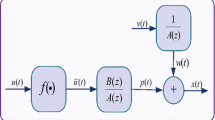
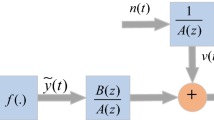
Abstract
In the present study, strength of stochastic computational paradigms is investigated for parameter estimation of Hammerstein control autoregressive (HCAR) model by exploiting differential evolution, genetic algorithms and pattern search methods. Multidimensional and nonlinear nature of the problem emerging in digital signal systems along with noise makes it a challenging optimization task, which is dealt with robustness and effectiveness of stochastic solvers to ensure convergence and avoid trapping in local minima. The performance of meta-heuristic approaches is validated through statistical performance indices based on absolute error, weight deviations and mean squared error. Comparative studies of HCAR system identification established efficacy of the designed methodology based on differential evolution over its counterparts.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Djurović, I.: Estimation of sinusoidal frequency-modulated signal parameters in high-noise environment. Signal Image Video Process. 11(8), 1537–1541 (2017)
Ma, W., Chen, B., Qu, H., Zhao, J.: Sparse least mean p-power algorithms for channel estimation in the presence of impulsive noise. Signal Image Video Process. 10(3), 503–510 (2016)
Djurović, I.: QML-RANSAC: PPS and FM signals estimation in heavy noise environments. Signal Process. 130, 142–151 (2017)
Li, L.: Joint parameter estimation and target localization for bistatic MIMO radar system in impulsive noise. Signal Image Video Process. 9(8), 1775–1783 (2015)
Yang, P., Liu, Z., Jiang, W.L.: Parameter estimation of multi-component chirp signals based on discrete chirp Fourier transform and population Monte Carlo. Signal Image Video Process. 9(5), 1137–1149 (2015)
Sudeep, P.V., Palanisamy, P., Kesavadas, C., Sijbers, J., Arnold, J., Rajan, J.: A nonlocal maximum likelihood estimation method for enhancing magnetic resonance phase maps. Signal Image Video Process. 11(5), 913–920 (2017)
Bey, N.Y.: Highly accurate frequency estimation of brief duration signals in noise. Signal Image Video Process. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1280-2
Ma, W., Zheng, D., Zhang, Z., Duan, J., Chen, B.: Robust proportionate adaptive filter based on maximum correntropy criterion for sparse system identification in impulsive noise environments. Signal Image Video Process. 12(1), 117–124 (2018)
Bai, E.W. (ed.): Block-Oriented Nonlinear System Identification, vol. 1. Springer, London (2010)
Billings, S.A.: Nonlinear system identification: NARMAX methods in the time, frequency, and spatio-temporal domains. Wiley, London (2013)
Ding, F., Liu, X., Liu, M.: The recursive least squares identification algorithm for a class of Wiener nonlinear systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 353(7), 1518–1526 (2016)
Pal, P.S., Kar, R., Mandal, D., Ghoshal, S.P.: A hybrid backtracking search algorithm with wavelet mutation-based nonlinear system identification of Hammerstein models. Signal Image Video Process. 11(5), 929–936 (2017)
Tang, Y., Bu, C., Liu, M., Zhang, L., Lian, Q.: Application of ELM-Hammerstein model to the identification of solid oxide fuel cells. Neural Comput. Appl. 29(2), 401–411 (2018)
Zhang, Q., Wang, Q., Li, G.: Nonlinear modeling and predictive functional control of Hammerstein system with application to the turntable servo system. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 72, 383–394 (2016)
Togun, N., Baysec, S.: Nonlinear identification of a spark ignition engine torque based on NFIS with NARX method. Expert Syst. 33(6), 559–568 (2016)
Ávila, F.R., Carvalho, H.T., Biscainho, L.W.: Bayesian blind identification of nonlinear distortion with memory for audio applications. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(4), 414–418 (2016)
Chagtmi, N., Boulejfen, N., Ghannouchi, F.M.: Augmented Hammerstein model for six-port-based wireless receiver calibration. IET Commun. 11(6), 951–960 (2017)
Cornejo-Aragón, L.G., Santos-Cuevas, C.L., Ocampo-García, B.E., Chairez-Oria, I., Diaz-Nieto, L., García-Quiroz, J.: Preclinical biokinetic modelling of Tc-99m radiophamaceuticals obtained from Semi-Automatic image processing. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 37(6), 887–898 (2017)
Ding, F., Wang, X., Mao, L., Xu, L.: Joint state and multi-innovation parameter estimation for time-delay linear systems and its convergence based on the Kalman filtering. Digit. Signal Process. 62, 211–223 (2017)
Li, M., Liu, X.: The least squares based iterative algorithms for parameter estimation of a bilinear system with autoregressive noise using the data filtering technique. Signal Process. 147, 23–34 (2018)
Chen, M., Ding, F., Xu, L., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: Iterative identification algorithms for bilinear-in-parameter systems with autoregressive moving average noise. J. Frankl. Inst. 354(17), 7885–7898 (2017)
Zhang, X., Ding, F., Alsaadi, F.E., Hayat, T.: Recursive parameter identification of the dynamical models for bilinear state space systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(4), 2415–2429 (2017)
Ding, F., Wang, X.: Hierarchical stochastic gradient algorithm and its performance analysis for a class of bilinear-in-parameter systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(4), 1393–1405 (2017)
Ding, F., Wang, Y., Dai, J., Li, Q., Chen, Q.: A recursive least squares parameter estimation algorithm for output nonlinear autoregressive systems using the input-output data filtering. J. Frankl. Inst. 354(15), 6938–6955 (2017)
Ding, F., Deng, K., Liu, X.: Decomposition based Newton iterative identification method for a Hammerstein nonlinear FIR system with ARMA noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(9), 2881–2893 (2014)
Mao, Y., Ding, F.: A novel parameter separation based identification algorithm for Hammerstein systems. Appl. Math. Lett. 60, 21–27 (2016)
Ding, F., Liu, X., Chu, J.: Gradient-based and least-squares-based iterative algorithms for Hammerstein systems using the hierarchical identification principle. IET Control Theory Appl. 7(2), 176–184 (2013)
Wang, D.: Hierarchical parameter estimation for a class of MIMO Hammerstein systems based on the reframed models. Appl. Math. Lett. 57, 13–19 (2016)
Ding, F.: Hierarchical multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for Hammerstein nonlinear system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. 37(4), 1694–1704 (2013)
Shen, Q., Ding, F.: Hierarchical multi-innovation extended stochastic gradient algorithms for input nonlinear multivariable OEMA systems by the key-term separation principle. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(1), 499–507 (2016)
Mao, Y., Ding, F., Yang, E.: Adaptive filtering-based multi-innovation gradient algorithm for input nonlinear systems with autoregressive noise. Int. J Adapt. Control Signal Process. 31(10), 1388–1400 (2017)
Mao, Y., Ding, F.: Data filtering-based multi-innovation stochastic gradient algorithm for nonlinear output error autoregressive systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(2), 651–667 (2016)
Chaudhary, N.I., Raja, M.A.Z.: Identification of Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX systems using nonlinear adaptive algorithms. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(2), 1385–1397 (2015)
Chaudhary, N.I., Raja, M.A.Z., Khan, A.U.R.: Design of modified fractional adaptive strategies for Hammerstein nonlinear control autoregressive systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 82(4), 1811–1830 (2015)
Chaudhary, N.I., Raja, M.A.Z.: Design of fractional adaptive strategy for input nonlinear Box-Jenkins systems. Signal Process. 116, 141–151 (2015)
Aslam, M.S., Chaudhary, N.I., Raja, M.A.Z.: A sliding-window approximation-based fractional adaptive strategy for Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(1), 519–533 (2017)
Chaudhary, N.I., Aslam, M.S., Raja, M.A.Z.: Modified Volterra LMS algorithm to fractional order for identification of Hammerstein non-linear system. IET Signal Process. 11(8), 975–985 (2017)
Raja, M.A.Z., Shah, F.H., Khan, A.A., Khan, N.A.: Design of bio-inspired computational intelligence technique for solving steady thin film flow of Johnson-Segalman fluid on vertical cylinder for drainage problems. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 60, 59–75 (2016)
Arqub, O.A., Abo-Hammour, Z.: Numerical solution of systems of second-order boundary value problems using continuous genetic algorithm. Inf. Sci. 279, 396–415 (2014)
Raja, M.A.Z., Mehmood, A., Niazi, S.A., Shah, S.M.: Computational intelligence methodology for the analysis of RC circuit modelled with nonlinear differential order system. Neural Comput. Appl. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2806-6
Raja, M.A.Z., Shah, F.H., Alaidarous, E.S., Syam, M.I.: Design of bio-inspired heuristic technique integrated with interior-point algorithm to analyze the dynamics of heartbeat model. Appl. Soft Comput. 52, 605–629 (2017)
Raja, M.A.Z., Manzar, M.A., Shah, F.H., Shah, F.H.: Intelligent computing for Mathieu’s systems for parameter excitation, vertically driven pendulum and dusty plasma models. Appl. Soft Comput. 62, 359–372 (2017)
Cárdenas-Montes, M., Vega-Rodríguez, M., Molla, M.: Modeling low-resolution galaxy spectral energy distribution with evolutionary algorithms. Neurocomputing (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.125
Raja, M.A.Z., Shah, A.A., Mehmood, A., Chaudhary, N.I., Aslam, M.S.: Bio-inspired computational heuristics for parameter estimation of nonlinear Hammerstein controlled autoregressive system. Neural Comput. Appl. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2677-x
Guedes, J., Castoldi, M., Goedtel, A., Agulhari, C., Sanches, D.: Parameters estimation of three-phase induction motors using differential evolution. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 154, 204–212 (2017)
Storn, R., Price, K.: Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 11(4), 341–359 (1997)
Price, K., Storn, R.M., Lampinen, J.A.: Differential Evolution: A Practical Approach to Global Optimization. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Goldberg, D.E., Holland, J.H.: Genetic algorithms and machine learning. Mach. Learn. 3(2), 95–99 (1988)
Gen, M., Cheng, R.: Genetic Algorithms and Engineering Optimization, vol. 7. Wiley, London (2000)
Kolda, T.G., Lewis, R.M., Torczon, V.: Optimization by direct search: new perspectives on some classical and modern methods. SIAM Rev. 45(3), 385–482 (2003)
Song, X., Gu, H., Zhang, X., Liu, J.: Pattern search algorithms for nonlinear inversion of high-frequency Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves. Comput. Geosci. 34(6), 611–624 (2008)
Arqub, O.A., Mohammed, A.S., Momani, S., Hayat, T.: Numerical solutions of fuzzy differential equations using reproducing kernel Hilbert space method. Soft Comput. 20(8), 3283–3302 (2016)
Arqub, O.A., Al-Smadi, M., Momani, S., Hayat, T.: Application of reproducing kernel algorithm for solving second-order, two-point fuzzy boundary value problems. Soft Comput. 21(23), 7191–7206 (2017)
Arqub, O.A.: Adaptation of reproducing kernel algorithm for solving fuzzy Fredholm-Volterra integrodifferential equations. Neural Comput. Appl. 28(7), 1591–1610 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehmood, A., Aslam, M.S., Chaudhary, N.I. et al. Parameter estimation for Hammerstein control autoregressive systems using differential evolution. SIViP 12, 1603–1610 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1317-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1317-6