Abstract
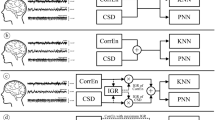
In this paper, an efficient simple system for classifying electroencephalogram (EEG) data of normal and epileptic subjects is presented using lagged Poincare plot parameters. To this effect, a benchmark for choosing delays is defined based on the autocorrelation function. For each lag, traditional indicators, including the number of points lying on the identity line, the length of the minor (SD1)/major axis (SD2) of the fitted ellipse on the plot, the SD1/SD2 ratio, and the area of the ellipse, were calculated. The efficiency of the features in discriminating between the groups was examined based on the statistical significance of the differences. K-nearest neighbor and probabilistic neural network were employed as the classifier. The performance of the suggested scheme was evaluated using a publicly available database that includes numerous EEG data of healthy, during the incidence of an epileptic seizure and seizure-free intervals cases. It is indicated that the method can provide the maximum correct rate of 98.33%. Our results indicated the proposed scheme could characterize the dynamics of EEG signals in three groups, and it is suitable for the detection of epileptic seizures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maggioni, E., Bianchi, A.M., Altamura, A.C., Soares, J.C., Brambilla, P.: The putative role of neuronal network synchronization as a potential biomarker for bipolar disorder: a review of EEG studies. J. Affect. Disord. 212, 167–170 (2017)
Tatum, W.O., Rubboli, G., Kaplan, P.W., Mirsatari, S.M., Radhakrishnan, K., Gloss, D., Caboclo, L.O., Drislane, F.W., Koutroumanidis, M., Schomer, D.L., Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenite, D., Cook, M., Beniczky, S.: Clinical utility of EEG in diagnosing and monitoring epilepsy in adults. Clin. Neurophysiol. 129(5), 1056–1082 (2018)
Vicario, C.M., Salehinejad, M.A., Felmingham, K., Martino, G., Nitsche, M.A.: A systematic review on the therapeutic effectiveness of non-invasive brain stimulation for the treatment of anxiety disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 96, 219–231 (2019)
Besedová, P., Vyšata, O., Mazurová, R., Kopal, J., Ondráková, J., Vališ, M., Procházka, A.: Classification of brain activities during language and music perception. SIViP (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01505-5
Al-dabag, M.L., Ozkurt, N.: EEG motor movement classification based on cross-correlation with effective channel. SIViP 13(3), 567–573 (2019)
Resalat, S.N., Saba, V.A.: practical method for driver sleepiness detection by processing the EEG signals stimulated with external flickering light. SIViP 9(8), 1751–1757 (2015)
Zangeneh Soroush, M., Maghooli, K., Setarehdan, S.K., Nasrabadi, A.M.: A novel EEG-based approach to classify emotions through phase space dynamics. SIViP (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01455-y
Goshvarpour, A., Goshvarpour, A.: EEG spectral powers and source localization in depressing, sad, and fun music videos focusing on gender differences. Cogn. Neurodyn. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-018-9516-y
Goshvarpour, A., Abbasi, A., Goshvarpour, A.: Combination of sLORETA and nonlinear coupling for emotional EEG source localization. Nonlinear Dyn. Psychol. 20(3), 353–368 (2016)
Prasad, D.K., Liu, S., Chen, S.H.A., Quek, C.: Sentiment analysis using EEG activities for suicidology. Expert Syst. Appl. 103, 206–217 (2018)
Mahapatra, A.G., Horio, K.: Classification of ictal and interictal EEG using RMS frequency, dominant frequency, root mean instantaneous frequency square and their parameters ratio. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 44, 168–180 (2018)
Scally, B., Burke, M.R., Bunce, D., Delvenne, J.F.: Resting-state EEG power and connectivity are associated with alpha peak frequency slowing in healthy aging. Neurobiol. Aging 71, 149–155 (2018)
Bachmann, M., Päeske, L., Kalev, K., Aarma, K., Lehtmets, A., Ööpik, P., Lass, J., Hinrikus, H.: Methods for classifying depression in single channel EEG using linear and nonlinear signal analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 155, 11–17 (2018)
Sikdar, D., Roy, R., Mahadevappa, M.: Epilepsy and seizure characterisation by multifractal analysis of EEG subbands. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 41, 264–270 (2018)
Gonzalez, C., Jensen, E.W., Gambus, P.L., Vallverdu, M.: Poincare plot analysis of cerebral blood flow signals: feature extraction and classification methods for apnea detection. PLoS ONE 13(12), e0208642 (2018)
Goshvarpour, A., Goshvarpour, A.: Gender and age classification using a new Poincare section-based feature set of ECG. SIViP 13(3), 531–539 (2019)
Goshvarpour, A., Goshvarpour, A.: Do meditators and non-meditators have different HRV dynamics? Cogn. Syst. Res. 54, 21–36 (2019)
Goshvarpour, A., Goshvarpour, A., Rahati, S.: Analysis of lagged Poincaré plots in heart rate signals during meditation. Digit. Signal. Process. 21(2), 208–214 (2011)
Goshvarpour, A., Goshvarpour, A.: Poincaré’s section analysis for PPG-based automatic emotion recognition. Chaos Solitons Fractal 114, 400–407 (2018)
Goshvarpour, A., Abbasi, A., Goshvarpour, A.: Indices from lagged Poincare plots of heart rate variability: an efficient nonlinear tool for emotion discrimination. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 40(2), 277–287 (2017)
Goshvarpour, A., Abbasi, A., Goshvarpour, A.: Fusion of heart rate variability and pulse rate variability for emotion recognition using lagged Poincare plots. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 40(3), 617–629 (2017)
Sadeghi Bajestani, G., Hashemi Golpayegani, M.R., Sheikhani, A., Ashrafzadeh, F.: Poincare section analysis of the electroencephalogram in autism spectrum disorder using complement plots. Kybernetes 46(2), 364–382 (2017)
Andrzejak, R.G., Lehnertz, K., Mormann, F., Rieke, C., David, P., Elger, C.E.: Indications of nonlinear deterministic and finite-dimensional structures in time series of brain electrical activity: dependence on recording region and brain state. Phys. Rev. E 64, 061907 (2001)
Altman, N.S.: An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am. Stat. 46(3), 175–185 (1992)
Demuth, H., Beale, M.: Neural Network Toolbox. The MathWorks, Inc., Natick (2000)
Goshvarpour, A., Abbasi, A., Goshvarpour, A.: Do men and women have different ECG responses to sad pictures? Biomed. Signal Process. Control 38, 67–73 (2017)
Goshvarpour, A., Goshvarpour, A.: A novel feature level fusion for HRV classification using correntropy and Cauchy–Schwarz divergence. J. Med. Syst. 42, 109 (2018)
Goshvarpour, A., Goshvarpour, A.: Human identification using a new matching Pursuit-based feature set of ECG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 172, 87–94 (2019)
Goshvarpour, A., Goshvarpour, A.: Human identification using information theory-based indices of ECG characteristic points. Expert Syst. Appl. 127, 25–34 (2019)
Kannathal, N., Lim, C.M., Acharya, U.R., Sadasivan, P.K.: Entropies for detection of epilepsy in EEG. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 80(3), 187–194 (2005)
Chua, K.C., Chandran, V., Acharya, R., Lim, C.M.: Automatic identification of epilepsy by HOS and power spectrum parameters using EEG signals: a comparative study. In: 30th Annual International IEEE EMBS Conference, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, 20–24 August 2008, pp. 3824–3827
Chua, K.C., Chandran, V., Acharya, R., Lim, C.M.: Automatic identification of epileptic electroencephalography signals using higher-order spectra. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H. 223(4), 485–495 (2009)
Acharya, U.R., Chua, C.K., Lim, T.C., Dorithy, Suri, J.S.: Automatic identification of epileptic EEG signals using nonlinear parameters. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 9(4), 539–553 (2009)
Acharya, U.R., Molinari, F., Sree, S.V., Chattopadhyay, S., Ng, K.-H., Suri, J.S.: Automated diagnosis of epileptic EEG using entropies. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 7(4), 401–408 (2012)
Acharya, U.R., Sree, S.V., Alvin, A.P., Yanti, R., Suri, J.S.: Application of non-linear and wavelet based features for the automated identification of epileptic EEG signals. Int. J. Neural Syst. 22(2), 1250002 (2012)
Acharya, U.R., Yanti, R., Wei, J.Z., Krishnan, M.M.R., Hong, T.J., Martis, R.J., Min, L.C.: Automated diagnosis of epilepsy using CWT, HOS and texture parameters. Int. J. Neural Syst. 23, 1350009 (2013)
Acharya, U.R., Fujita, H., Sudarshan, V.K., Bhat, S., Koh, J.E.W.: Application of entropies for automated diagnosis of epilepsy using EEG signals: a review. Knowl. Based Syst. 88, 85–96 (2015)
Martis, R.J., Acharya, U.R., Tan, J.H., Petznick, A., Tong, L., Chua, C.K., Ng, E.Y.K.: Application of intrinsic time-scale decomposition (ITD) to EEG signals for automated seizure prediction. Int. J. Neural Syst. 23, 1350023 (2013)
Abdulhay, E., Elamaran, V., Chandrasekar, M., Balaji, V.S., Narasimhan, K.: Automated diagnosis of epilepsy from EEG signals using ensemble learning approach. Pattern Recognit. Lett. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2017.05.021
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statements of ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goshvarpour, A., Goshvarpour, A. Diagnosis of epileptic EEG using a lagged Poincare plot in combination with the autocorrelation. SIViP 14, 1309–1317 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-020-01672-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-020-01672-w