Abstract
In this paper, we show how linear, but not necessarily shift-invariant, filters can be used to propagate sparse labels throughout an image. We propose a new propagation method based on the domain transform filter, a linear, shift-varying filter whose kernel width varies based on local edge information. We contrast this against the more well-known energy minimization approach and show that it can produce significantly better results when the input labels contain errors. Finally, we show how minimization-based methods are better suited for purely user-guided applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A filter is linear if \(h\{Ax[n] + By[n]\} = Ah\{x[n]\} + Bh\{y[n]\}.\)
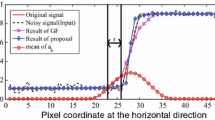
\(\sigma _s\) has minimal effect provided it is relatively large. See [15] for more information on the parameters.
References
Grady, L.: Random walks for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(11), 1768–1783 (2006)
Boykov, Y., Funka-Lea, G.: Graph cuts and efficient N-D image segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 70(2), 109–131 (2006). doi:10.1007/s11263-006-7934-5
Szeliski, R.: Computer vision: algorithms and applications. Springer, (2010). http://szeliski.org/Book/
Perona, P., Malik, J.: Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 12(7), 629–639 (1990)
Levin, A., Lischinski, D., Weiss, Y.: Colorization using optimization. ACM Trans. Graph. 23(3), 689–694 (2004). doi:10.1145/1015706.1015780
Lischinski, D., Farbman, Z., Uyttendaele, M., Szeliski, R.: Interactive local adjustment of tonal values. ACM Trans. Graph. 25(3), 646–653 (2006). doi:10.1145/1141911.1141936
Guttmann, M., Wolf, L., Cohen-Or, D.: Semi-automatic Stereo extraction from video footage. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), (2009)
Wang, O., Lang, M., Frei, M., Hornung, A., Smolic, A., Gross,M.: Stereobrush: interactive 2d–3d conversion using discontinuous warps. In: Proceedings of the Eighth Eurographics Symposium on Sketch-Based Interfaces and Modeling, ser. SBIM ’11. New York, NY, USA: ACM, pp. 47–54 (2011). http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/2021164.2021173
Phan, R., Androutsos, D.: Robust semi-automatic depth map generation in unconstrained images and video sequences for 2d to stereoscopic 3d conversion. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 16(1), 122–136 (2014)
Ward, B., Kang, S.B., Bennett, E.: Depth director: a system for adding depth to movies. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 31(1), 36–48 (2011)
Liao, M., Gao, J., Yang, R., Gong, M.: Video stereolization: combining motion analysis with user interaction. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 18(7), 1079–1088 (2012)
Becker, M., Baron, M., Kondermann, D., Bussler, M., Helzle,V.: Movie dimensionalization via sparse user annotations. In: 3DTV-Conference: The True Vision-Capture, Transmission and Dispaly of 3D Video (3DTV-CON), 2013, pp. 1–4 (2013)
Shepard, D.: A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM National Conference, ser. ACM ’68. New York, NY, USA: ACM, pp. 517–524 (1968). (Online) http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/800186.810616
Fattal, R.: Edge-avoiding wavelets and their applications. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(3), 1–10 (2009)
Gastal, E.S.L., Oliveira, M.M.: Domain transform for edge-aware image and video processing. ACM TOG 30(4), 69:1–69:12 (2011)
He, K., Sun, J., Tang, X.: Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(6), 1397–1409 (2013)
Lang, M., Wang, O., Aydin, T., Smolic, A., Gross, M.: Practical temporal consistency for image-based graphics applications. ACM Trans. Graph. 31(4), 34:1–34:8 (2012). doi:10.1145/2185520.2185530
Rzeszutek, R., Androutsos, D.: A framework for estimating relative depth in video. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 133(0), 15–29 (2015). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S107731421500003X
Rzeszutek, R., Androutsos, D.: Label propagation through edge-preserving filters. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 599–603 (2014)
Stefanoski, N., Bal, C., Lang, M., Wang, O., Smolic, A.: Depth estimation and depth enhancement by diffusion of depth features. In: 20th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1247–1251 (2013)
Paris, S., Durand, F.: A fast approximation of the bilateral filter using a signal processing approach. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 81(1), 24–52 (2009). doi:10.1007/s11263-007-0110-8
Chaudhury, K.: Acceleration of the shiftable o(1) algorithm for bilateral filtering and nonlocal means. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(4), 1291–1300 (2013)
Phan, R., Rzeszutek, R., Androutsos, D.: Semi-automatic 2d to 3d image conversion using scale-space random walks and a graph cuts based depth prior. In: 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 865–868 (2011)
Barash, D.: Fundamental relationship between bilateral filtering, adaptive smoothing, and the nonlinear diffusion equation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(6), 844–847 (2002)
Scharstein, D., Hirschmuller, H., Kitajima, Y., Krathwohl, G., Nesic, N., Wang, X., Westling, P.: High-resolution stereo datasets with subpixel-accurate ground truth. In: German Conference on Pattern Recognition (GCPR 2014), September 2014. http://www.cs.middlebury.edu/~schar/papers/datasets-gcpr2014.pdf
Shi, J., Tomasi, C.: Good features to track. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 1994. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on CVPR ’94, pp. 593–600 (1994)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was done while R. Rzeszutek was a Ph.D. candidate at Ryerson University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rzeszutek, R., Androutsos, D. Propagating sparse labels through edge-aware filters. SIViP 9 (Suppl 1), 17–24 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-015-0833-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-015-0833-x