Abstract
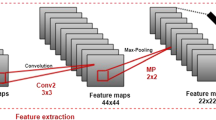
In this paper, we propose a novel CNN-based model named as Deep Cross Feature Adaptive Network (DCFA-CNN) for facial expression recognition. The proposed DCFA-CNN model holds two major components: shape feature (ShFeat) block and texture feature (TexFeat) block, respectively. The ShFeat block is responsible to extract high-level responses, which leads to discriminate features from different expressive regions, while TexFeat block leads to hold micro/minute variations which defines structural differences in the expressive regions. Moreover, DCFA-CNN embedded a two-branch cross-relationship to collect information of ShFeat and TexFeat block. These different responses boost discriminability of the network by incorporating complementary features. The effectiveness of the proposed DCFA-CNN is evaluated extensively with four datasets: CK+, MUG, ISED and OULU-CASIA, over single-domain subject independent and cross-domain ethnicity independent experimental setups. The experimental results show a significant improvement of 21.8%, 21.55% and 6.43%, 17.9% as compared with MobileNet for 6- and 7-classes over ISED and OULU-CASIA. The extensive ablation experiments have done to validate the role of each module in DCFA-CNN framework.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekman, P.: Basic emotions. Handbook of cognition and emotion vol. 98, pp. 45–60 (1999)
Hong, H., Neven, H., Von der Malsburg, C.: Online facial expression recognition based on personalized galleries. Proceedings Third IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 354–359 (1998)
Kotsia, I., Pitas, I.: Facial expression recognition in image sequences using geometric deformation features and support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(1), 172–187 (2006)
Shan, C., Gong, S., McOwan, P.W.: Facial expression recognition based on local binary patterns: A comprehensive study. Image Vis. Comput. 27(6), 803–816 (2009)
Jabid, T., Kabir, Md.H., Chae, O.: Robust facial expression recognition based on local directional pattern. ETRI J. 32(5), 784–794 (2010)
Rivera, A.R., Castillo, J.R., Chae, O.: Local directional number pattern for face analysis: Face and expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(5), 1740–1752 (2012)
Rivera, A.R., Castillo, J.R., Chae, O.: Local directional texture pattern image descriptor. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 51, 94–100 (2015)
Ryu, B., Rivera, A.R., Kim, J.: Local directional ternary pattern for facial expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(12), 6006–6018 (2017)
Mandal, M., Verma, M., Mathur, S., Vipparthi, S.K., Murala, S., Kumar, D.K.: Regional adaptive affinitive patterns (RADAP) with logical operators for facial expression recognition. IET Image Proc. 13(5), 850–861 (2019)
Verma, M., Sexena, P., Vipparthi, S. K., Santosh Singh, G:. QUEST: Quadriletral senary bit pattern for facial expression recognition, 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), pp. 1498–1503 (2018)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.E.: Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 25, 1097–1105 (2012)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition, arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 (2014)
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., Rabinovich, A.: Going deeper with convolutions. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 1–9 (2015)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Howard, A. G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D., Wang, W., Weyand, T., Andreetto, M., Adam, H.: Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications, arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861 (2017)
Majumder, A., Behera, L., Subramanian, V.K.: Automatic facial expression recognition system using deep network-based data fusion. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 48(1), 103–114 (2016)
Kim, Y., Yoo, B., Kwak, Y., Choi, C., Kim, J.: Deep generative-contrastive networks for facial expression recognition, arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07140 (2017)
Verma, M., Bhui, J. K., Vipparthi, S. K., Singh, G.: EXPERTNet: Exigent Features Preservative Network for Facial Expression Recognition, Proceedings of the 11th Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing, pp. 1–8 (2018)
Zhang, S., Pan, X., Cui, Y., Zhao, X., Liu, L.: Learning affective video features for facial expression recognition via hybrid deep learning. IEEE Access 7, 32297–32304 (2019)
Verma, Monu, SK, Vipparthi, Singh, G.: Hinet: Hybrid inherited feature learning network for facial expression recognition. IEEE Lett. Comput. Soc. 2(4), 36–39 (2019)
Georgescu, M., Ionescu, R.T., Popescu, M.: Local learning with deep and handcrafted features for facial expression recognition. IEEE Access 7, 64827–64836 (2019)
Liang, D., Liang, H., Yu, Z., Zhang, Y.: Deep convolutional BiLSTM fusion network for facial expression recognition. Vis. Comput. 36(3), 499–508 (2020)
Minaee, S., Abdolrashidi, A.: Deep-emotion: Facial expression recognition using attentional convolutional network, arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.01019, (2019)
Wang, K., Peng, X., Yang, J., Meng, D., Qiao, Y.: Region attention networks for pose and occlusion robust facial expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 4057–4069 (2020)
Verma, M., Saxena, P., Vipparthi, S. K., Singh, G., Girdhari , Nagar, S. K.: DEFINET: portable CNN network for facial expression recognition, ICT for Competitive Strategies: Proceedings of 4th international conference on information and communication technology for competitive strategies (ICTCS), vol. 217 (2020)
Xie, S., Hu, H.: Facial expression recognition using hierarchical features with deep comprehensive multipatches aggregation convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2(1), 211–220 (2018)
Verma, M., Vipparthi, S.K., Singh, G., Murala, S.: LEARNet: Dynamic imaging network for micro expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 1618–1627 (2019)
Verma, M., Vipparthi, S.K., Singh, G.: AffectiveNet: affective-motion feature learning for micro expression recognition. IEEE Multimed. 28, 17–27 (2020)
Schindler, A., Lidy, T., Rauber, A.: Comparing shallow versus deep neural network architectures for automatic music genre classification. FMT, 17–21 (2016)
Lucey, P., Cohn, J. F., Kanade, T., Saragih, J., Ambadar, Z., Matthews, I.: The extended cohn-kanade dataset (ck+): A complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression, 2010 IEEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition-workshops, pp. 94–101 (2010)
Aifanti, N., Papachristou, C., Delopoulos, A.: The MUG facial expression database, 11th International Workshop on Image Analysis for Multimedia Interactive Services WIAMIS 10, pp. 1–4 (2010)
Happy, S.L., Patnaik, P., Routray, A., Guha, R.: The indian spontaneous expression database for emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 8(1), 131–142 (2015)
Zhao, G., Huang, X., Taini, M., Li, S.Z., PietikäInen, M.: Facial expression recognition from near-infrared videos. Image Vis. Comput. 29(9), 607–619 (2011)
Verma, M., Vipparthi, S. K., Singh, G.: Non-Linearities Improve OrigiNet based on Active Imaging for Micro Expression Recognition, arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.07991 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, A.H., Kolli, K. & Kiran, Y.L. Deep cross feature adaptive network for facial emotion classification. SIViP 16, 369–376 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01941-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01941-2