Abstract
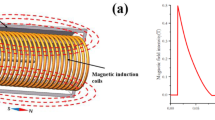
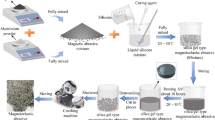
Magnetic abrasive processes combine characteristics of grinding and lapping. Due to deformable tool behavior, complex surface shapes and edges can be machined. Therefore, this process is predestined for preparation of drilled cutting tools. High quality finishing results require in depth process expertise. This paper focuses on the behavior of the magnetic abrasive tool taking Magnetfinish® kinematics into account. Main characteristics of the magnetic abrasive tool behavior during finishing end mills of 12 mm diameter are reshaping and in-process densification of magnetic abrasive layer. Consequently, flute surface modifications occur only in the cutting edge surrounding area. Furthermore, in-process displacements of magnetic abrasive cause non-uniform cutting edge rounding. SEM images indicate abrasive motion along the cutting edge as the best method to obtain smooth cutting edge surface.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furuno M et al (2010) Effect of ground surface roughness of tool on adhesion characteristics of PVD coating. Adv Mater Res 126–128:609–614
Buechel C et al (2007) Influence of edge preparation on the performance of coated cutting tools. Invited Talk of T. Cselle. International Conference on Metallurgical coatings and thin films. San Diego, May 2007
Rech J et al (2005) Influence of cutting edge radius on the wear resistance of PM-HSS milling inserts. Wear 259:1168–1176
Basset E et al (2012) On the honed cutting edge and its side effects during orthogonal turning operations of AISI1045 with coated WC-Co inserts. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 5:108–126
Denkena B et al (2011) Effects of the cutting edge microgeometry on tool wear and its thermo-mechanical load. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 60:73–76
Cheung FY et al (2008) Cutting edge preparation using magnetic polishing and its influence on the performance of high-speed steel drills. J Mater Process Technol 208:196–204
Gogaev KA et al (2006) Special features of the magnetic abrasive machining. Refract Ind Ceram 47(1):46–47
Karpuschewski B et al (2009) Magneto-abrasive machining for the mechanical preparation of high-speed steel twist drills. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 58:295–298
Yamaguchi H et al (2012) Magnetic abrasive finishing of cutting tools for machining of titanium alloys. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 61:311–314
Singh DK et al (2006) Experimental investigations into forces acting during a magnetic abrasive finishing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 30:652–662
Singh AK et al (2012) Nanofinishing of typical 3D ferromagnetic workpiece using ball end magnetorheological finishing process. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 63:21–31
Baron YM et al (2005) Characterization of the magnetic abrasive finishing method and it application to deburring. Key Eng Mater 291–292:291–296
Tikal F et al (2009) Schneidkantenpräparation–Ziele. Kassel University Press, Kassel, Verfahren und Messmethoden
Reichmann S (2011) Komplette Oberflächenbehandlung durch Magnetfinish. Schleifen und Polieren 3:76–78
Denkena B et al (2009) Cutting edge preparation for cemented carbide milling tools. Adv Mater Res 76–78:597–602
Acknowledgments
The presented investigations were undertaken with support of the German Research Foundation within the project “Modellierung des Materialabtrags bei der magnet-abrasiven Bearbeitung von Hartmetallwerkzeugen”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Denkena, B., Köhler, J. & Schindler, A. Behavior of the magnetic abrasive tool for cutting edge preparation of cemented carbide end mills. Prod. Eng. Res. Devel. 8, 627–633 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-014-0569-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11740-014-0569-4