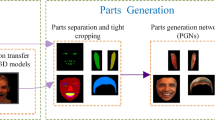
Abstract
Face frontalization is the process of synthesizing realistic and identity-preserving frontal views from face images in different poses and is an essential preprocessing step for face recognition. However, for side faces wearing glasses, the previous frontalization algorithms will distort the glasses after face reconstruction, affecting the image’s perceived quality and subsequent face recognition. Therefore, this paper first removes glasses, a factor that will cause distortion in face frontalization, and designs the perceptual and pixel-level face image quality assessment modules to improve the face frontalization performance. On the one hand, by constructing a saliency gradient, the pixel-level quality of face images is calculated and guides the network to generate frontal face images that are more conducive to face recognition. On the other hand, in order to obtain the perceptual quality for face image, the natural face images are used to construct a high-quality feature space, and the Bhattacharyya distance between it and the generated image is calculated to ensure the perceptual quality of the generated frontal image. Finally, the GAN network is used to generate a frontal face image that can consider both recognizability and perceptual quality. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations on controlled and in-the-wild databases show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Babnik, Ž., Damer, N., Štruc, V.: Optimization-based improvement of face image quality assessment techniques. In: 2023 11th International Workshop on Biometrics and Forensics (IWBF), IEEE, pp 1–6 (2023)
Bhattacharya, S., Kyal, C., Routray, A.: Simplified face quality assessment (sfqa). pp 108–114 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2021.03.037, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167865521001331
Boutros, F., Fang, M., Klemt, M., et al.: CR-FIQA: face image quality assessment by learning sample relative classifiability. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 5836–5845 (2023). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2112.06592
Cao, J., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., et al.: Learning a high fidelity pose invariant model for high-resolution face frontalization. In: Advances In Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 1–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1806.08472
Chen, K., Yi, T., Lv, Q.: Lightqnet: Lightweight deep face quality assessment for risk-controlled face recognition. IEEE 28, 1878–1882 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2021.3109781
Chen, Z., Yang, H.: L2rt-fiqa: Face image quality assessment via learning-to-rank transformer. In: Zhai, G., Zhou, J., Yang, H., et al. (eds.) Digital Multimedia Communications, pp. 270–285. Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore (2023)
Duan, X., Liu, H., Liang, J.: DIQA-FF: Dual image quality assessment for face frontalization. In: Multimedia Tools and Applications. Springer, pp 1–20 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15084-8
Guo, J., Zhu, X., Lei, Z., et al.: Face synthesis for eyeglass-robust face recognition (2018)
Hassner, T., Harel, S., Paz, E., et al.: Effective face frontalization in unconstrained images. IEEE (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299058
He, H., Liang, J., Hou, Z., et al.: Multi-pose face reconstruction and gabor-based dictionary learning for face recognition. In: Applied Intelligence. Springer, pp 1–15 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-04336-z
He, H., Liang, J., Hou, Z., et al.: Realistic feature perception for face frontalization with dual-mode face transformation. Elsevier, p 121344 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121344
Hernandez-Ortega, J., Galbally, J., Fierrez, J., et al.: Faceqnet: Quality assessment for face recognition based on deep learning. IEEE, pp 1–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.1904.01740
Hernandez-Ortega, J., Fierrez, J., Serna, I., et al.: FaceQgen: Semi-supervised deep learning for face image quality assessment. In: 2021 16th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2021), IEEE, pp 1–8 (2021). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2201.00770
Hu, Y., Wu, X., Yu, B., et al.: Pose-guided photorealistic face rotation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 8398–8406 (2018)
Huang, G.B., Mattar, M., Berg, T., et al.: Labeled faces in the wild: A database forstudying face recognition in unconstrained environments. In: Workshop on faces in’Real-Life’Images: detection, alignment, and recognition, pp 1–14 (2008)
Huang, R., Zhang, S., Li, T., et al.: Beyond face rotation: Global and local perception gan for photorealistic and identity preserving frontal view synthesis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference On Computer Vision, pp 2439–2448 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.267
Huang, Y.S., Alhlffee, M.H.: Improving face recognition by integrating decision forest into gan, vol. 37, p. 2175108. Taylor & Francis (2023). https://doi.org/10.1080/08839514
Ju, Y.J., Lee, G.H., Hong, J.H., et al.: Complete Face Recovery Gan: Unsupervised joint face rotation and de-occlusion from a single-view image. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp 3711–3721 (2022). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7416667
Karras, T., Laine, S., Aila, T.: A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1812.04948
Kavitha, M., RajivKannan, A.: Hybrid convolutional neural network and long short-term memory approach for facial expression recognition (2023)
Kwak, J.G., Li, Y., Yoon, D., et al.: Generate and edit your own character in a canonical view. In: arXiv preprint, pp 1–5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2205.02974
Li, S., Deng, W.: Reliable crowdsourcing and deep locality-preserving learning for unconstrained facial expression recognition. In: IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol 28. IEEE, pp 356–370 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2868382
Li, X., Zhang, S., Hu, J., et al.: image-to-image translation via hierarchical style disentanglement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 8639–8648 (2021). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2103.01456
Lin, X., Zheng, H., Zhao, P., et al.: Sd-hrnet: Slimming and distilling high-resolution network for efficient face alignment. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031532 (2023). https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/23/3/1532
Liu, Z., Luo, P., Wang, X., et al.: Deep learning face attributes in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference On Computer Vision, pp 3730–3738 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.425
Lyu, J., Wang, Z., Xu, F.: Portrait eyeglasses and shadow removal by leveraging 3d synthetic data. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 3429–3439 (2022). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.10474
Ma, N., Zhang, X., Zheng, H.T., et al.: Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp 116–131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1807.11164
Maze, B., Adams, J.C., Duncan, J.A., et al.: Iarpa janus benchmark - c: Face dataset and protocol. pp 158–165 (2018). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:28375094
Meng, Q., Zhao, S., Huang, Z., et al.: Magface: A universal representation for face recognition and quality assessment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 14,225–14,234 (2021). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2103.06627
Ou, F.Z., Chen, X., Zhang, R., et al.: SDD-FIQA: unsupervised face image quality assessment with similarity distribution distance. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 7670–7679 (2021). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2103.05977
Schlett, T., Rathgeb, C., Henniger, O., et al.: Face image quality assessment: A literature survey, vol. 54, pp. 1–49. ACM New York, NY (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3507901
Schroff, F., Kalenichenko, D., Philbin, J.: Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 815–823 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298682
Senguptam, S., Chenm, J.C., Castillom, C., et al.: Frontal to profile face verification in the wild. In: 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp 1–9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV.2016.7477558
Song, L., Gong, D., Li, Z., et al.: Occlusion robust face recognition based on mask learning with pairwise differential siamese network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 773–782 (2019). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1908.06290
Terhorst, P., Kolf, J.N., Damer, N., et al.: SER-FIQ: Unsupervised estimation of face image quality based on stochastic embedding robustness. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 5651–5660 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00569
Terhörst, P., Huber, M., Damer, N., et al.: Pixel-level face image quality assessment for explainable face recognition. In: IEEE Transactions on Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science. IEEE, pp 1–18 (2023). https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2110.11001
Tian, Y., Peng, X., Zhao, L., et al.: CR-GAN: learning complete representations for multi-view generation. In: arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.11191, pp 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1806.11191
Torbunov, D., Huang, Y., Yu, H., et al.: Uvcgan: Unet vision transformer cycle-consistent gan for unpaired image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp 702–712 (2023). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.02557
Tran, L., Yin, X., Liu, X.: Disentangled representation learning gan for pose-invariant face recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 1415–1424 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.141
Wang, H., Yang, X.: Efficient practices for profile-to-frontal face synthesis and recognition. In: ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), IEEE, pp 1–5 (2023)
Wang, H., Chi, J., Wu, C., et al.: Cross-view information interaction and feedback network for face hallucination. In: booktitle of Visual Communication and Image Representation. Elsevier, pp 103,758–103,768 (2023)
Wei, Y., Liu, M., Wang, H., et al.: Learning flow-based feature warping for face frontalization with illumination inconsistent supervision. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Springer, pp 558–574 (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2008.06843
Yin, X., Yu, X., Sohn, K., et al.: Towards large-pose face frontalization in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference On Computer Vision, pp 3990–3999 (2017). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1704.06244
Zhang, L., Zhang, L., Bovik, A.C.: A feature-enriched completely blind image uality evaluator. In: IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol 24. IEEE, pp 2579–2591 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2426416
Zhang, Z., Chen, X., Wang, B., et al.: Face frontalization using an appearance-flow-based convolutional neural network. In: IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, pp 2187–2199 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2883554
Zhao, J., Cheng, Y., Xu, Y., et al.: Towards pose invariant face recognition in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 2207–2216 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00235
Zhou, H., Liu, J., Liu, Z., et al.: Rotate-and-render: Unsupervised photorealistic face rotation from single-view images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 5911–5920 (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2003.08124
Zhu, X., Lei, Z., Yan, J., et al.: High-fidelity pose and expression normalization for face recognition in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 787–796 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298679
Funding
The research leading to these results received funding from the Basic Science (Natural Science) Research Projects of Universities in Jiangsu Province under Grant Agreement No[22KJB520011].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by XD. HL and JL provided supervision. The first draft of the manuscript was written by XD, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acquisition of the financial support for the project leading to this publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Duan, X. & Liang, J. FF-PPQA: Face frontalization without glasses based on perceptual quality and pixel-level quality assessment. SIViP 18, 2879–2893 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02957-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-023-02957-6