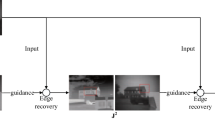
Abstract
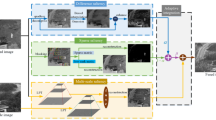
A VGG-based fusion method (named VMDM-Fusion) that employs multiple decision maps is proposed to fuse infrared and visible images. Our method first feeds the infrared and visible images into a pre-trained model of VGG-16 to extract the features. Then, a feature representation method we designed uses these features to construct saliency maps. Next, these maps, in combination with a guided filter, are used to construct multiple decision maps. Lastly, the final fused image is obtained by weighting the source images based on the multiple decision maps. This is the first time a decision map is introduced in the field of infrared and visible image fusion. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art infrared and visible image fusion methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, S., Kang, X., Fang, L., J, Hu., Yin, H.: Pixel-level image fusion: a survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 83, 100–112 (2017).
Xu, J., Yu, S., You, X., Leng, M., Jing, X.Y., Chen, C.: Multi-view hybrid embedding: a divide-and-conquer approach (2018)
Yu, L., Tillo, T., Xiao, J., Grangetto, M.: Convolutional neural network for intermediate view enhancement in multiview streaming. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 20(1), 15–28 (2018)
Gao, R., Vorobyov, S.A., Zhao, H.: Image fusion with cosparse analysis operator. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24(7), 943–947 (2017)
Yang, B., Li, S.: Multi-focus image fusion and restoration with sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 59(4), 884–892 (2010)
Li, S., Yin, H., Fang, L.: Group-sparse representation with dictionary learning for medical image denoising and fusion. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59(12), 3450–3459 (2012)
Wang, J., Peng, J., Feng, X., He, G., Fan, J.: Fusion method for infrared and visible images by using non-negative sparse representation. Infr. Phys. Technol. 67, 477–489 (2014)
Li, H., He, X., Tao, D., Tang, Y., Wang, R.: Joint medical image fusion, denoising and enhancement via discriminative low-rank sparse dictionaries learning. Pattern Recognit. 79, 130–146 (2018)
Li, H., Manjunath, B.S., Mitra, S.K.: Multi-sensor image fusion using the wavelet transform. Graph Models Image Process 57(3), 235–245 (1995)
Yang, Y., Tong, S., Huang, S., Lin. P.: Multi-focus image fusion based on NSCT and focused area detection. IEEE Sensors J. 15(5), 2824–2838, (2015).
Yang, Y., Que, Y., Huang, S., Lin. P.: Multimodal sensor medical image fusion based on type-2 fuzzy logic in NSCT domain. IEEE Sensors J. 16(10), 3735–3745, (2016).
Bhatnagar, G., Wu, Q.M.J., Liu, Z.: Directive contrast based multimodal medical image fusion in NSCT domain. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 15(5), 1014–1024 (2013)
Li, S., Kang, X., Hu, J.: Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(7), 2864–2875 (2013)
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Ward, R.K., Wang, Z.J.: Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(12), 1882–1886 (2016)
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Ward, R.K., Wang, Z.J.: Medical image fusion via convolutional sparsity based morphological component analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 26(3), 485–489 (2019)
Ma, J., Zhou, Z., Wang, B., Zong, H.: Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 82, 8–17 (2017)
Li, H., Wu, J., Kittle, J.: MDLatLRR: a novel decomposition method for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.2975984
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Wang, Z., Wang, Z.J., Ward, R.K., Wang, X.: Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: recent advances and future prospects. Inf. Fusion 42, 158–173 (2018)
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Peng, H., Wang, Z.: Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Inf. Fusion 36, 191–207 (2017)
Ma, J., Yu, W., Liang, P., Li, C., Jiang, J.: FusionGAN: a generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 48, 11–26 (2019)
Ma, J., Liang, P., Yu, W., Chen, C., Guo, X., Wu, J., Jiang, J.: Infrared and visible image fusion via detail preserving adversarial learning. Inf. Fusion 54, 85–98 (2020)
Li, H., Wu, X.J.: DenseFuse: a fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(5), 2614–2623 (2019)
Kumar, N., Sukavanam, N.: Weakly supervised deep network for spatiotemporal localization and detection of human actions in wild conditions. Vis. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01777-5
He, K., Sun, J., Tang, X.: Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(6), 1397–1409 (2013)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: NIPS (2015)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recog. 248–255 (2009).
Li, H., Wu, X.-J.: Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary learning and low-rank representation. In: Zhao, Y., Kong, X., Taubman, D. (eds.) ICIG 2017. LNCS, vol. 10666, pp. 675–686. Springer, Cham (2017)
Fashandi, H., Peters, J., Ramanna, S.: L2 norm length based image similarity measures: concrescence of image feature histogram distances. In: Signal and Image Processing, International Association of Science Technology Development, pp. 178–185. Honolulu (2009)
Zhang, X., Ma, Y., Fan, F., Zhang, Y., Huang, J.: Infrared and visible image fusion via saliency analysis and local edge-preserving multi-scale decomposition. J. Opt. Soc. Am. Opt. Image Sci. 34(8), 1400–1410, (2017).
Toet, A.: TNO image fusion dataset. Figshare. Data (2014). https://figshare.com/articles/TN_Image_Fusion_Dataset/1008029.
Xu, H., Ma, J., Guo, X., Ling, H.: U2Fusion: a unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3012548
Ma, J., Chen, C., Li, C., Huang, J.: Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inf. Fusion 31, 100–109 (2016)
Prabhakar, K.R., Srikar, V.S., Babu, R.V.: Deepfuse: a deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 4714–4722 (2017).
Ma, J., Ma, Y., Li, C.: Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: a survey. Inf. Fusion 45, 153–178 (2019)
Roberts, J.W., van Aardt, J., Ahmed, F.: Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2, 023522 (2008)
Qu, G., Zhang, D., Yan, P.: Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett. 38(7), 313–315 (2002)
Xydeas, C.S., Petrovic, V.: Objective image fusion performance measure. Electron. Lett. 36(4), 308–309 (2000)
Yang, C., Zhang, J Q., Wang, X R., Liu. X.: A novel similarity based quality metric for image fusion. Inf. Fusion 9, 156–160, (2008).
Eskicioglu, A.M., Fisher, P.S.: Image quality measures and their performance. IEEE Trans. Commun. 43, 2959–2965 (1995)
Cui, G., Feng, H., Xu, Z., Li, Q., Chen, Y.: Detail preserved fusion of visible and infrared images using regional saliency extraction and multi-scale image decomposition. Opt. Commun. 341, 199–209 (2015)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61862030 and No.62072218), by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (No.20192ACB20002, and No.20192ACBL21008), and by the Talent project of Jiangxi Thousand Talents Program (No. jxsq2019201056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Liu, JX., Huang, SY. et al. VMDM-fusion: a saliency feature representation method for infrared and visible image fusion. SIViP 15, 1221–1229 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01852-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01852-2