Abstract
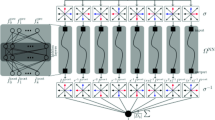
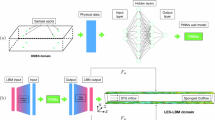
Compared with traditional computational fluid dynamics methods, the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) has the advantages of simple program structure, adaptability to complex boundaries, and easy parallel computation. However, since LBM is an explicit algorithm, there are many iterations in the computation process, which leads to an increase in computation time. In this paper, we improve LBM based on deep learning by combining a convolutional neural network (CNN) and a gated recurrent unit neural network (GRU). Based on previous test data, the CNN module extracts spatial features during the computation, while the GRU processes the corresponding temporal features. Compared with the conventional LBM, this method can significantly reduce the computation time and improve the computational efficiency with guaranteed low Reynolds numbers of 1000 and 2000. At the high Reynolds number of 4000, the prediction error of the proposed method is increasing but still has a better performance. In order to verify the effectiveness and accuracy of the proposed algorithm, an eddying model widely used in the computational fluid field is developed. The proposed method not only has impressive results but also deals with non-stationary processes and steady-state problems.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available since the data still have value for continued research but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Lallemand, P., Luo, L.-S., Krafczyk, M., Yong, W.-A.: The lattice Boltzmann method for nearly incompressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 431, 109713 (2021)
Aidun, C.K., Clausen, J.R.: Lattice-Boltzmann method for complex flows. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 42, 439–472 (2010)
Samanta, R., Chattopadhyay, H., Guha, C.: A review on the application of lattice Boltzmann method for melting and solidification problems. Comput. Mater. Sci. 206, 111288 (2022)
Lobovský, L., Vimmr, J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and finite volume modelling of incompressible fluid flow. Math. Comput. Simul. 76(1), 124–131 (2007)
Barad, M., Kocheemoolayil, J., Kiris, C.: Lattice Boltzmann and Navier-stokes cartesian cfd approaches for airframe noise predictions (2017)
Haussmann, M., Ries, F., Jeppener-Haltenhoff, J.B., Li, Y., Schmidt, M., Welch, C., Illmann, L., Böhm, B., Nirschl, H., Krause, M.J., Sadiki, A.: Evaluation of a near-wall-modeled large eddy lattice Boltzmann method for the analysis of complex flows relevant to IC engines. Computation 8, 43 (2020)
Krause, M.J., Kummerländer, A., Avis, S.J., Kusumaatmaja, H., Dapelo, D., Klemens, F., Gaedtke, M., Hafen, N., Mink, A., Trunk, R., Marquardt, J.E., Maier, M.-L., Haussmann, M., Simonis, S.: Openlb-open source lattice Boltzmann code. Comput. Math. Appl. 81, 258–288 (2021)
Lohner, R.: Towards overcoming the LES crisis. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 33, 1–11 (2019)
Hou, S., Sterling, J.D., Chen, S., Doolen, G.D.: A lattice Boltzmann subgrid model for high reynolds number flows. arXiv: Cellular Automata and Lattice Gases (1994)
Dong, Y.-H., Sagaut, P., Marié, S.: Inertial consistent subgrid model for large-eddy simulation based on the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Fluids 20, 035104 (2008)
Li, C., Zhao, Y., Ai, D., Wang, Q., Peng, Z., Li, Y.: Multi-component LBM-LES model of the air and methane flow in tunnels and its validation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 553, 124279 (2020)
Premnath, K.N., Pattison, M.J., Banerjee, S.: Dynamic subgrid scale modeling of turbulent flows using lattice-Boltzmann method. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 388(13), 2640–2658 (2009)
Weickert, M., Teike, G., Schmidt, O., Sommerfeld, M.: Investigation of the les wale turbulence model within the lattice Boltzmann framework. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(7), 2200–2214 (2010)
Malaspinas, O., Sagaut, P.: Consistent subgrid scale modelling for lattice Boltzmann methods. J. Fluid Mech. 700, 514 (2012)
Sagaut, P.: Toward advanced subgrid models for lattice-Boltzmann-based large-eddy simulation: theoretical formulations. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(7), 2194–2199 (2010)
Malaspinas, O., Sagaut, P.: Advanced large-eddy simulation for lattice Boltzmann methods: the approximate deconvolution model. Phys. Fluids 23, 105103 (2011)
Marié, S., Gloerfelt, X.: Adaptive filtering for the lattice Boltzmann method. J. Comput. Phys. 333, 212–226 (2017)
Nathen, P., Haussmann, M., Krause, M., Adams, N.: Adaptive filtering for the simulation of turbulent flows with lattice Boltzmann methods. Comput. Fluids 172, 510–523 (2018)
Jacob, J., Malaspinas, O., Sagaut, P.: A new hybrid recursive regularised Bhatnagar-Gross-Krook collision model for lattice Boltzmann method-based large eddy simulation. J. Turbul. 19, 1–26 (2018)
Pruett, C.: Temporal large-eddy simulation: theory and implementation. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 22, 275–304 (2008)
Zhang, D., Luo, Y., Zhao, Y., Li, Y., Mei, N., Yuan, H.: LBM-PFM simulation of directional frozen crystallisation of seawater in the presence of a single bubble. Desalination 542, 116065 (2022)
Oberle, D., Pruett, C., Jenny, P.: Temporal large-eddy simulation based on direct deconvolution. Phys. Fluids 32, 065112 (2020)
Yang, D., Karimi, H.R., Sun, K.: Residual wide-kernel deep convolutional auto-encoder for intelligent rotating machinery fault diagnosis with limited samples. Neural Netw. 141, 133–144 (2021)
D’Humières, D., Ginzburg, I., Krafczyk, M., Lallemand, P., Luo, L.-S.: Multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann models in three dimensions. Philos. Trans. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 360, 437–51 (2002)
Dey, S., Mahato, R., Ali, S.: Linear stability of sand waves sheared by a turbulent flow. Environ. Fluid Mech. 22, 429 (2022)
Haussmann, M., Simonis, S., Nirschl, H., Krause, M.: Direct numerical simulation of decaying homogeneous isotropic turbulence - numerical experiments on stability, consistency and accuracy of distinct lattice Boltzmann methods. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 30, 1950074 (2019)
Geurts, B.: A framework for predicting accuracy limitations in large-eddy simulation. Phys. Fluids 14, L41 (2002)
Meng, F., Karimi, H.: Emerging methodologies in stability and optimization problems of learning-based nonlinear model predictive control: A survey. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 50, 4146 (2022)
Chen, X., Yang, G., Yao, Q., Nie, Z., Jiang, Z.: A compressed lattice Boltzmann method based on ConvLSTM and ResNet. Comput. Math. Appl. 97, 162–174 (2021)
Lei, Y., Karimi, H.R., Chen, X.: A novel self-supervised deep LSTM network for industrial temperature prediction in aluminum processes application. Neurocomputing 502, 177–185 (2022)
Wu, C., Kinnas, S.A.: Parallel implementation of a viscous vorticity equation (visve) method in 3-d laminar flow. J. Comput. Phys. 426, 109912 (2021)
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U2006228, 52171313).
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Meng, F. & Lu, X. Improvement of lattice Boltzmann methods based on gated recurrent unit neural network. SIViP 17, 3283–3291 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02543-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02543-w