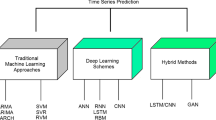
Abstract
In recent years, cloud computing has revolutionized computing. The resource usage prediction of machine workloads has been one of the most important and challenging problems. Load prediction in cloud computing is challenging due to the inefficiency of feature extraction and complex loading environment. Attention mechanism based Multi-level Feature Extraction (MFE) model has been developed. Empirical mode decomposition has been selected to extract the sequence surface features. Multi-level LSTM has been used to extract multi-level features of the decomposed load in the empirical mode decomposition. Attention mechanism has been adopted to get different weights for the extracted features. In order to further get causal relationship of time series data, Empirical mode decomposition based Temporal Convolutional Network (ETCN) model has been developed. Multiple temporal convolutional network residual blocks are stacked to improve the historical memory ability and increase the local receptive field. An adaptive weight strategy has been proposed to assign different weights to the developed MFE and ETCN. The weights are updated adaptively according to the errors in MFE and ETCN, respectively. The proposed method has excellent performance in cloud computing on some challenging datasets by comparison with some state-of-the-art ones. The proposed method achieves an average improvement of 30.23% and 41.5% on the NASA datasets and Saskatchewan datasets, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
All datasets available in the Internet Traffic Archive. http://ita.ee.lbl.gov/html/ traces.html.
References
Tang, Z., Xiao, Z., Yang, L., et al.: A network load perception-based task scheduler for parallel distributed data processing systems. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 1(1), 1–15 (2021)
Chen, J., Li, K.: A parallel random forest algorithm for big data in a spark cloud computing environment. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 28(4), 919–933 (2016)
Tang, Z., Du, L., Zhang, X., et al.: AEML: An acceleration engine for multi-GPU load-balancing in distributed heterogeneous environment. IEEE Trans. Comput. 71(6), 1344–1357 (2021)
Chen, J., Li, K., Ronga, H., et al.: A periodicity-based parallel time series prediction algorithm in cloud computing environments. Inf. Sci. 496(1), 506–537 (2019)
Chen, J., Li, K., Deng, Q., et al.: Distributed deep learning model for intelligent video surveillance systems with edge computing. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 1(1), 1–9 (2019)
Singh, A., Kumar, J.: Secure and energy aware load balancing framework for cloud data centre networks. Electron. Lett. 55(2), 540–541 (2019)
D. Kirchoff, M. Xavier, J. Mastella, et al. A preliminary study of machine learning workload prediction techniques for cloud applications. Proceedings of Euromicro International Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Network-Based Processing (PDP), 2019: 222–227.
Bi, J., Li, S., Yuan, H., et al.: Integrated deep learning method for workload and resource prediction in cloud systems. Neurocomputing 424(1), 35–48 (2021)
Maryam, C., Faramarz, S.: ARIMA: predictive consolidation of virtual machines applying ARIMA method. J. Supercomput. 77(3), 2172–2206 (2021)
Dhaval, B., Deshpande, A.: Short-term load forecasting using method of multiple linear regression. New Approaches Eng. Research 14(1), 67–77 (2021)
Kaur, M., Kaur, P., Sood, S.: Energy efficient IoT-based cloud framework for early flood prediction. Nat. Hazards 109(3), 2053–2076 (2021)
Calheiros, R., Masoumi, E., Ranjan, R., et al.: Workload prediction using ARIMA model and its impact on cloud applications’ QoS. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 3(4), 449–458 (2014)
Sanchez, R., Juan, F.: Structural combination of seasonal exponential smoothing forecasts applied to load forecasting. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 275(3), 916–924 (2019)
Tan, M., Wong, S., Xu, J., et al.: An aggregation approach to short-term traffic flow prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 10(1), 60–69 (2009)
Peng, H., Wen, W., Tseng, M., et al.: A cloud load forecasting model with nonlinear changes using whale optimization algorithm hybrid strategy. Soft. Comput. 25(15), 10205–10220 (2021)
Lang, K., Zhao, Y.: Cloud computing resource scheduling based on improved ANN model takeaway order volume forecast. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 40(4), 5905–5915 (2021)
Gong, G., An, X., Mahato, N., et al.: Research on short-term load prediction based on Seq2seq model. Energies 12(16), 3199–3216 (2019)
D. Janardhanan, E. Barrett. CPU workload forecasting of machines in data centers using LSTM recurrent neural networks and ARIMA models. Proc. International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions, 2017: 55–60.
Fan, J., Zhang, K., Huang, Y., et al.: Parallel spatio-temporal attention-based TCN for multivariate time series prediction. Neural Comput. Appl. 1(1), 1–10 (2021)
Kumar, J., Singh, A., Buyya, R.: Self directed learning based workload forecasting model for cloud resource management. Inf. Sci. 543(1), 345–366 (2021)
Kumar, J., Singh, A., Buyya, R.: Ensemble learning based predictive framework for virtual machine resource request prediction. Neurocomputing 397(1), 20–30 (2020)
Saxena, D., Singh, A.: A proactive autoscaling and energy-efficient VM allocation framework using online multi-resource neural network for cloud data center. Neurocomputing 426(1), 248–264 (2021)
Kumar, J., Singh, A.: Decomposition based cloud resource demand prediction using extreme learning machines. J. Netw. Syst. Manage. 28(4), 1775–1793 (2020)
Bi, J., Yuan, H., Zhou, M.: Temporal prediction of multiapplication consolidated workloads in distributed clouds. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 16(4), 1763–1773 (2019)
Chen, L., Zhang, W., Ye, H.: Accurate workload prediction for edge data centers: Savitzky-Golay filter, CNN and BiLSTM with attention mechanism. Appl. Intell. 1(1), 1–16 (2022)
Ma, Q., Wang, H., Luo, P., et al.: Ultra-short-term railway traction load prediction based on DWT-TCN-PSO_SVR combined model. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 135(1), 107595–107605 (2022)
Wang, D., Li, M.: Stochastic configuration networks: fundamentals and algorithms. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(10), 3466–3479 (2017)
Bi, J., Yuan, H., Zhang, L., et al.: Sgw-scn: an integrated machine learning approach for workload forecasting in geo-distributed cloud data centers. Inf. Sci. 481(1), 57–68 (2019)
Altan, A., Karasu, S., Zio, E.: A new hybrid model for wind speed forecasting combining long short-term memory neural network, decomposition methods and grey wolf optimizer. Appl. Soft Comput. 100(1), 106996–107016 (2021)
Singh, V., Pandey, M., Singh, P., et al.: An empirical mode decomposition (EMD) enabled long sort term memory (LSTM) based time series forecasting framework for web services recommendation. Fuzzy systems and data mining V. IOS Press 1(1), 715–723 (2019)
Zhang, C., Wei, H., Zhao, J., et al.: Short-term wind speed forecasting using empirical mode decomposition and feature selection. Renew. Energy 96(1), 727–737 (2016)
Li, H., Wang, J., Lu, H., et al.: Research and application of a combined model based on variable weight for short term wind speed forecasting. Renew. Energy 116(1), 669684–669720 (2018)
Xie, Y., Jin, M., Xu, G., et al.: Real-time prediction of docker container resource load based on a hybrid model of ARIMA and triple exponential smoothing. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 1(1), 1–17 (2020)
Lang, X., Du, G., Zhu, Z., et al.: Median ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Signal Process. 176(1), 107686–107694 (2020)
Wang, J., Du, G., Zhu, Z., et al.: Fault diagnosis of rotating machines based on the EMD manifold. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 135(1), 106443–106464 (2020)
Jiang, F., Zhu, Z., Li, W.: An improved VMD with empirical mode decomposition and its application in incipient fault detection of rolling bearing. IEEE Access 6(1), 44483–44493 (2018)
Huang, F., Li, X., Yuan, C., et al.: Attention-emotion-enhanced convolutional LSTM for sentiment analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 1(1), 1–14 (2021)
Arlitt, M., Williamson, C.: Web server workload characterization: the search for invariants. ACM Sigmetrics Perform. Eval. Rev. 24(1), 126–137 (1996)
Kumar, J., Singh, A.: Workload prediction in cloud using artificial neural network and adaptive differential evolution. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 81(1), 41–52 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by National Key R&D Program of China (Grant no. 2020YFC1523004).
Funding
This work is supported in part by National Key R&D Program of China (Grant no. 2020YFC1523004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.X. conceived of the presented idea. C.X. developed the theory and performed the computations. C.X. wrote the main manuscript version and completed all experiments, and Y.G. revised the manuscript. C.X. and Y.G. verified the analytical methods. Y.G. encouraged C.X. to investigate and supervised the findings of this work. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, C., Guan, Y. A cloud computing load prediction hybrid model with adaptive weight strategy. SIViP 17, 2101–2109 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02424-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-022-02424-8