Abstract
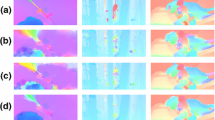
The motion history image (MHI) is a global spatiotemporal representation for video sequences. It is computationally very simple and efficient. It has been widely used for many real-time action recognition tasks. However, the conventional MHI assigns a fixed motion strength to each detected foreground point and then updates it with a small constant for the background point. Local body parts with different movement speeds and durations will then have the same intensity in the MHI. Similar actions may generate indistinguishable MHI patterns. In this paper, we propose a new motion history representation that incorporates both optical flow and a revised MHI. The motion strength of each pixel point is adaptively accumulated by the optical flow length at that location. It is then exponentially updated over time. It can better describe local movements of body parts in the global temporal template. The motion duration is implicitly given by the update rate for better description of various actions in the scene. For action classification, a set of training action samples are first collected and form the basis templates. An action sequence is then constructed as the linear combination of the basis templates. The coefficients of the combination give the feature vector. The Euclidean distance is finally used to evaluate the similarity between the feature vectors. Experimental results on the widely used KTH and Weizmann datasets have shown that the proposed scheme yields 100 % recognition rates on both test datasets with a fast processing rate of 47 fps on \(200\times 150\) images.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sundaresan, A., Chellappa, R.: Segmentation and probabilistic registration of articulated body models. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, vol. 2, pp. 92–96 (2006)
Thi, T.H.: Human body articulation for action recognition in video. In: IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, pp. 92–97 (2009)
Poppe, R.: A survey on vision-based human action recognition. Image Vis. Comput. 28, 976–990 (2010)
Aggarwal, J.K., Ryoo, M.S.: Human activity analysis: A review. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 43, 1–43 (2011)
Weinland, D., Ronfard, R., Boyer, E.: A survey of vision-based methods for action representation, segmentation and recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 115, 224–241 (2011)
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., Caputo, B.: Recognizing human actions: a local SVM approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 3, pp. 32–36 (2004)
Liu, J., Shah, M.: Learning human actions via information maximization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Yuan, J., Liu, Z., Wu, Y.: Discriminative subvolume search for efficient action detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2442–2449 (2009)
Cao, L., Liu, Z., Huang, T.S.: Cross-dataset action detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1998–2005 (2010)
Kim, T.-K., Wong S.-F., Cipolla, R.: Tensor canonical correlation analysis for action classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Noguchi, A., Yanai, K.: A SURF-based spatio-temporal feature for feature-fusion-based action recognition. Lecture Notes Comput. Sci. 6553, 153–167 (2012)
Ali, S., Shah, M.: Human action recognition in video using kinematic features and multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 32, 288–303 (2010)
Seo, H.J., Milanfar, P.: Action recognition from one example. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 33, 867–882 (2011)
Jargalsaikhan, I., Little, S., Direkoglu, C., O’Connor, N.E.: Action recognition based on sparse motion trajectories. In: IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, 2013. (To appear)
Goudelis, G., Karpouzis, K., Kollias, S.: Exploring trace transform for robust human action recognition. Patt. Recogn. 46, 3238–3248 (2013)
Nasri, S., Behrad, A., Razzaszi, F.: Spatio-temporal 3D surface matching for hand gesture recognition using ICP algorithm. Signal Image Video Process. 1, 1–16 (2013). doi:10.1007/s11760-013-558-7
Mahbub, U., Imtiaz, H., Ahad, Md A.R.: Action recognition based on statistical analysis from clustered flow vectors. Signal Image Video Process. 8, 243–253 (2014)
Davis, J., Bobick, A.: The representation and recognition of human movement using temporal templates. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 928–934 (1997)
Bobick, A.F., Davis, J.W.: The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 23, 257–267 (2001)
Xiang, T., Gong, S.: Beyond tracking: modeling activity and understanding behaviour. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 67, 21–51 (2006)
Chen, C., Liang, J., Zhao, H., Hu, H., Tian, J.: Frame difference energy image for gait recognition with incomplete silhouettes. Patt. Recogn. Lett. 30, 977–984 (2003)
Yu, C.-C., Cheng, H.-Y., Cheng, C.-H., Fan, K.-C.: Efficient human action and gait analysis using multiresolution motion energy histogram, EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. (2010) Article ID 975291
Nguyen, Q., Novakowski, S., Boyd, J.E., Jacob, C., Hushlak, G.: Motion swarms: video interaction for art in complex environments. In: Proceedings of ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 461–469 (2006)
Lee, S.-Y., Ahn, S.C., Lim, M.-T., Kim, H.-G.: Tangible video Avatar for natural tele-interaction. In: Proceedings of International Workshop on the Tangible Space Initiative (2007)
Wang, F., Jiang, Y.-G., Ngo, C.-W.: Video event detection using motion relativity and visual relatedness. In: Proceedings of ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 239–248 (2008)
Oikonomopoulos, A., Patras, I., Pantic, M.: Spatiotemporal localization and categorization of human actions in unsegmented image sequences. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20, 1126–1140 (2011)
Ahad, Md A.R., Tan, J.K., Kim, H., Ishikawa, S.: Motion history image: its variants and applications. Mach. Vis. Appl. 23, 255–281 (2012)
Ahad, Md A.R., Tan, J.K., Kim, H., Ishikawa, S.: Temporal motion recognition and segmentation approach. Int. J. Imag. Syst. Tech. 19, 91–99 (2009)
Ahmad, M., Lee, S.-W.: Recognizing human actions based on silhouette energy image and global motion description, In: Proceedings of IEEE Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 523–588 (2008)
Bradski, G., Davis, J.: Motion segmentation and pose recognition with motion history gradients. Mach. Vis. Appl. 13, 174–184 (2002)
Ahmad, M., Hossain, M.Z.: SEI and SHI representations for human movement recognition. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, pp. 521–526 (2008)
Vitaladevuni, S.N., Kellokumpu, V., Davis, L.S.: Action recognition using ballistic dynamics. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Meng, H., Pears, N., Bailey, C.: Human action classification using SVM\_2K classifier on motion features. In: LNCS: Multimedia Content Representation, Classification and Security 4105, 458–465 (2006)
Md, A.R., Ahad, J.K., Tan, H.: Analysis of motion self-occlusion problem due to motion overwriting for human activity recognition. J. Multimed. 5, 36–46 (2009)
Babu, R., Ramakrishnan, K.: Recognition of human actions using motion history information extracted from the compressed video. Image Vis. Comput. 22, 597–607 (2004)
Valstar, M., Pantic, M., Patras, I.: Motion history for facial action detection in video. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on SMC, vol. 1, pp. 635–640 (2004)
Orrite, C., Martinez, F., Herrero, E., Ragheb, H., Velastin, S.: Independent viewpoint silhouette-based human action modeling and recognition. In: Proceedings of International Workshop on Machine Learning for Vision-Based Motion Analysis with ECCV, pp. 1–12 (2008)
kellokumpu, V., Zao, G., Pietikanen, M.: Recognition of human actions using texture descriptors. Mach. Vis. Appl. 22, 767–780 (2011)
Wu, D., Shao, L.: Silhouette analysis based action recognition via exploiting human poses, IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Video Technol. 2013 (To appear)
Tian, Y., Cao, L., Liu, Z., Zhang, Z.: Hierarchical filtered motion for action recognition in crowded videos. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 45, 313–323 (2012)
Barron, J.L., Fleet, D.J., Beauchemin, S.S.: Performance of optical flow techniques. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 12, 43–77 (1994)
Baker, S., Scharstein, D., Lewis, J.P., Roth, S., Black, M.J., Szeliski, R.: A database and evaluation methodology for optical flow. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 92, 1–31 (2011)
Lucas, B.D., Kanade, T.: An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision In: Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Artifical Intelligence. pp. 674–679 (1981)
Baker, S., Matthews, I.: Lucas-Kanade 20 years on: a unifying framework. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 56, 221–255 (2004)
Gorelick, L., Blank, M., Shechtman, E., Irani, M., Basri, R.: Actions as space-time shapes. IEEE Trans. Patt. Anal. Mach. Intell. 29, 2247–2253 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, DM., Chiu, WY. & Lee, MH. Optical flow-motion history image (OF-MHI) for action recognition. SIViP 9, 1897–1906 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-014-0677-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-014-0677-9