Abstract
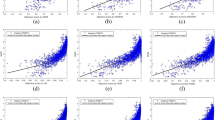
This paper investigates the impacts of image quality level on the prediction accuracy of image quality metrics. While many state-of-the-art perceptual image quality assessment methods have achieved fairly well performances in terms of the correlation between the quality predictions and the subjective scores, none of them took into account the effects of the quality levels of those test images on prediction accuracy of the quality metrics. In this work, inspired by the mechanism of human perception under high- and low-quality conditions, we propose a new image quality assessment paradigm based on image quality level classification. Our investigation on TID2008 and other three publicly available databases (LIVE, CSIQ and Toyama-MICT) results in two valuable findings. First, the performances of major well-known image quality assessment methods are significantly affected by image quality level. Second, through combining different quality metrics for different quality levels, superior performance can be achieved as compared to some of the best image quality metrics, e.g., SSIM, MS-SSIM, VIF and VIFP. Experiments and comparative studies are provided to confirm the effectiveness of the proposed new paradigm by differentiating quality levels for image quality assessment.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eskicioglu, A.M., Fisher, P.S.: Image quality measures and their performance. In: IEEE Trans. Commun. 43, 2959–2965 (1995)
Miller, G.A.: The cognitive revolution: a historical perspective. Trends Cogn. Sci. 7(3), 141–144 (2003)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheikh, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Wang, Z., Simoncelli, E.P., Bovik, A.C.: Multi-scale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In: IEEE Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computer, vol. 2, pp. 1398–1402 (2003)
Sheikh, H.R., Bovik, A.C.: Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(2), 430–444 (2006)
Lu, Z., Lin, W., Yang, X., Ong, E.P., Yao, S.S.: Modeling visual attentions modulatory aftereffects on visual sensitivity and quality evaluation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 14(11), 1928–1942 (2005)
Sadaka, N.G., Karam, L.J., Ferzli, R., Abousleman, G.P.: A no-reference perceptual image sharpness metric based on saliency weighted foveal pooling. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 369–372 (2008)
Noorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: Visual importance pooling for image quality assessment. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 3(2), 193–201 (2009)
Ninassi, A., Meur, O.L., Callet, P.L., Barba, D.: Does where you gaze on an image affect your perception of quality? Applying visual attention to image quality metric. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp. 169–172 (2007)
Liu, H., Heynderickx, I.: Visual attention in objective image quality assessment: based on eye-tracking data. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 21(7), 971–982 (2011)
Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: A two-step framework for constructing blind image quality indices. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(5), 513–516 (2010)
Moorthy, A.K., Bovik, A.C.: Statistics of natural image distortions. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, pp. 962–965 (2010)
Capodiferro, L., Jacovitti, G., Di Claudio, E.D.: Two-dimensional approach to full reference image quality. Assessment based on positional structural information. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(2), 505–516 (2012)
Vu, C.T., Larson, E.C., Chandler, D.M.: Visual fixation patterns when judging image quality: effects of distortion type, amount, and subject experience. In: IEEE Southwest Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation, pp. 73–76 (2008)
Ponomarenko, N., Lukin, V., Zelensky, A., Egiazarian, K., Carli, M., Battisti, F.: TID2008-A database for evaluation of full-reference visual quality assessment metrics. Adv. Mod. Radioelectron. 10, 30–45 (2009)
Sheikh, H.R., Seshadrinathan, K., Moorthy, A.K., Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Cormack, L.K.: Image and video quality assessment research at LIVE. [Online] Available: http://live.ece.utexas.edu/research/quality/
Larson, E.C., Chandler, D.M.: Categorical image quality (CSIQ) database. [Online] Available: http://vision.okstate.edu/csiq
Horita, Y., Shibata, K., Kawayoke, Y., Sazzad, Z.M.P.: MICT image quality evaluation database. [Online] Available: http://mict.eng.u-toyama.ac.jp/mict/index2.html
Gaubatz, M.: Metrix MUX visual quality assessment package. http://foulard.ece.cornell.edu/gaubatz/metrix_mux/
Sheikh, H.R., Bovik, A.C., de Veciana, G.: An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 14(12), 2117–2128 (2005)
Damera-Venkata, N., Kite, T.D., Geisler, W.S., Evans, B.L., Bovik, A.C.: Image quality assessment based on a degradation model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 9, 636–650 (2000)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C.: A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9, 81–84 (2002)
Chandler, D.M., Hemami, S.S.: VSNR: a wavelet-based visual signal-to-noise ratio for natural images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(9), 2284–2298 (2007)
Mitsa, T., Varkur, K.: Evaluation of contrast sensitivity functions for the formulation of quality measures incorporated in halftoning algorithms. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, vol. 5, pp. 301–304 (1993)
VQEG: Final report from the video quality experts group on the validation of objective models of video quality assessment. (2000). http://www.vqeg.org/
Zhai, G., Wu, X., Yang, X., Lin, W., Zhang, W.: A psychovisual quality metric in free-energy principle. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(1), 41–52 (2012)
Wang, Z., Li, Q.: Information content weighting for perceptual image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(5), 1185–1198 (2011)
Lin, W., Jay Kuo, C.-C.: Perceptual visual quality metrics: a survey. J. Vis. Commun. Image R. 22(4), 297–312 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by postdoctoral foundation of Shanghai 11R21414200, postdoctoral foundation of China 20100480603, 201104276, NSERC, NSFC (61025005, 60932006, 61001145), SRFDP (20090073110022), the 111 Project (B07022) and STCSM (12DZ2272600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by NSERC, NSFC (61025005, 60932006, 61001145), SRFDP (20090073110022), postdoctoral foundation of China 20100480603, postdoctoral foundation of Shanghai 11R21414200 and the 111 Project (B07022).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, K., Zhai, G., Yang, X. et al. A new psychovisual paradigm for image quality assessment: from differentiating distortion types to discriminating quality conditions. SIViP 7, 423–436 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-013-0445-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-013-0445-2