Abstract
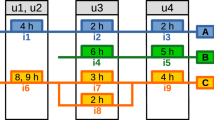
There is a decent number of possible heuristic methods to solve an actual problem in production planning and control. Usually, each solving method leads to a different alternative. In dynamic production environments, decision makers often have to decide between uncertainty and risk. Making multi-criteria decisions under risk is a well-known problem. In this paper, we will consider rescheduling as an example for decision-making in a dynamic production environment. It is used to present an intelligent manufacturing approach for multi-criteria decisions under risk that combines a method for decision-making under risk and a multi-attribute decision-making method. Moreover, for frequently appearing problems, such as rescheduling, a procedure to evaluate the used solving methods is presented. We use this information to achieve a sustainable improvement for the solving procedure of future manufacturing problems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aytug H et al (2005) Executing production schedules in the face of uncertainties: a review and some future directions. Eur J Oper Res 161:86–110
Blohm H, Lüder K, Schaefer C (2012) Investition –Schwachstellen-analyse des Investitionsbereichs und Investitionsrechnung. Vahlen, Franz, München
Butler J, Jia J, Dyer J (1997) Simulation techniques for the sensitivity analysis of multi-criteria decision models. Eur J Oper Res 103:531–546
Götze U (2008) Investitionsrechnung - Modelle und Analysen zur Beurteilung von Investitionsvorhaben. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Guitouni A, Martel J (1998) Tentative guidelines to help choosing an appropriate MCDA method. Eur J Oper Res 109:501–521
Herroelen W, Leus R (2005) Project scheduling under uncertainty: survey and research potentials. Eur J Oper Res 165:289–306
Horn J (1997) Multicriterion decision making. Handbook of evolutionary computation. Oxford, IOP Publishing and Oxford University Press, pp F1.9:1–F1.9:15
Hwang C, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attribute decision making methods and applications: a state-of-the-art survey. Springer, Berlin
Katragjini K, Vallada E, Ruiz R (2013) Flow shop rescheduling under different types of disruption. Int J Prod Res 51(3):780–797
Kempf K, Uzsoy R, Smith S, Garty K (2000) Evaluation and comparison of production schedules. Comput Ind 42:203–220
Laaribi A, Chevallier J, Martel J (1996) A spatial decision aid—a multicriterion evaluation approach. Comput Environ Urban Syst 20(6):351–366
Matos M (2007) Decision under risk as a multicriteria problem. Eur J Oper Res 181:1516–1529
Roy B, Bouyssou D (1991) Decision-aid: an elementary introduction with emphasis on multiple criteria. Investigación Operativa 2:95–110
Schneeweiß H (1967) Entscheidungskriterien bei Risiko. Springer, Berlin
Ude J (2010) Entscheidungsunterstützung für die Konfiguration globaler Wertschöpfungsnetzwerke: Ein Bewertungsansatz unter Berücksichtigung multikriterieller Zielsysteme, Dynamik und Unsicherheit. Shaker, Aachen
Vieira G, Herrmann J, Lin E (2003) Rescheduling manufacturing systems—a framework of strategies, policies, and methods. J Sched 6:39–62
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stricker, N., Kopf, R. & Lanza, G. Solving multi-criteria problems under risk: an approach explained using the example of rescheduling in dynamic environments. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 8, 535–541 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-014-0556-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-014-0556-9