Abstract
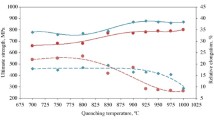
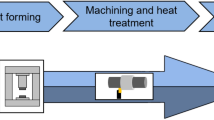
Excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance combined with low weight qualify β-titanium materials for lightweight applications in aviation, automotive and energy engineering. Thus far, actual applications of these materials have been limited due to high material costs and limited processing knowledge. One approach for developing resource-efficient manufacturing methods is the application of incremental forming methods. This article focuses on the development of the incremental spin extrusion process, which creates hollow profiles from solid bars. This method allows hollow shape manufacturing with a much higher flexibility than other forming methods and a significantly improved material utilization in comparison to machining methods, such as deep hole drilling. Beta-titanium alloys basically have very good cold forming suitability and the resulting material properties can be controlled. The application of incremental forming methods with high hydrostatic compressive stress is a promising manufacturing approach. The β-titanium Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al material has an excellent combination of the properties strength, ductility and fatigue strength. In order to utilize these properties the forming conditions and the temperature control need to be optimized. The investigations show that the Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al material can be formed only in a narrow semi-hot forming temperature window. The paper describes the investigation and presents results on the design of partial forming process sequences, forming properties, microstructure formation and failure prevention. The process design objective is a very fine microstructure with a homogeneous secondary α-phase and very small grained β-phase.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peters M, Leyens C (2000) Titan und Titanlegierungen. Wiley, Germany
Neugebauer R, Sterzing A, Hellfritzsch U, Glaß R (2010) Innovative cold forming processes for increasing efficiency of energy consumption and resources process chains for manufacturing of power train components. In: Tagungsband 25. Jahrestreffen der Kaltmassivumformer, 10–11. February 2010, Düsseldorf: VDI-Gesellschaft Produktion und Logistik
Donachie MJ (2000) Titanium: a technical guide. ASM International, USA
Drechsler A Einfluss des Festwalzens auf das Dauerschwingverhalten der metastabilen Beta-Titanlegierung Ti-10 V-2Fe-3Al, Fortschritt- Berichte VDI Reihe 5, Nr.633
Wagener HW, Haats J (1993) Kaltfließpressen von Titan und Titanlegierungen. In: K. Pöhlandt (eds) Werkstoffe und Werkstoffprüfung für die Kaltmassivumformung, Expert Verlag Ehringen S. 48-67
Steffens K, Wilhelm H, Werkstoffe, Oberflächentechnik und Fertigungsverfahren für die nächste Generation von Flugtriebwerken
Bania P (1993) Beta titanium alloys and their role in the titanium industry, in: Beta Titanium Alloys in the 1990 s. TMS, Warrendale, PA
Hahn F (2003) Untersuchung des zyklisch plastischen Werkstoffverhaltens unter umformnahen Bedingungen, Dissertation, TU Chemnitz
Weißbach U, Herold G (1994) Bohrungsdrücken—vom Stangenmaterial zum Präzisionshohlteil. In: Sächsische Fachtagung Umformtechnik, Chemnitz, Tagungsband, Germany, pp 1–26
Kiese J, Wagner L (1996) Fatigue behaviour in Ti-10 V–2Fe-3Al: Microstructural effects on crack nucleation and microcrack growth, Fatigue’96. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neugebauer, R., Meyer, L.W., Halle, T. et al. Manufacture of a β-titanium hollow shaft by incremental forming. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 5, 227–232 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-010-0280-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-010-0280-z