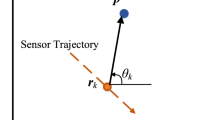
Abstract
In this paper, we propose an effective method to estimate the target location using two receiver stations and bi-static geometry. In this method, the least squares criterion-based optimization problem is formed using a combination of the time difference of arrival (TDOA) and angle of arrival (AOA) measurements to estimate the target location. This problem is solved by semi-definite relaxation without requiring an initial estimation of the response or comprehensive search. The proposed method can effectively localize the target location with high accuracy in the presence of high noise level and, consequently, inaccurate TDOA and AOA measurements of the input signal. The numerical results show that the proposed method estimates the target location more accurately than some state-of-the-art methods in the presence of inaccurate input parameters.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rui, L., Ho, K.C.: Efficient closed-form estimators for multistatic sonar localization. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 51(1), 600–614 (2015)
Coraluppi, S.: Multistatic sonar localization. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 31(4), 964–974 (2006)
Indelman, V., Gurfil, P., Rivlin, E., Rotstein, H.: Real-time vision-aided localization and navigation based on three-view geometry. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 48(3), 2239–2259 (2012)
Mantilla-Gaviria, I.A., Leonardi, M., Galati, G., Balbastre-Tejedor, J.V.: Localization algorithms for multilateration (MLAT) systems in airport surface surveillance. Signal Image Video Process. 9(7), 1549–1558 (2015)
Zhou, B., Liu, A., Lau, V.K.N.: Successive localization and beamforming in 5g mmwave MIMO communication systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 67(6), 1620–1635 (2019)
Li, W., Wang, L., Xiao, M., Li, Y., Zhang, H.: Closed form solution for 3D localization based on joint RSS and AOA measurements for mobile communications. IEEE Access. 8, 12-632–12-643 (2020)
Aubry, A., Carotenuto, V., De Maio, A., Pallotta, L.: Localization in 2D PBR with multiple transmitters of opportunity: a constrained least squares approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 68, 634–646 (2020)
Marino, A., Aubry, A., De Maio, A., Braca, P.: 2D constrained PBR localization via active radar designation. In: 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), 2020, pp. 1–6
Noroozi, A., Oveis, A.H., Sebt, M.A.: Iterative target localization in distributed MIMO radar from bistatic range measurements. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24(11), 1709–1713 (2017)
Li, L.: Joint parameter estimation and target localization for bistatic MIMO radar system in impulsive noise. Signal Image Video Process. 9(8), 1775–1783 (2015)
Feraidooni, M.M., Gharavian, D., Peimany, M., Imani, S.: 3-D target localization based on bi-static range measurements in widely separated mimo radars. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08197-6
Poisel, R.A.: Electronic Warfare Target Location Methods. Artech House, Boston (2012)
Ho, D.K.C., Xu, W.: An accurate algebraic solution for moving source location using TDOA and FDOA measurements. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52(9), 2453–2463 (2004)
Ho, K.C., Vicente, L.M.: Sensor allocation for source localization with decoupled range and bearing estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(12), 5773–5789 (2008)
Wang, Y., Ho, K.C.: An asymptotically efficient estimator in closed-form for 3-D AOA localization using a sensor network. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 14(12), 6524–6535 (2015)
Yin, J., Wan, Q., Yang, S., Ho, K.C.: A simple and accurate TDOA-AOA localization method using two stations. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 23(1), 144–148 (2016)
Noroozi, A., Sebt, M.A.: Target localization in multistatic passive radar using SVD approach for eliminating the nuisance parameters. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 53(4), 1660–1671 (2017)
Sari, R., Zayyani, H.: RSS localization using unknown statistical path loss exponent model. IEEE Commun. Lett. 22(9), 1830–1833 (2018)
Kay, S.M.: Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing: Estimation Theory. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1993)
Chan, Y., Hang, H.Y.C., Ching, P.: Exact and approximate maximum likelihood localization algorithms. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 55(1), 10–16 (2006)
Destino, G., Abreu, G.: On the maximum likelihood approach for source and network localization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(10), 4954–4970 (2011)
Foy, W.H.: Position-location solutions by taylor-series estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 12(2), 187–194 (1976)
Chan, Y., Ho, K.C.: A simple and efficient estimator for hyperbolic location. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 42(8), 1905–1915 (1994)
Ho, K.C., Lu, X., Kovavisaruch, L.: Source localization using TDOA and FDOA measurements in the presence of receiver location errors: analysis and solution. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(2), 684–696 (2007)
Beck, A., Stoica, P., Li, J.: Exact and approximate solutions of source localization problems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(5), 1770–1778 (2008)
Wang, G., Chen, H.: An importance sampling method for TDOA-based source localization. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun 10(5), 1560–1568 (2011)
Briechle, K., Hanebeck, U.D.: Localization of a mobile robot using relative bearing measurements. IEEE Trans. Robot. 20(1), 36–44 (2004)
Lin, Z., Han, T., Zheng, R., Fu, M.: Distributed localization for 2-D sensor networks with bearing-only measurements under switching topologies. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(23), 6345–6359 (2016)
Dogancay, K.: Bearings-only target localization using total least squares. Signal Process. 85(9), 1695–1710 (2005)
Tomic, S., Beko, M., Dinis, R.: 3-D target localization in wireless sensor networks using RSS and aoa measurements. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 66(4), 3197–3210 (2017)
Dogancay, K.: 3D pseudolinear target motion analysis from angle measurements. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(6), 1570–1580 (2015)
Cong, L., Zhuang, W.: Hybrid TDOA/AOA mobile user location for wideband CDMA cellular systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun 1(3), 439–447 (2002)
Bishop, A.N., Fidan, B., Dogancay, K., Anderson, B.D.O., Pathirana, P.N.: Exploiting geometry for improved hybrid AOA/TDOA-based localization. Signal Process. 88(7), 1775–1791 (2008)
Jia, T., Wang, H., Shen, X., Jiang, Z., He, K.: Target localization based on structured total least squares with hybrid TDOA-AOA measurements. Signal Process. 143, 211–221 (2018)
Wang, Y., Ho, D.K.C.: Unified near-field and far-field localization for AOA and hybrid AOA-TDOA positionings. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun 17(2), 1242–1254 (2018)
Wang, G., Li, Y., Ansari, N.: A semidefinite relaxation method for source localization using TDOA and FDOA measurements. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 62(2), 853–862 (2013)
Guo, X., Chu, L., Sun, X.: Accurate localization of multiple sources using semidefinite programming based on incomplete range matrix. IEEE Sens. J. 16(13), 5319–5324 (2016)
Wang, Y., Wu, Y.: An efficient semidefinite relaxation algorithm for moving source localization using TDOA and FDOA measurements. IEEE Commun. Lett. 21(1), 80–83 (2017)
Zou, Y., Liu, H.: Semidefinite programming methods for alleviating clock synchronization bias and sensor position errors in TDOA localization. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 27, 241–245 (2020)
Boyd, S., Vandenberghe, L.: Convex Optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Grant, M., Boyd, S.: CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming, version 2.1. http://cvxr.com/cvx, Mar. 2014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imani, S., Peimany, M., Hasankhan, M.J. et al. Bi-static target localization based on inaccurate TDOA-AOA measurements. SIViP 16, 239–245 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01985-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-01985-4