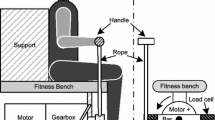
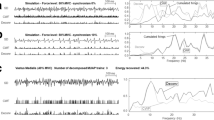
Abstract
It is well known that there is a change in the spectrum of surface electromyogram (sEMG) with the onset of muscle fatigue. This change has largely been attributed to the change in muscle conduction velocity. We have investigated this theory by using our previously developed sEMG model with the various neuromuscular parameters. The change of spectrum of the experimental results has been compared with simulated sEMG in response to the change in muscle conduction velocity using similar conditions. In this study, the designed model implemented the change in the muscle conduction velocity (\(\Delta v\)) as a parameter to simulate the sEMG. The shift in spectrum was identified by computation of the median frequency (MDF) of the sEMG before and after the implementation of the rate of the slow down (RS or \(\Delta v\)) parameter in the model. The results based on the simulation of the model show that the rate of change in MDF was consistent in all levels of contractions and it is not same with experimental conditions. The results also suggest that the large change in MDF in the simulated sEMG than in experimental conditions may be attributable to other factors such as change in the recruitment pattern and the level of contraction not only due to the change in the muscle conduction velocity (\(\Delta v\)).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardi, M., Solomonow, M., Nguyen, G., Smith, A., Baratta, R.: Motor unit recruitment strategy changes with skill acquisition. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 74, 52–59 (1996)
Bernardi, M., Solomonow, M., Baratta, R.V.: Motor unit recruitment strategy of antagonist muscle pair during linearly increasing contraction. EMG Clin. Neurophysiol. 37, 3–12 (1997)
Gerdle, B., Henriksson-Larsén, K., Lorentzon, R., Wretling, M.L.: Dependence of the mean power frequency of the electromyogram on muscle force and fibre type. Acta Physiol. Scand. 142, 457–465 (1991)
Gydikov, A., Kosarov, D.: Some features of different motor units in human biceps brachii. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 347(1), 75–88 (1974)
Arendt-Nielsen, L., Mills, K.R.: The relationship between mean power frequency of the EMG spectrum and muscle fibre conduction velocity. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 60(2), 130–134 (1985)
Lindstrom, L., Magnusson, R.: Interpretation of myoelectric power spectra: a model and its applications. Proc. IEEE 65, 653–662 (1977)
Farina, D.: Counterpoint: spectral properties of the surface EMG do not provide information about motor unit recruitment and muscle fiber type. J. Appl. Physiol. 105, 1673–1674 (2008)
Onishi, H., Yagi, R., Akasaka, K., Momose, K., Ihashi, K., Handa, Y.: Relationship between EMG signals and force in human vastus lateralis muscle using multiple bipolar wire electrodes. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 10, 59–67 (2000)
Elfving, B., Liljequist, D., Mattsson, E., Németh, G.: Influence of interelectrode distance and force level on the spectral parameters of surface electromyographic recordings from the lumbar muscles. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 12(4), 295–304 (2002)
Wheeler, K., Kumar, D.K., Shimada, H.: An accurate biceps muscle model with sEMG and muscle force outputs. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 34, 101–119 (2010)
Broman, H., Bilotto, G., De Luca, C.J.: Myoelectric signal conduction velocity and spectral parameters: influence of force and time. J. Appl. Physiol. 58(5), 1428–1437 (1985)
Sadoyama, T., Masuda, T., Miyano, H.: Relationships between muscle fibre conduction velocity and frequency parameters of surface EMG during sustained contraction. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 51(2), 247–256 (1983)
Lee, Y.S., Jeon, C.I., Lee, S.H.: A model for myoelectric signal with localized muscle fatiguing. J. Korean Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 7(1), 79–86 (2003)
Merletti, R., Lo, Conte L.: Modeling of surface myoelectric signals. I. Model implementation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 46(7), 810–820 (1999)
Merletti, R., Roy, S.H., Kupa, E., Roatta, S., Granata, A.: Modeling of surface myoelectric signals. II. Model-based signal interpretation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 46(7), 821–829 (1999)
van Veen, B.K., Wolters, H., Wallinga, W., Rutten, W.L., Boom, H.B.: The bioelectrical source in computing single muscle fiber action potentials. Biophys. J. 64(5), 1492–1498 (1993)
Lowery, M.M., Vaughan, C.L., Nolan, P.J., O’Malley, M.J.: Spectral compression of the electromyographic signal due to decreasing muscle fiber conduction velocity. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 8(3), 353–361 (2000)
Krogh-Lund, C., Jørgensen, K.: Modification of myo-electric power spectrum in fatigue from 15% maximal voluntary contraction of human elbow flexor muscles, to limit of endurance: reflection of conduction velocity variation and/or centrally mediated mechanisms? Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 64(4), 359–370 (1992)
Farina, D., Fattorini, L., Felici, F., Filligoi, G.: Nonlinear surface EMG analysis to detect changes of motor unit conduction velocity and synchronization. J. Appl. Physiol. 93(5), 1753–1763 (2002)
Roeleveld, K., Blok, J.H., Stegeman, D.F., van Oosterom, A.: Volume conduction models for surface EMG; confrontation with measurements. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 7(4), 221–232 (1997)
Dumitru, D., King, J.C., Rogers, W.E.: Motor unit action potential components and physiologic duration. Muscle Nerve 22(6), 733–741 (1997)
Kukulka, C.G., Clamann, H.P.: Comparison of the recruitment and discharge properties of motor units in human brachial biceps and adductor pollicis during isometric contractions. Brain Res. 219(1), 45–55 (1981)
Moritani, T., Muro, M.: Motor unit activity and surface electromyogram power spectrum during increasing force of contraction. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 56, 260–265 (1987)
Van der hoeven, J.H., Van weerden, T.W., Zwarts, M.J.: Long-lasting supernormal conduction velocity after sustained maximal isometric contraction in human muscle. Muscle Nerve 16(3), 312–320 (1993)
De Luca, C.J., et al.: Inter-electrode spacing of surface EMG sensors: reduction of crosstalk contamination during voluntary contractions. J. Biomech. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2011.11.010
Basmajian, J.V., De Luca, C.J.: Muscles Alive, 5th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poosapadi Arjunan, S., Kumar, D.K., Wheeler, K. et al. Spectral properties of surface electromyogram signal and change in muscle conduction velocity during isometric muscle contraction. SIViP 9, 261–266 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-013-0437-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-013-0437-2