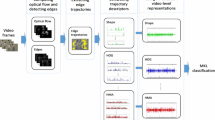
Abstract
Velocity descriptors based on optical flow are the core of most of the existing video analysis techniques. We hypothesize that acceleration is crucial as velocity to represent videos and consequently develop a method to compute optical acceleration. To effectively encode the motion information, we develop two acceleration descriptors—histogram of optical acceleration and histogram of spatial gradient of acceleration (HSGA). To assess the significance of optical acceleration for motion description, we applied it for human action recognition. Action recognition system presented in this paper uses our acceleration descriptor—HSGA, in conjunction with the velocity descriptor—motion boundary histogram. Experiments performed on standard action recognition datasets reveal that the use of acceleration in combination with velocity results in a superior motion descriptor.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amraee, S., Vafaei, A., Jamshidi, K., Adibi, P.: Abnormal event detection in crowded scenes using one-class SVM. Signal Image Video Process. 12(6), 1115–1123 (2018)
Lu, X., Yao, H., Sun, X., Zhang, Y.: Locally aggregated histogram-based descriptors. Signal Image Video Process. 12(2), 323–330 (2018)
Li, J., Nikolov, S.G., Benton, C.P., Scott-Samuel, N.E.: Adaptive summarisation of surveillance video sequences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, pp. 546–551 (2007)
Van Luong, H., Raket, L.L., Huang, X., Forchhammer, S.: Side information and noise learning for distributed video coding using optical flow and clustering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(12), 4782–4796 (2012)
Prince, J.L., McVeigh, E.R.: Motion estimation from tagged MR image sequences. IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging 11(2), 238–249 (1992)
Yamato, J., Ohya, J., Ishii, K.: Recognizing human action in time-sequential images using hidden markov model. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 379–385 (1992)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 568–576 (2014)
Laptev, I., Marszalek, M., Schmid, C., Rozenfeld, B.: Learning realistic human actions from movies. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Dedeoğlu, Y., Töreyin, B.U., Güdükbay, U., Çetin, A.E.: Silhouette-based method for object classification and human action recognition in video. In: ECCV Workshop on Computer Vision in Human-Computer Interaction, pp. 64–77 (2006)
Laptev, I.: On space-time interest points. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 64(2–3), 107–123 (2005)
Scovanner, P., Ali, S., Shah, M.: A 3-dimensional SIFT descriptor and its application to action recognition. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 357–360 (2007)
Klaser, A., Marszałek, M., Schmid, C., et al.: A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3D-gradients. In: Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference (2008)
Willems, G., Tuytelaars, T., Gool, L.: An efficient dense and scale-invariant spatio-temporal interest point detector. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 650–663 (2008)
Matikainen, P., Hebert, M., Sukthankar, R.: Trajectons: Action recognition through the motion analysis of tracked features. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 514–521 (2009)
Messing, R., Pal, C., Kautz, H.: Activity recognition using the velocity histories of tracked keypoints. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 104–111 (2009)
Wang, H., Kläser, A., Schmid, C., Liu, C.L.: Dense trajectories and motion boundary descriptors for action recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 103(1), 60–79 (2013)
Islam, S., Qasim, T., Yasir, M., Bhatti, N., Mahmood, H., Zia, M.: Single- and two-person action recognition based on silhouette shape and optical point descriptors. Signal Image Video Process. 12(5), 853–860 (2018)
Jiang, Y.G., Dai, Q., Xue, X., Liu, W., Ngo, C.W.: Trajectory-based modeling of human actions with motion reference points. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 425–438 (2012)
Vig, E., Dorr, M., Cox, D.: Space-variant descriptor sampling for action recognition based on saliency and eye movements. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 84–97 (2012)
Wang, H., Schmid, C.: Action recognition with improved trajectories. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3551–3558 (2013)
Lan, Z., Lin, M., Li, X., Hauptmann, A.G., Raj, B.: Beyond gaussian pyramid: Multi-skip feature stacking for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 204–212 (2015)
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4489–4497 (2015)
Karpathy, A., Toderici, G., Shetty, S., Leung, T., Sukthankar, R., Fei-Fei, L.: Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1725–1732 (2014)
Liu, J., Wang, G., Hu, P., Duan, L.Y., Kot, A.C.: Global context-aware attention LSTM networks for 3d action recognition. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 7, p. 43 (2017)
Liu, J., Shahroudy, A., Xu, D., Kot, A.C., Wang, G.: Skeleton-based action recognition using spatio-temporal LSTM network with trust gates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(12), 3007–3021 (2018)
Liu, J., Shahroudy, A., Wang, G., Duan, L.Y., Kot, A.C.: SSNet: Scale selection network for online 3d action prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8349–8358 (2018)
Edison, A., Jiji, C.: Optical acceleration for motion description in videos. In: Proceedings of the CVPR Workshops, pp. 39–47 (2017)
Nallaivarothayan, H., Fookes, C., Denman, S., Sridharan, S.: An MRF based abnormal event detection approach using motion and appearance features. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance, pp. 343–348 (2014)
Kataoka, H., He, Y., Shirakabe, S., Satoh, Y.: Motion representation with acceleration images. In: Proceedings of the ECCV Workshops, pp. 18–24 (2016)
Farnebäck, G.: Two-frame motion estimation based on polynomial expansion. In: Proceedings of Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis, vol. 2749 (2003)
Edison, A., Jiji, C.: HSGA: A novel acceleration descriptor for human action recognition. In: Proceedings of the National Conference on Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition, Image Processing and Graphics, pp. 1–4 (2015)
Peng, X., Wang, L., Wang, X., Qiao, Y.: Bag of visual words and fusion methods for action recognition: comprehensive study and good practice. Comput Vis Image Underst 150, 109–125 (2016)
Liu, J., Luo, J., Shah, M.: Recognizing realistic actions from videos in the wild. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1996–2003 (2009)
Reddy, K.K., Shah, M.: Recognizing 50 human action categories of web videos. Mach. Vis. Appl. 24(5), 971–981 (2013)
Soomro, K., Zamir, A.R., Shah, M.: UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. CRCV-TR-12-01 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edison, A., Jiji, C.V. Automated video analysis for action recognition using descriptors derived from optical acceleration. SIViP 13, 915–922 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01428-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01428-1