Abstract
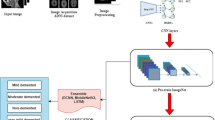
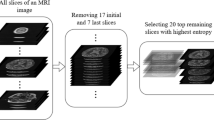
Dementia is a type of brain disease that affects the mental abilities. Various studies utilize PET features or some two-dimensional brain perspectives to diagnose dementia. In this study, we have proposed an ensemble approach, which employs volumetric and axial perspective features for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and the patients with mild cognitive impairment. We have employed deep learning models and constructed two disparate networks. The first network evaluates volumetric features, and the second network assesses grid-based brain scan features. Decisions of these networks were combined by an adaptive majority voting algorithm to create an ensemble learner. In the evaluations, we compared ensemble networks with single ones as well as feature fusion networks to identify possible improvement; as a result, the ensemble method turned out to be promising for making a diagnostic decision. The proposed ensemble network achieved an average accuracy of 91.83% for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease; to the best of our knowledge, it is the highest diagnosis performance in the literature.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzheimers, A.: 2015 Alzheimers disease facts and figures. Alzheimers and dementia: the journal of the Alzheimers Association 11(3), 322 (2015)
Gambhir, S.S.: Molecular imaging of cancer with positron emission tomography. Nature Rev. Cancer 2(9), 683 (2002)
Jagust, W.J., Eberling, J.L., Reed, B.R., Mathis, C.A., Budinger, T.F.: Clinical studies of cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 826(1), 254–262 (1997)
Jellinger, K.A.: Criteria for the neuropathological diagnosis of dementing disorders: routes out of the swamp? Acta Neuropathologica 117(2), 101–110 (2009)
Petersen, R.C., Smith, G.E., Waring, S.C., Ivnik, R.J., Tangalos, E.G., Kokmen, E.: Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch. Neurol. 56(3), 303–308 (1999)
Cabral, C., Morgado, P.M., Costa, D.C., Silveira, M.: Predicting conversion from MCI to AD with FDG-PET brain images at different prodromal stages. Comput. Biol. Med. Alzheimer’s Dis. Neuroimaging Initiatie 58, 101–109 (2015)
Mudali, D., Teune, L.K., Renken, R.J., Leenders, K.L., Rerdink, J.B.T.M.: Classification of Parkinsonian Syndromes from FDG-PET Brain Data Using Decision Trees with SSM/PCA Features. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 10 (2015)
Kerr, W.T., Nguyen, S.T., Cho, A.Y., Lau, E.P., Silverman, D.H., Douglas, P.K., Stern, J.M.: Computer-aided diagnosis and localization of lateralized temporal lobe epilepsy using interictal FDG-PET. Front. Neurol. 4, 31 (2013)
Kang, H., Kim, W.G., Yang, G.S., Kim, H.W., Jeong, J.E., Yoon, H.J., Kang, D.Y.: VGG-based BAPL score classification of 18F-Florbetaben Amyloid Brain PET. Biomed. Sci. Lett. 24(4), 418–425 (2018)
Lizuka, T., Fukasawa, M., Kameyama, M.: Deep-learning-based imaging-classification identified cingulate island sign in dementia with Lewy bodies. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 8944 (2019)
Vu, T.D., Yang, H.J., Nguyen, V.Q., Oh, A.R., Kim, M.S.: Multimodal learning using convolution neural network and sparse autoencoder. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp), 309–312 (2017)
Liu, M., Zhang, D., Shen, D.: Ensemble sparse classification of Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage 60(2), 1106–1116 (2012)
Ortiz, A., Munilla, J., Gorriz, J.M., Ramirez, J.: Ensembles of deep learning architectures for the early diagnosis of the Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Neural Syst. 26(07), 1650025 (2016)
Yao, D., Calhoun, V.D., Fu, Z., Du, Y., Sui, J.: An ensemble learning system for a 4-way classification of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurosci. Methods 302, 75–81 (2018)
An, N., Ding, H., Yang, J., Au, R., Ang, T.F.: Deep ensemble learning for Alzheimer’s disease classification. J. Biomed. Inform. 105, 103411 (2020)
Cheng, D., Liu, M.: Classification of Alzheimer’s disease by cascaded convolutional neural networks using PET images. In: International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Springer, Cham, 106–113 (2017)
Choi, H., Jin, K.H.: Predicting cognitive decline with deep learning of brain metabolism and amyloid imaging. Behav. Brain Res. 344, 103–109 (2018)
Huang, Y., Xu, J., Zhou, Y., Tong, T., Zhuang, X.: Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease via multi-modality 3D convolutional neural network. Front. Neurosci. 13 (2019)
Weiner, M., Veitch, D., Aisen, P., Beckett, L., Cairns, N.: The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative 3: continued innovation for clinical trial improvement. Alzheimer’s and Dementia 13(5), 561–571 (2017)
Ding, Y., Sohn, J.H., Kawczynski, M.G., Trivedi, H., Harnish, R., Jenkins, N.W., Behr, S.C.: A deep learning model to predict a diagnosis of Alzheimer disease by using 18F-FDG PET of the brain. Radiology 290(2), 456–464 (2019)
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) (2014)
Guo, C., Pleiss, G., Sun, Y., Weinberger, K.Q.: On calibration of modern neural networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, 1321–1330 (2017)
Neumann, L., Zisserman, A., Vedaldi, A.: Relaxed softmax: efficient confidence auto-calibration for safe pedestrian detection. In: NIPS Workshop on Machine Learning for Intelligent Transportation Systems (2018)
Kristiadi, A., Hein, M., Hennig, P.: Being bayesian, even just a bit, fixes overconfidence in relu networks. In: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 5436–5446 (2020)
Nguyen, A., Yosinski, J.: Clune J. High confidence predictions for unrecognizable images, In CVPR, Deep neural networks are easily fooled (2015)
Bertens, D., Vos, S., Kehoe, P., et al.: Use of mild cognitive impairment and prodromal AD/MCI due to AD in clinical care: a European survey. Alz Res Therapy 11, 74 (2019)
Hinrichs, C., Singh, V., Mukherjee, L., Xu, G., Chung, M.K., Johnson, S.C.: Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative, spatially augmented LPboosting for AD classification with evaluations on the ADNI dataset. Neuroimage 48(1), 138–149 (2009)
Gray, K.R., Wolz, R., Heckemann, R.A., Aljabar, P., Hammers, A., Rueckert, D.: Multi-region analysis of longitudinal FDG-PET for the classification of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 60, 221–229 (2012)
Liu, M., Cheng, D., Wang, K., Wang, Y.: Multi-modality cascaded convolutional neural networks for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Neuroinformatics 16(3–4), 295–308 (2018)
Kim, H.W., Lee, H.E., Oh, K., et al.: Multi-slice representational learning of convolutional neural network for Alzheimer’s disease classification using positron emission tomography. BioMed Eng OnLine 19, 70 (2020)
Gray, K. R., Wolz, R., Keihaninejad, S., Heckemann, R. A., Aljabar, P., Hammers, A.: et al., Regional analysis of FDG-PET for use in the classification of Alzheimer’s disease. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro San Francisco, (2011)
Liu, M., Cheng, D., Yan, W.: Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative, classification of Alzheimer’s disease by combination of convolutional and recurrent neural networks using FDG-PET images. Front. Neuroinform. 12, 35 (2018)
Acknowledgements
A. Yiğit is supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) 2211-C Scholarship. Data collection and sharing for this project were funded by the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (National Institutes of Health Grant U01 AG024904) and DOD ADNI (Department of Defense award number W81XWH-12-2-0012). ADNI data are disseminated by the Laboratory for Neuro Imaging at the University of Southern California.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yiğit, A., Baştanlar, Y. & Işık, Z. Dementia diagnosis by ensemble deep neural networks using FDG-PET scans. SIViP 16, 2203–2210 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02185-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02185-4