Abstract
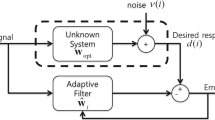
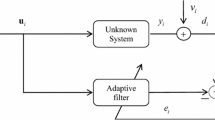
This study proposes a scaler for the normalized least-mean-square algorithm, which is derived based on a cost function designed to retain robustness to a sudden change. A novel step-size updating strategy is designed to improve the tracking speed when the system encounters an impulsive interference. We illustrate that the proposed method is effective for abruptly changed systems with both colored noises and white Gaussian noises. In particular, we perform the theoretical analysis for steady-state excess mean square error based on a Taylor expansion approach. Several representative scaler-based adaptive algorithms are performed in impulsive interference environments for comparisons, including system identification and system tracking. Simulations and echo cancellation experiment are conducted to demonstrate the improvement of the proposed method and support the theoretical analysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jahromi, M.N., Salman, M.S., Hocanin, A., Kukrer, O.: Mean-square deviation analysis of the zero-attracting variable step-size LMS algorithm. Signal, Image Video Proces. 11(3), 533–540 (2017)
Haykin, S.: Adaptive Filter Theory, Fourth, edition Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA (2002)
Wu, F.Y., Song, Y.C., Tian, T., Yang, K., Duan, R., Sheng, X.: A mixed norm constraint IPNLMS algorithm for sparse channel estimation. Signal, Image Video Proces. 16(2), 457–464 (2022)
Liang, T., Li, Y., Xue, W., Li, Y., Jiang, T.: Performance and analysis of recursive constrained least Lncosh algorithm under impulsive noises. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 68(6), 2217–2221 (2020)
Zheng, Z., Liu, Z., Zhao, J.: Bias-compensated sparsity-aware NLMM algorithms for robust adaptive echo cancellation. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I Regul. Pap. 67(7), 2383–2396 (2020)
Song, I., Park, P., Newcomb, R.W.: A normalized least mean squares algorithm with a step-size scaler against impulsive measurement noise. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II, Exp. Briefs 60(7), 442–445 (2013)
Zeng, J., Lin, Y., Shi, L.: A normalized least mean squares algorithm based on the arctangent cost function robust against impulsive interference. Circ. Syst. Signal Process. 35, 3040–3047 (2015)
Guo, P., Yu, Y., Yang, T., He, H., de Lamare, R.C.: Robust NLMS algorithms with combined step-size against impulsive noises. Digital Signal Process. 128, 103609 (2022)
Bakri, K.J., Kuhn, E.V., Matsuo, M.V., Seara, R.: On the behavior of a combination of adaptive filters operating with the NLMS algorithm in a nonstationary environment. Signal Process. 196, 108465 (2022)
Maurya, A.K., Agrawal, P., Dixit, S.: Modified model and algorithm of lms adaptive filter for noise cancellation. Circ. Syst. Signal Process. 38, 2351–2368 (2019)
Li, Y.P., Lee, T.S., Wu, B.F.: A variable step-size sign algorithm for channel estimation. Signal Process. 102, 304–312 (2014)
Yu, Y., Zhao, H., Chen, B.: Steady-state mean-square-deviation analysis of the sign subband adaptive filter algorithm. Signal Process. 120, 36–42 (2016)
Chen, B., Xing, L., Zhao, H., Zheng, N., Principe, J.C.: Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(13), 3376–3387 (2016)
Huang, F., Zhang, J., Zhang, S.: Adaptive filtering under a variable kernel width maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II, Exp. Briefs 64(10), 1247–1251 (2017)
Shao, T., Zheng, Y.R., Benesty, J.: An affine projection sign algorithm robust against impulsive interferences. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(4), 327–330 (2010)
Wu, F.Y., Yang, K., Duan, R., Tian, T.: Compressive sampling and reconstruction of acoustic signal in underwater wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sens. J. 18(14), 5876–5884 (2018)
Gu, Y., Jin, J., Mei, S.: \(\ell _0\) norm constraint LMS algorithm for sparse system identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 16(9), 774–777 (2009)
Tian, T., Wu, F.Y., Yang, K.D.: Block-sparsity regularized maximum correntropy criterion for structured-sparse system identification. J. Frank. Inst. 357(17), 12960–12985 (2020)
Wu, F.Y., Yang, K., Sheng, X.: A blocked MCC estimator for group sparse system identification. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 115, 153033–153038 (2020)
Huang, F., Zhang, J., Zhang, S.: NLMS algorithm based on a variable parameter cost function robust against impulsive interferences. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II, Exp. Briefs 64(5), 600–604 (2017)
Zou, Y., Chan, S.C., Ng, T.S.: A recursive least M-estimate (RLM) adaptive filter for robust filtering in impulse noise. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 7(11), 324–326 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 62171369, 61701405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, FY., Song, YC. Optimal design of NLMS algorithm with a variable scaler against impulsive interference. SIViP 17, 2705–2712 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02487-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02487-1