Abstract
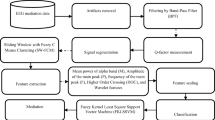
Meditation has a metaphysical impact on human brain functioning. It is of utmost required to infer the cognitive effects of meditation using an electroencephalogram (EEG). In this novel work, the analyses of EEG signals’ features are extracted for cognitive effects on a human brain for meditation intervention of 25 subjects. To analyze the meditation effects, this study examines the feasibility of statistical, spatial, spectral, coherence features, and time–frequency analysis of EEG signals for control and meditator group. Based on the effective features the various classifiers are used to compare the accuracy and distinguish a subject as control or meditator. The results demonstrate that the Support Vector Machine (SVM) gives better accuracy than Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN). The statistical analysis shows that the Variance and Sample Entropy decreased in meditators whereas, in spatial analysis, the Mahalanobis distance increased. The spectral analysis stated that theta power has increased 88% of subjects whereas the alpha power is increased for the entire subjects after meditation. The coherence observed in the pre-frontal lobes’ electrode pair is more in the meditators than in the control group. Eventually, meditation improves relaxation, cognitive functions, calmness, and mental concentration.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yaribeygi, H., Panahi, Y., Sahraei, H., Johnston, T.P., Sahebkar, A.: The impact of stress on body function: a review. EXCLI J. 16, 1057–1072 (2017)
Mohd Razali, S.: Life event, stress and illness, Malaysian. J. Med. Sci. 15(4), 9–18 (2008)
Wang, S. F., Lee, Y. H., Shiah, Y. J., & Young, M. S.: Time-frequency analysis of EEGS recorded during meditation, robot, Vision and Signal Processing (RVSP), 2011 First International Conference on, pp.73–76. (2011)
Newberga, A.B., Winteringa, N., Khalsab, D.S., Roggenkampa, H., Waldmanb, M.R.: Meditation effects on cognitive function and cerebral blood flow in subjects with memory loss: a preliminary study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 20(2), 517–526 (2010)
Benbadis, S. R., Husain, A. M., Kaplan, P. W., Tatum, W. O., William, T., Selim, B., Aatif, H. Peter, K.: Handbook of EEG interpretation, Demos Medical Publishing, (2007)
On, F. R., Jailani, R., Norhazman, H., Mohamad Zaini, N.: Binaural beat effect on brainwaves based on EEG, IEEE 9th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and its Applications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, pp.339–343. (2013)
Lagopoulos, J., Jian, Xu., Rasmussen, I., Vik, A., Malhi, G.S., Eliassen, C.F., Arntsen, I.E.: Increased theta and alpha EEG activity during nondirective meditation. J. Alternative Complement. Med. 15(11), 1187–1192 (2009)
Dillbeck, M.C., Edward, C.: Bronson Short-term longitudinal effects of the transcendental meditation technique on eeg power and coherence. Intern. J. Neurosci. 14(3–4), 147–151 (1981)
Subha, D.P., Joseph, P.K., Acharya, R., Lim, C.M.: EEG signal analysis: a survey. J. Med. Syst. 34, 195–212 (2008)
Asieh ,A., Helane, W., Meghan, M., Nezamfar, H., Erdogmus, D., Oken, B.: Change in physiological signals during mindfulness meditation, 6th Annual International IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, San Diego, California, pp. 1738–1381 (2013)
Liu, M., Utama, N.P.: Meditation effect on human brain compared with psychological questionnaire. Int. J. Inform. Education Technol. 4(3), 264 (2014)
Vyšata, O., Schätz, M., Kopal, J., Burian, J., Procházka, A., Jiří, K., Vališ, M.: Non-Linear EEG measures in meditation. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 7(09), 731 (2014)
Chandana, V., Kochupillai, V.: Quantitative analysis of EEG signal before and after sudharshanakriya yoga. Int. J. Public Mental Health and Neurosci. 2(2), 20–22 (2015)
Traisak Yamsa-ard, and YodchananWongsawat, The Observation of Theta Wave Modulation on Brain Training by 5 Hz-Binaural Beat Stimulation in Seven Days,37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2015, pp. 6667–6670.
Jadhav, N., Manthalkar, R., Joshi, Y.: Effect of meditation on emotional response: an EEG-based study”. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 34, 107–113 (2017)
Sharma, K., Chandra, S., Dubey, A.K.: Exploration of lower frequency EEG dynamics and cortical alpha asymmetry in long-term rajyoga meditators. Int. J. Yoga 11(1), 30 (2018)
Mariappan, R., & Subramanian, M. R.: Experimental Investigation of Cognitive Impact of Yoga Meditation on Physical and Mental Health Parameters Using Electro Encephalogram, Soft Computing and Medical Bioinformatics, Springer Briefs in Forensic and Medical Bioinformatics, pp. 129–139. (2019)
Gaurav, G., Sahani, A. K., & Sahoo, A.: An EEG based Quantitative Analysis of Absorbed Meditative State, 9th International IEEE EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering San Francisco, CA, USA, pp. 57–60. (2019)
Travis, F.: Temporal and spatial characteristics of meditation EEG. Psychol. Trauma Theory Res. Pract. Policy 12(2), 111 (2020)
Kora, P., Meenakshi, K., Swaraja, K., Rajani, A., Raju, M.S.: EEG based interpretation of human brain activity during yoga and meditation using machine learning: a systematic review. Complement. Therapies in Clin. Practice 43, 101329 (2021)
Shaw, L., & Routray, A.: A critical comparison between SVM and k-SVM in the classification of Kriya Yoga meditation state-allied EEG." In 2016 IEEE International WIE Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (WIECON-ECE), pp. 134–138. IEEE, (2016)
Edla, D.R., Mangalorekar, K., Dhavalikar, G., Dodia, S.: Classification of EEG data for human mental state analysis using Random Forest Classifier. Procedia Comput. Sci. 132, 1523–1532 (2018)
Rahul, I., Oimbe, S., Kehri, V., Awale, R.N.: Classification of EEG signals during meditation and controlled state using PCA, ICA, LDA and support vector machines. Int. J. Pure and Appl. Math. 118, 3179–3190 (2018)
Sharma, H., Raj, R., Juneja, M.: EEG signal based classification before and after combined Yoga and Sudarshan Kriya. Neurosci. Lett. 707, 134300 (2019)
Al-Fahoum, A. S., & Al-Fraihat, A. A.: Methods of EEG Signal Features Extraction Using Linear Analysis in Frequency and Time-Frequency Domains, Hindawi Publishing Corporation ISRN Neuroscience Volume 2014 730218, pp. 1-7.
Srinivasan, N.: Cognitive neuroscience of creativity: EEG based approaches. Methods 42(1), 109–116 (2007)
Hincks, S.W., Bratt, S., Poudel, S., Phoha, V.V., Jacob, R.J., Dennett, D.C. and Hirshfield, L.M.: Entropic Brain-computer Interfaces-Using fNIRS and EEG to Measure Attentional States in a Bayesian Framework. In PhyCS (pp. 23-34). (2017)
Tibdewal, M.N., Dey, H.R., Mahadevappa, M., Ray, A., Malokar, M.: Multiple entropies performance measure for detection and localization of multi-channel epileptic EEG. Biomed. Sig. Process. Control 38, 158–167 (2017)
Distance Measures, Chapter 6, https://www.umass. edu/ landeco/ teaching/multivariate/ readings/ McCune.and. Grace. 2002.chapter6.pdf
Wang, R., Wang, J., Haitao, Yu., Wei, X., Yang, C., Deng, B.: Power spectral density and coherence analysis of Alzheimer’s EEG. Cogn Neurodyn 9(3), 291–304 (2015)
Murugappan, M., Ramachandran, N., Sazali, Y.: Classification of human emotion from EEG using discrete wavelet transform. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 3, 390–439 (2010)
Moosavian, A., Ahmadi, H., Tabatabaeefar, A., Khazaee, M.: Comparison of two classifiers; K-nearest neighbor and artificial neural network, for fault diagnosis on a main engine journal-bearing. Shock. Vib. 20(2), 263–272 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3233/SAV-2012-00742
Jakkula, V.: Tutorial on support vector machine (svm). School of EECS, Washington State University 37 (2006).
Ingle, R., Oimbe, S., Kehri, V. and Awale, R.N.: Classification of EEG Signals during Meditation and Controlled Using PCA, ICA, LDA and Support Vector Machines, International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, Volume 118 No. 18 2018, (pp. 3179–3190).
Delimayanti, M.K., Purnama, B., Nguyen, N.G., Faisal, M.R., Mahmudah, K.R., Indriani, F., Kubo, M., Satou, K.: Classification of Brainwaves for sleep stages by high-dimensional FFT features from EEG signals. Appl. Sci. 10(5), 1797 (2020)
Guerriero, L. E.: Impact of short meditation on attentional performance (2021).
Khare, K.C., Nigam, S.K.: A Study of Electroencephalogram in Meditators. Indian J Phys. Pharma. 44(2), 173–178 (2000)
Majnik, M., Bosnić, Z.: ROC analysis of classifiers in machine learning: a survey. Intell. Data Anal. 17(3), 531–558 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tibdewal, M.N., Nagbhide, D.N., Mahadevappa, M. et al. Multi-feature extraction, analysis, and classification for control and meditators’ electroencephalogram. SIViP 16, 2259–2267 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02191-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02191-6