Abstract
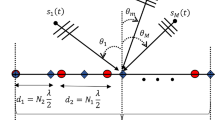
Underdetermined direction of arrival (DOA) estimation with coprime array is discussed in the framework of multiple measurement sparse Bayesian learning (MSBL). Exploiting the extended difference coarray, a larger number of degrees of freedom can be obtained for locating more sources than sensors. A linear operation and a prewhitening procedure are incorporated into the sparse signal recovery model to eliminate the influence of noise. Then, MSBL employs an empirical Bayesian strategy to resolve \(l_{0}\) minimization problem. Simulation results show the superiority of the MSBL algorithm in underdetermined DOA detection performance, resolution ability and estimation accuracy when there are multiple measurement vectors for on-grid and off-grid sources, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, W.K., Hsieh, T.H., Chi, C.Y.: DOA estimation of quasi-stationary signals with less sensors than sources and unknown spatial noise covariance: a Khatri–Rao subspace approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58, 2168–2180 (2010)
Shen, Q., Liu, W., Cui, W., Wu, S.: Underdetermined DOA estimation under the compressive sensing framework: a review. IEEE Access 4, 8865–8878 (2016)
Mohammadzadeh, S., Kukrer, O.: Robust adaptive beamforming based on covariance matrix and new steering vector estimation. SIViP 8, 1–8 (2019)
Pal, P., Vaidyanathan, P.P.: Nested arrays: a novel approach to array processing with enhanced degrees of freedom. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58, 4973–4973 (2010)
Vaidyanathan, P.P., Pal, P.: Sparse sensing with co-prime samplers and arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59, 573–587 (2011)
Qin, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, J., Yu, Z.: Underdetermined wideband DOA estimation for off-grid sources with coprime array using sparse Bayesian learning. Sensors 18, 253–264 (2018)
Nannuru, S., Koochakzadeh, A., Gemba, K.L., Pal, P., Gerstoft, P.: Sparse Bayesian learning for beamforming using sparse linear arrays. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 144, 2719–2729 (2018)
Ciuonzo, D.: On time-reversal imaging by statistical testing. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24, 1024–1028 (2017)
Ciuonzo, D., Romano, G., Solimene, R.: Performance analysis of time-reversal MUSIC. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63, 2650–2662 (2015)
Ciuonzo, D., Rossi, P.S.: Noncolocated time-reversal MUSIC: high-SNR distribution of null spectrum. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24, 397–401 (2017)
Vaidyanathan, P.P., Pal, P.: Why does direct-MUSIC on sparse-arrays work? In: Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA (2013)
Tan, Z., Nehorai, A.: Sparse direction of arrival estimation using co-prime arrays with off-grid targets. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21, 26–29 (2014)
Shen, Q., Liu, W., Cui, W., Wu, S., Zhang, Y.D., Amin, M.G.: Low-complexity direction-of-arrival estimation based on wideband co-prime arrays. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 23, 1445–1456 (2015)
Li, J., Li, D., Jiang, D., Zhang, X.: Extended-aperture unitary root MUSIC-based DOA estimation for coprime array. IEEE Commun. Lett. 22, 752–755 (2018)
Zhou, C., Gu, Y., He, S., Shi, Z.: A robust and efficient algorithm for coprime array adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67, 1099–1112 (2018)
Zhou, C., Gu, Y., Fan, X., Shi, Z., Mao, G., Zhang, Y.D.: Direction-of-arrival estimation for coprime array via virtual array interpolation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 66, 5956–5971 (2018)
Shi, Z., Zhou, C., Gu, Y., Goodman, N.A., Qu, F.: Source estimation using coprime array: a sparse reconstruction perspective. IEEE Sens. J. 17, 755–765 (2017)
Tan, Z., Eldar, Y.C., Nehorai, A.: Direction of arrival estimation using co-prime arrays: a super resolution viewpoint. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62, 5565–5576 (2014)
Balkan, O., Kreutz-Delgado, K., Makeig, S.: Localization of more sources than sensors via jointly-sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 21, 131–134 (2014)
Wipf, D.P., Rao, B.D.: Sparse Bayesian learning for basis selection. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52, 2153–2164 (2004)
Zhang, Z., Rao, B.D.: Sparse signal recovery in the presence of correlated multiple measurement vectors. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA (2010)
Zhang, Z., Rao, B.D.: Sparse signal recovery with temporally correlated source vectors using sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Proces. 5, 912–926 (2011)
Zhang, Z., Rao, B.D.: Extension of SBL algorithms for the recovery of block sparse signals with intra-block correlation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61, 2009–2015 (2013)
Tipping, M.E.: Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 1, 211–244 (2001)
Tan, X., Roberts, W., Li, J., Stoica, P.: Sparse learning via iterative minimization with application to MIMO radar imaging. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59, 1088–1101 (2011)
Addabbo, P., Aubry, A., Maio, A.D., Pallotta, L., Ullo, S.L.: High range resolution profile estimation using sparse learning via iterative minimization. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 13, 512–521 (2019)
Cotter, S.F., Rao, B.D., Engan, K., Kreutz-Delgado, K.: Sparse solutions to linear inverse problems with multiple measurement vectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53, 2477–2488 (2005)
Wipf, D.P., Rao, B.D.: An empirical Bayesian strategy for solving the simultaneous sparse approximation problem. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55, 3704–3716 (2007)
Qin, S., Zhang, Y.D., Amin, M.G.: Generalized coprime array configurations for direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63, 1377–1390 (2015)
Hu, N., Sun, B., Zhang, Y., Dai, J., Wang, J., Chang, C.: Underdetermined DOA estimation method for wideband signals using joint nonnegative sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24, 535–539 (2017)
He, Z.Q., Shi, Z.P., Huang, L., So, H.C.: Underdetermined DOA estimation for wideband signals using robust sparse covariance fitting. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22, 435–439 (2015)
Pal, P., Vaidyanathan, P.P.: Coprime sampling and the MUSIC algorithm. In: Digital Signal Processing and Signal Processing Education Meeting (DSP/SPE), Sedona, AZ, USA (2011)
Tibshirani, R.: Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 58, 267–288 (1994)
Yang, Z., Xie, L., Zhang, C.: Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61, 38–43 (2013)
Zhang, Z., Rao, B.D.: Iterative reweighted algorithms for sparse signal recovery with temporally correlated source vectors. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic (2011)
Stoica, P., Nehorai, A.: Performance study of conditional and unconditional direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 38, 1783–1795 (1990)
Trees, H.L.Van: Optimum Array Processing: Part IV of Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory. Wiley, New York (2002)
Shaghaghi, M., Vorobyov, S.A.: Cramér–Rao bound for sparse signals fitting the low-rank model with small number of parameters. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22, 1497–1501 (2015)
Chun-Lin, L., Vaidyanathan, P.P.: Cramér bounds for coprime and other sparse arrays, which find more sources than sensors. Digit. Signal Process. 61, 43–61 (2017)
Wang, M., Nehorai, A.: Coarrays, MUSIC, and the Cramér bound. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 65, 933–946 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their many insightful comments and suggestions, which help improve the quality and readability of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Y., Liu, Y. & Yu, Z. Underdetermined DOA estimation using coprime array via multiple measurement sparse Bayesian learning. SIViP 13, 1311–1318 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01480-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01480-x