Abstract
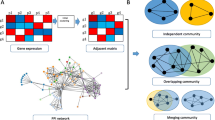
Community detection is an important task in social network analysis, and communities in network usually appear interrelated feature. Meanwhile, there exist many communities in biological network and module network inference is an effective and established method to analyze the gene expression data. Hence, exploring and analyzing the interaction between modules or independent modules will improve our understanding of cancer mechanism. To this end, we proposed a novel method, InFun, for reconstructing different module networks. Our method applies two-ways clustering which contains Bayesian approach and overlapping community method to detect gene communities via combing gene omics data and prior information between proteins. On the basis of the cancer genome Atlas breast cancer and colon cancer data, we observe that InFun can recognize module networks which are significantly more enriched in the known pathways than another method like Lemon-tree. These gene communities can serve as bio-markers to estimate the survival time of patients which is critical for cancer therapy. Discovering single function communities can predict breast cancer subtype by using different feature sets, and multiple function communities can communicate with other community which can be used to explain cancer processes. InFun brings new sight for understanding cancer mechanism and novel technique for clustering genes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, X., Qian, X., Li, X., Miao, Q., Peng, S.: DMCM: a data-adaptive mutation clustering method to identify cancer-related mutation clusters. Bioinformatics 35, 389–3979 (2018)
Tao, H., Min, J., Kong, X., Cai, Y.D.: Dysfunctions associated with methylation, MicroRNA expression and gene expression in lung cancer. PLoS ONE 7(8), e43441 (2012)
Zhang, S., Zhao, H., Ng, M.K.: Functional module analysis for gene coexpression networks with network integration. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 12(5), 1146 (2015)
Luo, Y., Yang, K., Tang, Q., Zhang, J., Li, P., Qiu, S.: An optimal data service providing framework in cloud radio access network. Eurasip J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2016(1), 23 (2016)
Yang, L., Zhou, Y., Zheng, Y.: Annotating the literature with disease ontology. Chin. J. Electron. 26(6), 1261 (2017)
Odena, A.: Semi-supervised learning with generative adversarial networks. Comput. Mater. Cont. 55(2), 243 (2018)
Liu, B., Li, C.C., Yan, K.: DeepSVM-fold: Protein fold recognition by combining support vector machines and pairwise sequence similarity score generated by deep learning networks. Brief. Bioinf. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbz098
Hudson, T.J., Anderson, W., Artez, A., Barker, A.D., Bell, C., Bernabã, R.R., Bhan, M.K., Calvo, F., Eerola, I., Gerhard, D.S.: International network of cancer genome projects. Nature 464(7291), 993 (2010)
Chen, Y., Xu, W., Zuo, J., Kai, Y.: The fire recognition algorithm using dynamic feature fusion and IV-SVM classifier. Clust. Comput. 22, 7665–7675 (2018)
Chen, Y., Jie, X., Xu, W., Zuo, J.: A novel online incremental and decremental learning algorithm based on variable support vector machine. Clust. Comput. 22, 7435–7445 (2018)
Yin, B., Gu, K., Wei, X., et al.: A cost-efficient framework for finding prospective customers based on reverse skyline queries. Knowl.-Based Syst. 152, 117 (2018)
Benson, D., Boguski, M., Lipman, D.J., Ostell, J.: The national center for biotechnology information. Genomics 6(2), 389 (1990)
Curtis, C., Shah, S., Chin, S., et al.: The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature 486, 346 (2012)
Liu, B., Gao, X., Zhang, H.: BioSeq-Analysis2. 0: an updated platform for analyzing DNA, RNA and protein sequences at sequence level and residue level based on machine learning approaches. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(20), e127 (2019)
Girvan, M., Newman, M.E.J.: Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99(12), 7821 (2002)
Lu, X., Li, X., Liu, P., Qian, X., Miao, Q., Peng, S.: The integrative method based on the module-network for identifying driver genes in cancer subtypes. Molecules 23(2), 183 (2018)
Jiao, Y., Widschwendter, M., Teschendorff, A.E.: A systems-level integrative framework for genome-wide dna methylation and gene expression data identifies differential gene expression modules under epigenetic control. Bioinformatics 30(16), 2360 (2014)
Huang, T., Li, B., Cai, Y.: The integrative network of gene expression, microRNA, methylation and copy number variation in colon and rectal cancer. Curr. Bioninf. 11(1), 59 (2016)
Akavia, U.D., Litvin, O., Kim, J., Sanchezgarcia, F., Kotliar, D., Causton, H.C., Pochanard, P., Mozes, E., Garraway, L.A., Pe’Er, D.: An integrated approach to uncover drivers of cancer. Cell 143(6), 1005 (2010)
Lu, X., Lu, J., Liao, B., Li, X., Qian, X., Li, K.: Driver pattern identification over the gene co-expression of drug response in ovarian cancer by integrating high throughput genomics data. Sci. Rep. 16188(1), 1 (2017)
Lee, J., Gross, S.P., Lee, J.: Improved network community structure improves function prediction. Sci. Rep. 3(2197), 1 (2013)
Jin, D., Gabrys, B., Dang, J.: Combined node and link partitions method for finding overlapping communities in complex networks. Sci. Rep. 5, 8600 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08600
Nabavi, S., Schmolze, D., Maitituoheti, M., Malladi, S., Beck, A.H.: EMDomics: a robust and powerful method for the identification of genes differentially expressed between heterogeneous classes. Bioinformatics 32(4), 533 (2016)
Anagha, J., Yves, V.D.P., Tom, M.: Analysis of a Gibbs sampler method for model-based clustering of gene expression data. Bioinformatics 24(2), 176 (2008)
Farkas, I., Palla, G., Derényi, I., Vicske, T.: Uncovering the overlapping community structure of complex networks in nature and society. Nature 435, 814 (2005)
Bindea, G., Mlecnik, B.H., Charoentong, P., Tosolini, M., Kirilovsky, A.: ClueGO: a cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 25(8), 1091 (2009)
Maere, S., Heymans, K., Kuiper, M.: BiNGO: A Cytoscape Plugin to Assess Overrepresentation of Gene Ontology Categories in Biological Networks. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2005)
Stein, L., DEustachio, P., Gopinathrao, G., Gillespie, M.: Reactome: a knowledgebase of biological pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 33(Database issue), 428 (2005)
Prasad, T.S.K., Renu, G., Kumaran, K., Shivakumar, K., Sameer, K.: Human protein reference database-2009 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(5), 767 (2009)
Jörnsten, R., Abenius, T., Kling, T., Schmidt, L., Johansson, E.: Network modeling of the transcriptional effects of copy number aberrations in glioblastoma. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7(1), 486 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Zhu, Z., Peng, X. et al. InFun: a community detection method to detect overlapping gene communities in biological network. SIViP 15, 681–686 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-020-01638-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-020-01638-y