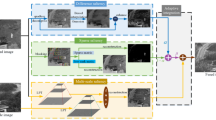
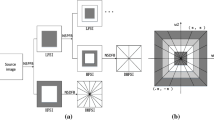
Abstract
Among existing region-based infrared (IR) and visible (VIS) fusion methods, source images are segmented into thermal targets and backgrounds. Background areas typically have a small grayscale range and are less contrasty, which makes nontarget objects difficult to discern, reducing visual effects of the fused image. To solve this problem, an environment enhancement method based on saliency measure for IR-VIS fusion is proposed. This paper analyses the relationship between gray level of IR data and semantic importance information. The Fuzzy C-means algorithm is used to divide IR images into different ranks of semantic importance, which can provide the most accurate semantic representation of an IR image. Moreover, to maintain the thermal targets highlighted, an effective enhancement strategy termed saliency assignment, is proposed so that the low-level features are arranged to provide viewers with directed attention. Finally, a weighted averaging fusion algorithm based on the importance ranks, to obtain fused images. The experiment is performed on common datasets, which consists of subjective and objective tests, and proves the validity of the proposed algorithm.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used in this study are publicly available and can be found online.
References
Ma, J., Ma, Y., Li, C.: Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: a survey. Inf. Fusion 45, 153–178 (2019)
Singh, S., Mittal, N., Singh, H.: Review of various image fusion algorithms and image fusion performance metric. Arch. Comput, Methods Eng. 28(5), 3645–3659 (2021)
Li, S., Yang, B., Jianwen, H.: Performance comparison of different multi-resolution transforms for image fusion. Inf. Fusion 12(2), 74–84 (2011)
Jin, H., Wang, Y.: A fusion method for visible and infrared images based on contrast pyramid with teaching learning based optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 64, 134–142 (2014)
Jin, X., Jiang, Q., Yao, S., Zhou, D., Nie, R., Lee, S.-J., He, K.: Infrared and visual image fusion method based on discrete cosine transform and local spatial frequency in discrete stationary wavelet transform domain. Infrared Phys. Technol. 88, 1–12 (2018)
Ma, T., Ma, J., Fang, B., Fangyu, H., Quan, S., Huajun, D.: Multi-scale decomposition based fusion of infrared and visible image via total variation and saliency analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 92, 154–162 (2018)
Singh, S., Mittal, N., Singh, H.: A feature level image fusion for IR and visible image using MNMRA based segmentation. Neural Comput. Appl. 34(10), 8137–8154 (2022)
Ma, J., Wei, Yu., Liang, P., Li, C., Jiang, J.: Fusiongan: a generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 48, 11–26 (2019)
Zhang, H., Le, Z., Shao, Z., Han, X., Ma, J.: MFF-GAN: an unsupervised generative adversarial network with adaptive and gradient joint constraints for multi-focus image fusion. Inf. Fusion 66, 40–53 (2021)
Tang, L.L., Liu, G., Xiao, G., Bavirisetti, D.P., Zhang, X.B.: Infrared and visible image fusion based on guided hybrid model and generative adversarial network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 120, 103914 (2022)
Hou, J., Zhang, D., Wei, W., Ma, J., Zhou, H.: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion based on semantic segmentation. Entropy 23(3), 376 (2021)
Tang, L., Yuan, J., Ma, J.: Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: a semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 82, 28–42 (2022)
Pozzer, S., Rezazadeh Azar, E., Dalla Rosa, F., Chamberlain Pravia, Z.M.: Semantic segmentation of defects in infrared thermographic images of highly damaged concrete structures. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 35(1), 04020131 (2021)
Hou, Q., Wang, Z., Tan, F., Zhao, Y., Zheng, H., Zhang, W.: RISTDNET: robust infrared small target detection network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1–5 (2021)
Müller, D., Ehlen, A., Valeske, B.: Convolutional neural networks for semantic segmentation as a tool for multiclass face analysis in thermal infrared. J. Nondestr. Eval. 40(1), 1–10 (2021)
Chen, X., Fang, Y., Yang, M., Nie, F., Zhao, Z., Huang, J.Z.: Purtreeclust: a clustering algorithm for customer segmentation from massive customer transaction data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 30(3), 559–572 (2017)
MacQueen, J.B.: Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. Berkeley Sympos. Math. Stat. Probab. 1, 281–297 (1967)
Krinidis, S., Chatzis, V.: A robust fuzzy local information c-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(5), 1328–1337 (2010)
Yang, F., Liu, Z., Bai, X., Zhang, Y.: An improved intuitionistic fuzzy c-means for ship segmentation in infrared images. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30, 332–344 (2020)
Cheng, M.-M., Mitra, N.J., Huang, X., Torr, P.H.S., Shi-Min, H.: Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(3), 569–582 (2014)
Achanta, R., Estrada, F., Wils, P., Süsstrunk, S.: Salient region detection and segmentation. In: International Conference on Computer Vision Systems, pp. 66–75. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Zhai, Y., Shah, M.: Visual attention detection in video sequences using spatiotemporal cues. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 815–824 (2006)
Cheng, H.-D., Jiang, X.-H., Sun, Y., Wang, J.: Color image segmentation: advances and prospects. Pattern Recogn. 34(12), 2259–2281 (2001)
Judd, T., Ehinger, K., Durand, F., Torralba, A.: Learning to predict where humans look. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2106–2113. IEEE (2009)
Bianco, S., Buzzelli, M., Ciocca, G., Schettini, R.: Neural architecture search for image saliency fusion. Inf. Fusion 57, 89–101 (2020)
Su, S.L., Durand, F., Agrawala, M.: An inverted saliency model for display enhancement. In: Proceedings of 2004 MIT Student Oxygen Workshop, Ashland, MA. Citeseer (2004)
Wong, L.-K., Low, K.-L.: Saliency retargeting: An approach to enhance image aesthetics. In: 2011 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 73–80. IEEE (2011)
Mejjati, Y.A., Gomez, C.F., Kim, K.I., Shechtman, E., Bylinskii, Z.: Look here! a parametric learning based approach to redirect visual attention. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 343–361. Springer, Berlin (2020)
Pizer, S.M., Amburn, E.P., Austin, J.D., Cromartie, R., Geselowitz, A., Greer, T., Haar Romeny, B., Zimmerman, J.B., Zuiderveld, K.: Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput. Vision Graph. Image Process. 39(3), 355–368 (1987)
Li, S., Jin, W., Li, L., Li, Y.: An improved contrast enhancement algorithm for infrared images based on adaptive double plateaus histogram equalization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 90, 164–174 (2018)
Paul, A., Sutradhar, T., Bhattacharya, P., Maity, S.P.: Infrared images enhancement using fuzzy dissimilarity histogram equalization. Optik 247, 167887 (2021)
Wan, M., Guohua, G., Qian, W., Ren, K., Chen, Q., Maldague, X.: Particle swarm optimization-based local entropy weighted histogram equalization for infrared image enhancement. Infrared Phys. Technol. 91, 164–181 (2018)
Acharya, U.K., Kumar, S.: Genetic algorithm based adaptive histogram equalization (GAAHE) technique for medical image enhancement. Optik 230, 166273 (2021)
Srinivasan, S., Balram, N.: Adaptive contrast enhancement using local region stretching. In: Proceedings of the 9th Asian symposium on information display, pp. 152–155. Citeseer (2006)
Bezdek, J.C., Ehrlich, R., Full, W.: FCM: the fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 10(2–3), 191–203 (1984)
Bavirisetti, D.P., Xiao, G., Liu, G.: Multi-sensor image fusion based on fourth order partial differential equations. In: International Conference on Information Fusion 7 (2017)
Li, H., Xiao-Jun, W., Kittler, J.: MDLATLRR: a novel decomposition method for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 4733–4746 (2020)
Zhang, Yu., Zhang, L., Bai, X., Zhang, L.: Infrared and visual image fusion through infrared feature extraction and visual information preservation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 83, 227–237 (2017)
Li, H., Xiao-Jun, W., Kittler, J.: RFN-nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion 73, 72–86 (2021)
Li, H., Wu, X.-J.: Densefuse: a fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(5), 2614–2623 (2018)
Ram Prabhakar, K., Sai Srikar, V., Venkatesh Babu, R.: Deepfuse: a deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4714–4722 (2017)
Ma, J., Han, X., Jiang, J., Mei, X., Zhang, X.-P.: DDCGAN: a dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 4980–4995 (2020)
Han, X., Ma, J., Jiang, J., Guo, X., Ling, H.: U2FUSION: a unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(1), 502–518 (2020)
Roberts, W., van Aardt, J., Ahmed, F.: Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2(1), 1–28 (2008)
Hossnym, M., Nahavandi, S., Creighton, D., Bhatti, A.: image fusion performance metric based on mutual information and entropy driven quadtree decomposition. Electron. Lett. 46, 1266–1268 (2010)
Yu, H., Cai, Y., Cao, Y.: Xu, X: a new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity. Inf. Fusion 14, 127–135 (2013)
Cui, G., Feng, H., Xu, Z., Li, Q., Chen, Y.: Detail preserved fusion of visible and infrared images using regional saliency extraction and multi-scale image decomposition. Opt. Commun. 341, 199–209 (2015)
Aslantas, V., Bendes, E.: A new image quality metric for image fusion: the sum of the correlations of differences. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 69, 1890–1896 (2015)
Xydeas, C., Petrovic, V.: Objective evaluation of signal-level image fusion performance. Opt. Eng. 44(8), 141–155 (2005)
Zhao, J., Chen, Y., Feng, H., Zhihai, X., Li, Q.: Infrared image enhancement through saliency feature analysis based on multi-scale decomposition. Infrared Phys. Technol. 62, 86–93 (2014)
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (62203224), Capacity Building Plan for some Non-military Universities and Colleges of Shanghai Scientific Committee (22010501300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW performed experiments and wrote the main manuscript text. XZ and GL guided the experiments. HT drew the figures. Everyone participated in reviewing the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Declaration on ethical approval is not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Liu, G., Zhang, X. et al. Environment enhanced fusion of infrared and visible images based on saliency assignment. SIViP 18, 1443–1453 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02860-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02860-0