Abstract
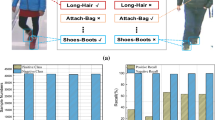
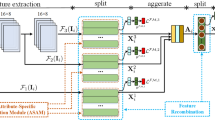
The objective of pedestrian attribute recognition (PAR) is to recognize human attributes based on the appearance of pedestrians in images. The PAR is a challenging task in video surveillance scenarios due to its two inherent challenges, variety and ambiguity of attributes, as well as imbalanced attributes distribution. To tackle these challenges, this paper proposes a new PAR approach, called focal label smoothing regularization (FLSRNet). The proposed FLSRNet approach has two key mechanisms. First, the label smoothing mechanism is applied to shrink a certain degree from the true label. Second, the focal mechanism dynamically guides the degree in which labels are smoothed, where an attribute-adaptive smoothing factor is proposed to automatically down-weight the contributions of majority attributes examples throughout the procedure of the model training and focus the model on minority attributes examples. This is in distinction to the conventional label smoothing approach, which neglects the imbalanced attributes distribution and applies a fixed smoothing factor uniformly on all attributes. To validate the performance of the proposed method, experiments are conducted utilizing two benchmark datasets.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, X., Zheng, S., Yang, R., Luo, B., Tang, J.: Pedestrian attribute recognition: a survey, arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.07474, 2019. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07474
Saeidi, M., Ahmadi, A.: A novel approach for deep pedestrian detection based on changes in camera viewing angle. Signal Image Video Process. 14(6), 1273–1281 (2020)
Li, Z., Chen, Z., Wu, Q., Liu, C.: Real-time pedestrian detection with deep supervision in the wild. Signal Image Video Process. 13(4), 761–769 (2019)
Wu, Q., Dai, P., Chen, P., Huang, Y.: Deep adversarial data augmentation with attribute guided for person re-identification. Signal Image Video Process. 15(4), 655–662 (2021)
Liu, X., Chen, S., Song, L., Wozniak, M., Liu, S.: Self-attention negative feedback network for real-time image super-resolution. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. (2021)
Li, D., Chen, X., Huang, K.: Multi-attribute learning for pedestrian attribute recognition in surveillance scenarios. In: IAPR Asian Conf. on Pattern Recognition, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, pp. 111–115 (2015)
Sudowe, P., Spitzer, H., Leibe, B.: Person attribute recognition with a jointly-trained holistic CNN model. In: IEEE Int, pp. 87–95. Santiago, Chile, Conf. on Computer Vision (2015)
Zhou, Y., Yu, K., Leng, B., Zhang, Z., Li, D., Huang, K.: Weakly-supervised learning of mid-level features for pedestrian attribute recognition and localization. In: British Machine Vision Conference, London, United Kingdom, pp. 69.1–69.12 (2017)
Tang, C., Sheng, L., Zhang, Z.-X., Hu, X.: Improving pedestrian attribute recognition with weakly-supervised multi-scale attribute-specific localization. In: IEEE Int, pp. 4996–5005. Seoul, Korea, Conf. on Computer Vision (2019)
Yaghoubi, E., Borza, D., Neves, J., Kumar, A., Proença, H.: An attention-based deep learning model for multiple pedestrian attributes recognition. Image Vis. Comput. 102, 103981 (2020)
Tan, Z., Yang, Y., Wan, J., Hang, H., Guo, G., Li, S.Z.: Attention-based pedestrian attribute analysis. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(12), 6126–6140 (2019)
Sarfraz, M. S., Schumann, A., Wang, Y., Stiefelhagen, R.: Deep view-sensitive pedestrian attribute inference in an end-to-end model. In: British Machine Vision Conference, London, United Kingdom, pp. 134.1–134.13 (2017)
Zhang, X., Jia, J., Gao, K., Zhang, Y., Zhang, D., Li, J., Tian, Q.: Trip outfits advisor: location-oriented clothing recommendation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 19(11), 2533–2544 (2017)
Zeng, H., Ai, H., Zhuang, Z., Chen, L.: Multi-task learning via co-attentive sharing for pedestrian attribute recognition. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Multimedia and Expo, London, United Kingdom (2020)
Wozniak, M., Silka, J., Wieczorek, M.: Deep neural network correlation learning mechanism for CT brain tumor detection. Neural Comput. Appl. (2021)
Dong, W., Wu, J., Bai, Z., Hu, Y., Li, W., Qiao, W., Wozniak, M.: MobileGCN applied to low-dimensional node feature learning. Pattern Recogn. 112, 107788 (2021)
Deng, Y., Luo, P., Loy, C.C., Tang, X.: Pedestrian attribute recognition at far distance. In: ACM Int, pp. 789–792. Orlando, USA, Conf. on Multimedia (2014)
Li, D., Zhang, Z., Chen, X., Huang, K.: A richly annotated pedestrian dataset for person retrieval in real surveillance scenarios. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(4), 1575–1590 (2019)
Szegedy, C., Vanhoucke, V., Ioffe, S., Shlens, J., Wojna, Z.: Rethinking the Inception architecture for computer vision. In: IEEE Int, pp. 2818–2826. Los Alamitos, USA, Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Liu, S., Guo, H., Hu, J.-G., Zhao, X., Zhao, C., Wang, T., Zhu, Y., Wang, J., Tang, M.: A novel data augmentation scheme for pedestrian detection with attribute preserving GAN. Neurocomputing 401, 123–132 (2020)
Fukui, H., Yamashita, T., Yamauchi, Y., Fujiyoshi, H., Murase, H.: Robust pedestrian attribute recognition for an unbalanced dataset using mini-batch training with rarity rate. In: IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, pp. 322–327. Sweden, Gothenburg (2016)
Sarafianos, N., Xu, X., Kakadiaris, I.A.: Deep imbalanced attribute classification using visual attention aggregation. In: Conf, European (ed.) on Computer Vision, pp. 680–697. Munich, Germany (2018)
Ji, Z., He, E., Wang, H., Yang, A.: Image-attribute reciprocally guided attention network for pedestrian attribute recognition. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 120, 89–95 (2019)
Ji, Z., Hu, Z., He, E., Han, J., Pang, Y.: Pedestrian attribute recognition based on multiple time steps attention. Pattern Recog. Lett. 138, 170–176 (2020)
Pereyra, G., Tucker, G., Chorowski, J., Kaiser, L., Hinton, G.: Regularizing neural networks by penalizing confident output distributions. In: Int. Conf. on Learning Representations, Toulon, France (2017)
Müller, R., Kornblith, S., Hinton, G.E.: When does label smoothing help?’. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 4694–4703. Canada, Vancouver (2019)
Yuan, L., Tay, F.E., Li, G., Wang, T., Feng, J.: Revisiting knowledge distillation via label smoothing regularization. In: IEEE Int, pp. 3902–3910. Seattle, USA, Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2020)
Chen, Y., Li, J., Xiao, H., Jin, X., Yan, S., Feng, J.: Dual path networks. In: Proc, pp. 4470–4478. Long Beach, USA, Int. Conf. on Neural Information Processing Systems (2017)
Qian, N.: On the momentum term in gradient descent learning algorithms. Neural Netw. 12(1), 145–151 (1999)
Yaghoubi, E., Khezeli, F., Borza, D., Kumar, S.A., Neves, J., Proença, H.: Human attribute recognition: a comprehensive survey. Appl. Sci. 10(16), 5608 (2020)
Polap, D., Wozniak, M.: Image features extractor based on hybridization of fuzzy controller and meta-heuristic. In: IEEE Int. Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Luxembourg, Luxembourg, pp. 1–6 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Yam, G.P.D., Lu, J. et al. FLSRNet: pedestrian attribute recognition using focal label smoothing regularization. SIViP 16, 1463–1470 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-02099-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-021-02099-7