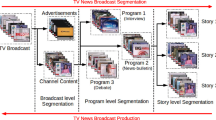
Abstract
With the continuous development of the social economy, the ways people obtain news information are becoming increasingly diversified, but with that comes too much data. The research on Extracting useful information from too much data is extremely effective. Given these needs and deficiencies, this paper introduces a conditional random field knowledge recognition algorithm, designing a Segmentation analysis model for audience news with the segmentation technology of key frames and shots by sorting the business logic of automatic news Segmentation, realizing the analysis of the news video picture., and then analyze the news Segmentation to ensure that the production and dissemination of news programs are intelligent and smart. The simulation experiment results show that the conditional random field knowledge recognition algorithm is effective and can effectively support the analysis of automatic news Segmentation.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Osti, F., Ceruti, A., Liverani, A., Caligiana, G.: Semi-automatic design for disassembly strategy planning: an augmented reality approach. Proc. Manuf. 11, 1481–1488 (2017)
Vongbunyong, S., Kara, S., Pagnucco, M.: Learning and revision in cognitive robotics disassembly automation. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 34, 79–94 (2015)
Marin, A., Denimal, E., Bertheau, L., Guyot, S., Journaux, L., Molin, P.: Automatic counting of intra-cellular Ribonucleo-protein aggregates in saccharomyces Cerevisiae using a textural approach. Microsc. Microanal.. Microanal. 25(1), 164–179 (2019)
Tucker, P.S., Scanlan, A.T., Dalbo, V.J.: Chronic kidney disease influences multiple systems: describing the relationship between oxidative stress, inflammation, kidney damage, and concomitant disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev 2015 (2015)
Hefler, M.: Worldwide News and Comment. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (2017)
Cahen, D., Crabtree, G., Yalisove, S.M.: Energy quarterly: news and analysis on materials solutions to energy challenges. MRS Bull. 36(9), 677 (2011)
Whittingham, S.: Energy quarterly news and analysis on materials solutions to energy challenge. In: MRS Bulletin, vol. 42, no. 6. Cambridge Univ Press 32 Avenue of the Americas, New York, pp. 10013–2473, USA, p. 413 (2017)
Bettacchioli, E., Nafai, S., Renaudineau, Y.: News and meta-analysis regarding anti-Beta 2 glycoprotein I antibodies and their determination. Clin. Immunol. 205, 106–115 (2019)
Li, X., Xie, H., Song, Y., Zhu, S., Li, Q., Wang, F.L.: Does summarization help stock prediction? A news impact analysis. IEEE Intell. Syst. 30(3), 26–34 (2015)
Zhang, C., Wu, X., Shyu, M.-L., Peng, Q.: Integration of visual temporal information and textual distribution information for news web video event mining. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 46(1), 124–135 (2015)
Li, J., Ma, S.: Survival Analysis in Medicine and Genetics. CRC Press (2013)
Wasfy, J.H., Zigler, C.M., Choirat, C., Wang, Y., Dominici, F., Yeh, R.W.: Readmission rates after passage of the hospital readmissions reduction program: a pre–post analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 166(5), 324–331 (2017)
Yablonovitch, E.: News and analysis on materials solutions to energy challenges: www. mrs. org/energy-quarterly. MRS Bull. 40(7), 551–553 (2015)
Patton, E.W., Moniz, M.H., Hughes, L.S., Buis, L., Howell, J.: National network television news coverage of contraception: a content analysis. Contraception 95(1), 98–104 (2017)
Lam, T.C., Kwan, E., Luo, H., Yip, P.S.: Emergency admissions and bad news disclosure as precipitators of suicide: a territory-wide cohort analysis of 458 oncology patients who completed suicides. Ann. Oncol.Oncol. 30, v661 (2019)
Lord, J., et al.: Prenatal exome sequencing analysis in fetal structural anomalies detected by ultrasonography (PAGE): a cohort study. The Lancet 393(10173), 747–757 (2019)
Abraham, A., Zhang, A.J., Ahn, R., Woodbridge, A., Korenstein, D., Keyhani, S.: Media content analysis of marijuana’s health effects in news coverage. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 33, 1438–1440 (2018)
Blair, B., Zimny-Schmitt, D., Rudd, M.A.: US news media coverage of pharmaceutical pollution in the aquatic environment: a content analysis of the problems and solutions presented by actors. Environ. Manage. 60, 314–322 (2017)
Funding
This study did not receive any funding in any form.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CX contributed to Writing-original draft preparation, conceptualization, supervision, project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, C. Analysis of automatic news segmentation combining with conditional random field knowledge recognition algorithm. SIViP 18, 3867–3875 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03048-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03048-w