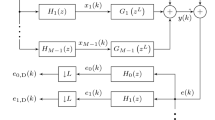
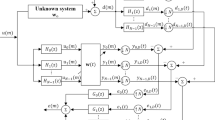
Abstract
In practice, adaptive filter could work in an under-modeling scenario, meaning that its length is less than that of the unknown system. In this realistic situation, therefore, the existing analysis for the improved normalized subband adaptive filter (INSAF) algorithm is not applicable. To this end, this paper analyzes the mean square steady-state performance of the INSAF for under-modeling. In addition, we propose a variable step size INSAF algorithm suitable for under-modeling scenario, to obtain fast convergence rate and low steady-state error. Simulation results have supported our theoretical analysis and proposed algorithm.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This condition is consistent with the sufficient length case, i.e., \(M=L\), see appendix in [29].
References
Benesty, J., Huang, Y.: Adaptive Signal Processing—Applications to Real-World P. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (2003)
Guan, S., Li, Z.: Optimal step size of least mean absolute third algorithm. Signal Image Video Process (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1064-0
Liu, J., Grant, S.L.: Proportionate adaptive filtering for block-sparse system identification. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process 24(4), 623–630 (2016)
Lee, K.A., Gan, W.S., Kuo, S.M.: Subband Adaptive Filtering: Theory and Implementation. Wiley, Hoboken (2009)
Lee, K.A., Gan, W.S.: Improving convergence of the NLMS algorithm using constrained subband updates. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11(9), 736–739 (2004)
Ni, J., Li, F.: A variable step-size matrix normalized subband adaptive filter. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 18(6), 1290–1299 (2010)
Jeong, J.J., Koo, K., Choi, G.T., Kim, S.W.: A variable step size for normalized subband adaptive filters. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 19(12), 906–909 (2012)
Yu, Y., Zhao, H., Chen, B.: A new normalized subband adaptive filter algorithm with individual variable step sizes. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(4), 1407–18 (2016)
Yu, Y., Zhao, H.: A joint-optimization NSAF algorithm based on the first-order Markov model. Signal Image Video Process. 11(3), 509–516 (2017)
Song, M.K., Kim, S.E., Choi, Y.S., Song, W.J.: Selective normalized subband adaptive filter with subband extension. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Pap. 60(2), 101–105 (2013)
Petraglia, M.R., Haddad, D.B., Marques, E.L.: Normalized subband adaptive filtering algorithm with reduced computational complexity. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Pap. 62(12), 1164–1168 (2015)
Lu, L., Zhao, H., Chen, C.: A new normalized subband adaptive filter under minimum error entropy criterion. Signal Image Video Process. 10(6), 1097–1103 (2016)
Ni, J.: Improved normalised subband adaptive filter. Electron. Lett. 48(6), 320–321 (2012)
Lee, K.A., Gan, W.S., Kuo, S.M.: Mean-square performance analysis of the normalized subband adaptive filter. In: Proceedings of 40th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, pp. 248–252 (2006)
Yin, W., Mehr, A.S.: Stochastic analysis of the normalized subband adaptive filter algorithm. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst I Reg. Pap. 58(5), 1020–1033 (2011)
Jeong, J.J., Koo, K., Koo, G., Kim, S.W.: Steady-state mean-square deviation analysis of improved normalized subband adaptive filter. Signal Process. 106, 49–54 (2015)
Paleologu, C., Ciochină, S., Benesty, J.: Variable step-size NLMS algorithm for under-modeling acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 15, 5–8 (2008)
Paleologu, C., Ciochină, S., Benesty, J.: Double-talk robust VSS-NLMS algorithm for under-modeling acoustic echo cancellation. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustic, Speech, Signal Process. (ICASSP), Las Vegas, NV, pp. 245–248 (2008)
Mayyas, K.: Performance analysis of the deficient length LMS adaptive algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(8), 2727–2734 (2005)
Zhang, Y., Chambers, J.A., Sanei, S., Kendrick, P., Cox, T.J.: A new variable tap-length LMS algorithm to model an exponential decay impulse response. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 14(4), 263–266 (2007)
Wu, M., Yang, J., Xu, Y., Qiu, X.: Steady-state solution of the deficient length constrained FBLMS algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(12), 6681–6687 (2012)
Azarnia, G., Tinati, M.A.: Steady-state analysis of the deficient length incremental LMS adaptive networks. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34(9), 2893–2910 (2015)
Jeong, J.J., Kim, S.H., Koo, G., Kim, S.W.: Mean-square deviation analysis of multiband-structured subband adaptive filter algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(4), 985–994 (2016)
Yu, Y., Zhao, H., Lu, L.: Steady-state mean-square analysis of the deficient-length NLMS algorithm with reusing coefficient vector for white input. In: Proceedings of the 35th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Chengdu, China, pp. 4787-4791, July 27–29 (2016)
Bhotto, M.Z.A., Antoniou, A.: family of shrinkage adaptive filtering algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(7), 1689–1697 (2013)
Yu, Y., Zhao, H.: Performance analysis of the deficient length NSAF algorithm and a variable step size method for improving its performance. Digit. Signal Process. 62, 157–167 (2017)
Eweda, E., Zerguine, A.: New insights into the normalization of the least mean fourth algorithm. Signal Image Video Process. 7(2), 255–262 (2013)
Eweda, E., Bershad, N.J., Bermudez, J.C.M.: Stochastic analysis of the least mean fourth algorithm for non-stationary white Gaussian inputs. Signal Image Video Process. 8(1), 133–142 (2014)
Yu, Y., Zhao, H., Chen, B.: Set-membership improved normalized subband adaptive filter algorithms for acoustic echo cancellation. IET Sig Process (2017). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-spr.2017.0131
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Science Foundation of P.R. China (Grant: 61571374, 61271340 and 61433011). The work of Y. Yu was also partially supported by the China Scholarship Council Funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: derivation of (13)
Appendix: derivation of (13)
Postmutiplying (9) by its transpose \({{\varvec{A}}}^{T}(k)\) gives
To obtain (34), we employ the fact that different subband input signals are mutually orthogonal, i.e., \({\varvec{u}}_i^T (k){\varvec{u}}_j (k)\approx 0,i\ne j\), called the diagonal assumption, which has been used in the derivation of the INSAF algorithm [13]. Taking the expectation of (34) and using the assumption (A.3), we get
From the assumption (A.4), we obtain
Substituting (36) and (37) into (35) and again using the assumption (A.4), (13) is obtained.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Zhao, H. & Lu, L. Steady-state behavior of the improved normalized subband adaptive filter algorithm and its improvement in under-modeling. SIViP 12, 617–624 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1199-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-017-1199-z