Abstract
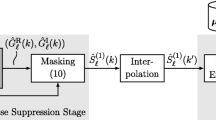
Transient noise has a high short-time energy, a high degree of randomness, a wide frequency-domain distribution, and only causes local signal pollution. Traditional denoising methods usually establish the assumption of a certain kind of relationship between speech and noise, and this assumption does not necessarily match real-life scenarios. Therefore, using traditional denoising methods does not effectively suppress transient noise. For the above reasons, this paper proposes a new denoising scheme. First, based on the conventional optimally-modified log-spectral amplitude (OM-LSA) estimation algorithm, the minima controlled recursive averaging algorithm is replaced by the improved mean recurrence time algorithm, and the transient noise spectrum is estimated. Second, transient noise segments are determined using thresholds and fed into a deep complex-valued U-Net (DCU-Net) network for speech enhancement. Third, insert the enhanced results into the original sequence to reconstruct the denoised speech signal. Finally, this paper uses the Voice Bank corpus speech and homemade noise datasets to perform experimental tests. The test results show that the segmented signal-to-noise ratio, speech quality perception, and short-term target intelligibility of the proposed method in 0 dB, − 5 dB, and − 10 dB environments have improved than the traditional OM-LSA algorithm. When the signal-to-noise ratio is − 10 dB, the segmented signal-to-noise ratio is improved by 9.8%. The test results show that this paper's proposed method can solidly suppress transient noise at low signal-to-noise ratios and simultaneously improve speech quality.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All the data included in this study are available upon request by contacting the corresponding author.
Not applicable.
References
Cao, K., Wang, M.: Transient noise suppression algorithm in speech system. AIP Conf. Proc. 1864(1), 20006–20006 (2017)
Vaseghi, S.V.: Advanced Digital Signal Processing and Noise Reduction. Wiley, New York (2000)
Kammi, S., Mollaei, M.: A novel regularization framework for transient noise reduction. Appl. Acoust. 129, 135–143 (2018)
Fennick, J.H.: A report on some characteristics of impulse noise in telephone communication. IEEE Trans. Commun. 83(75), 700–705 (1964)
Boll, S.F.: A spectral subtraction algorithm for suppression of acoustic noise in speech. In: ICASSP'79. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Process, pp. 200–203 (1979)
Richards, D.S.: VLSI median filters. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. ASSP 38(1), 145–153 (1990)
Choi, M.S., Kang, H.G.: Transient noise reduction in speech signal with a modified long-term predictor. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Processing. 2011(1), 1–9 (2011)
Wang, J., Zhang, X., Zhu, J., Wu, Y.: Impulsive noise suppression based on time-frequency spectrogram. J. Vib. Shock. 29(2), 149–153 (2010)
Tanwar, P., Somkuwar, A.: Hard component detection of transient noise and its removal using empirical mode decomposition and wavelet-based predictive filter. IET Signal Process. 12(7), 907–916 (2018)
Nongpiur, R.C.: Impulse noise removal in speech using wavelets. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Process, pp. 1593–1596 (2008)
He, Z., Zhu, Z., Zhang, M.: Impulsive noise removal based on noise energy distribution in wavelet packet domain. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 32(9), 2071–2078 (2011)
Ram, R., Mohapatra, S.K., Nayak, P.K., Mohanty, M.N.: Single Channel Speech Enhancement Using Fractional Wavelet Transform Advances in Intelligent Computing and Communication, pp. 629–643. Springer, Singapore (2021)
Hirszhorn, A., Dov, D., Talmon, R., Cohen, I.: Transient interference suppression in speech signals based on the OM-LSA algorithm. International Workshop on Acoustic Signal Enhancement, VDE, pp. 1–4 (2012)
Talmon, R., Cohen, I., Gannot, S.: Clustering and suppression of transient noise in speech signals using diffusion maps. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 5084–5087 (2011)
Ullah, R., Islam, M.S., Ye, Z., Asif, M.: Semi-supervised transient noise suppression using omlsa and snmf algorithms. Appl. Acoust. 170, 107533 (2020)
Hao, Y., Cheng, S., Chen, G., Chen, Y., Ruan, L.: A neural network based noise suppression method for transient noise control with low-complexity computation. INTER-NOISE NOISE-CON Congr. Conf. Proc. 263(1), 5902–5909 (2021)
Choi, H.S., Kim, J.H., Huh, J., Kim, A., Ha, J.W., Lee, K.: Phase-aware speech enhancement with deep complex u-net. In: International Conference on Learning Representations (2018)
Choi, H.S., Heo, H., Lee, J.H., Lee, K.: Phase-aware single-stage speech denoising and dereverberation with u-net. arXiv:2006.00687, (2020)
Rajamani, K.T., Rani, P., Siebert, H., ElagiriRamalingam, R., Heinrich, M.P.: Attention-augmented U-Net (AA-U-Net) for semantic segmentation. Signal Image Video Process. pp. 1–9 (2022)
Liang, R., Xie, Y., Cheng, J., Tang, G., Sun, S.: Real-time speech enhancement algorithm for transient noise suppression. Multimed. Tools Appl. 80(3), 3681–3702 (2021)
Williamson, D.S., Wang, Y., Wang, D.L.: Complex ratio masking for monaural speech separation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 24(3), 483–492 (2016)
Chen, R., Xue, J., Chen, D.: Transient noise suppression algorithm based on deep learning. Commun. Electroacoust. 44(06), 107–110 (2020)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, Cham, pp. 234–241 (2015)
Wang, M., Lin, F., Chen, K., Luo, W., Qiang, S.: TEM-NLnet: a deep denoising network for transient electromagnetic signal with noise learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–14 (2022)
Venkataramani, S., Casebeer, J., Smaragdis, P.: End-to-end Source Separation with Adaptive Front-Ends. (2017).
Funding
This research was received by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. LH2020F033), the National Natural Science Youth Foundation of China (No.11804068), and Research Project of the Heilongjiang Province Health Commission(20221111001069).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL contributed to the conception of the study and contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; LZ and SZ made important contributions in making adjustments to the structure, revising the paper, English editing, and revisions of this manuscript; ZS performed the experiment, the data analyses, and wrote the original manuscript; HC made significant contributions to the structure, English modification, and data analysis of the paper; MZ carried on the data analysis and did the major revision of the paper; and XG and CH made important contributions in making adjustments to the proofread English.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, C., Zhao, S., Zhang, L. et al. DCU-Net transient noise suppression based on joint spectrum estimation. SIViP 17, 3265–3273 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02541-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02541-y