubben K, Mohrbacher M, Leirman E (1997) Advantages of using and oscillating laser beam for the production of tailored blanks. In: Leo HB (ed) Laser in materials processing, proceedings of SPIE, vol 3097, pp 228–243
Stol I, Martukanitz RP (2004) Laser welding with beam oscillation. US Patent 6,740,845
Meier O (2005) Hochfrequentes Strahlpendeln zur Erhöhung der Prozessstabilität beim Laserstrahlschweißen mit hoher Schmelzbaddynamik. In: Zwischenbericht AiF 13.600 N/DVS-Nr.: 6.049. http://www.dvs-forschungsvereinigung.de
Kägeler C, Albert F, Mys I, Grimm A, Urmoneit U (2007) Observation of process oscillations during high power laser welding. In: Proceedings of 7th LANE 2007, conference on laser assisted net shape engineering, Erlangen 25, Meisenbach, Bamberg, 25–28 Aug 2007, pp 123–135
DIN EN 10346: Kontinuierlich schmelztauch-veredelte Flacherzeugnisse aus Stahl - Technische Lieferbedingungen; Deutsche Fassung prEN 10346:2007/as replacement of DIN EN 10292 (2007–06), DIN EN 10326 (2004–09), DIN EN 10327 (2004–09), DIN EN 10336 (2007–07)
Zäh MF, Trautmann A (2004) Vergleich des hybriden, bifokalen Laserschutzgasschweißens mit Laser-MIG-Hybridverfahren. Alum Int J Ind Res Appl 80(12):1387–1391
Trautmann A, Roeren S, Zaeh MF (2004) Welding of extruded aluminium profiles by a hybrid bifocal laser system. In: Geiger M, Otto A (eds) Laser assisted net shape engineering, proceedings of 4th LANE ’04, Erlangen, Germany, 21–24 Sept pp 169–180
Trautmann A, Zaeh MF (2005) Hybrid bifocal laser welding of aluminum. In: Proceedings of 24th international congress on applications of lasers and electro-optics, ICALEO 2005, Miami, FL, USA, 31 Oct–3 Nov 2005, pp 153–162
Trautmann A, Zäh MF (2007) Prozesssicheres Fügen von Aluminium-Tragwerkstrukturen mit einem hybriden, bifokalen Lasersystem. In: Kleiner M, Baier H, Fleischer J, Löhe D, Weinert K, Zäh M, Schikorra M (eds) Integration von Umformen, Trennen und Fügen für die flexible Fertigung von leichten Tragwerkstrukturen, Fortschritt-Berichte VDI: Ergebnisbericht der Phase 1, Düsseldorf, Germany, Jan 2003 – Dez 2006, Reihe 2, pp 153–181
Trautmann A, Zaeh MF (2006) Laser bifocal hybrid welding of aluminum. In: Advanced materials research, flexible manufacture of lightweight frame structures, vol 10, pp 65–79
Huber S, Trautmann A, Zäh MF (2007) Bifocal hybrid laser welding of aluminium. In: Geiger M, Otto A, Schmidt M (eds) Proceedings of 7th LANE 2007, conference on laser assisted net shape engineering, Erlangen, Meisenbach, Bamberg, 25–28 Aug 2007, pp 151–162
Trautmann A, Zäh MF (2007) Increase of process robustness of zinc-coated steels in bifocal hybrid laser welding. In: Geiger M, Otto A, Schmidt M (eds) Proceedings of 7th LANE 2007, conference on laser assisted net shape engineering, Erlangen, Meisenbach, Bamberg, 25–28 Aug 2007, pp 197–208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milberg, J., Trautmann, A. Defect-free joining of zinc-coated steels by bifocal hybrid laser welding. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 3, 9–15 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-008-0140-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-008-0140-2