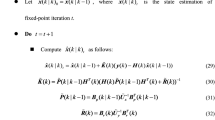Abstract
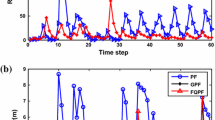
This paper proposes a Maximum Correntropy Quadrature Kalman Filter Based Interacting Multiple Model approach (IMM-MCQKF) for the state estimation with the non-Gaussian noise and model uncertainty problem in the maneuvering target tracking. The performance of Quadrature Kalman Filter (QKF) will significantly decrease when the noise is non-Gaussian, especially under the heavy tailed noise. The proposed IMM-MCQKF approach not only solves this problem, but also ensures a good tracking accuracy with the mode switching caused by the target maneuvering. Specifically, a Maximum Correntropy Quadrature Kalman Filter (MCQKF) combines the maximum correntropy criterion and statistical linearization regression model into the QKF algorithm to increase the estimation accuracy under the non-Gaussian noise. Moreover, we introduce a fixed-point iteration method to ensure that the MCQKF algorithm has a closed solution. Secondly, the MCQKF is embedded into the interacting multiple model framework to address the problem of mode switching caused by target maneuvering. Finally, the simulation results demonstrate the tracking effectiveness of the IMM-MCQKF in maneuvering target tracking scenarios with non-Gaussian noise compared with IMM-EKF, IMM-UKF, IMM-CKF, IMM-QKF, AIMM-UKF, and IMM-AMTP algorithms.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the authors upon request.
References
Muhamamd, I.H., Shoaib, A., Farzeen, M.: Multiple objects tracking using radar for autonomous driving. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference, pp. 1–14 (2020)
Zhou, L.F., Kumar, V.: Robust multi-robot active target tracking against sensing and communication attacks. IEEE T. Robot. 39(3), 1768–1780 (2023)
Dai, H., Zheng, R.: Adaptive tracking strategy for the positioning of millimeter-wave radar security robots. IEEE Sensors J. 24(13), 21321–21330 (2024)
Du, H.C., Xie, W.X.: Track-oriented marginal Poisson multi-Bernoulli mixture filter for extended target tracking. Chinese J Electron. 32(5), 1106–1119 (2023)
Li, X.R., Jilkov, V.P.: Survey of maneuvering target tracking. Part V. Multiple-model methods. IEEE T. Aero. Elec. Sys. 41(4), 1255–1321 (2005)
Zhang, L., Lan, J., Li, X.R.: Normal-gamma IMM filter for linear systems with non-Gaussian measurement noise. In: 2019 22th International Conference on Information Fusion, pp. 1–8 (2019)
Arasaratnam, I., Simon, H., Elliott, R.J.: Discrete-time nonlinear filtering algorithms using Gauss–Hermite quadrature. P. IEEE. 95(5), 953–977 (2007)
Chen, G., Chen, Y., Li, J.: Gaussian Kernel quadrature Kalman filter. Eur. J. Control. 71(3), 100805–100819 (2023)
Huo, Y.: Robust maximum correlation entropy Kalman filtering algorithm based on S-functions under impulse noise. Signal. Image. Video. P. 44(16), 500–505 (2024)
Liu, B., Lan, J., Li, X.R.: A 2-SPRT based approach to multiple-model testing for multi-distribution detection. IEEE T. Signal. Proces. 64(12), 3221–3236 (2016)
Seo, J.W., Kim, J.S., Kim, Y.S.: Vehicle localization using convolutional neural networks with IMM-EKF for automated vertical parking. In: 2022 Chinese Automation Congress, pp. 1976–1981 (2022)
Nie, C., Ju, Z.Y., Sun, Z.F.: 3D object detection and tracking based on lidar-camera fusion and IMM-UKF algorithm towards highway driving. IEEE T. Emer. Topi. Comp. Inte. 7(4), 1242–1252 (2023)
Zhang, C., Cai, Y.: Estimation of aerodynamic coefficients based on IMM-CKF. In: 3rd International Conference on Control Theory and Applications, pp. 74–77 (2023)
Tang, D.J., Li, G.P.: An improved AIMM-UKF maneuvering target tracking algorithm. In: 2024 5th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 752–758 (2024)
Huang, G.: Adaptive modified transition probability IMM algorithm for maneuvering target tracking. In: 2024 9th International Conference on Electronic Technology and Information Science, pp. 427–431 (2024)
Wang, W.L., Tse, C.K., Wang, S.Y.: Generalized correntropy sparse Gauss–Hermite quadrature filter for epidemic tracking on complex networks. IEEE T. Syst. Man. Cy. Sys. 20(5), 831–842 (2020)
Liu, B., Yang, H.N., Zhai, X.H.: Maximum correntropy AMM filter for linear systems with non-Gaussian noise. In: 2023 42nd Chinese Control Conference, pp. 162–170 (2023)
Lan, J., Li, X.R., Jilkov, V.P.: Second-order Markov chain based multiple-model algorithm for maneuvering target tracking. IEEE T. Aero. Elec. Sys. 49(1), 3–19 (2013)
Guo, L., Lan, J., Li, X.R.: Multiple-model approach to over-the-horizon radar tracking based on target perceivability. IEEE T. Aero. Elec. Sys. 58(1), 108–123 (2022)
Hou, X.Y., Zhao, H.Q.: An innovative transient analysis of adaptive filter with maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal. Proclet. 29(3), 1689–1693 (2022)
Wang, Z., Li, Y.: Compressed positive quadrature filter. IEEE T. Automat. Contr. 78(7), 3633–3640 (2022)
Agarwal, K., Rai, C.S., Zhang, Z.Y.: Constrained complex correntropy applied to adaptive beamforming in non-Gaussian noise environment. Signal. Image. Video. P. 18(1), 2333–2343 (2024)
Shi, L.: An efficient parameter optimization of maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal. Proc. Let. 30(14), 538–542 (2023)
Osinsky, A.: Regularization for Cholesky decomposition in MIMO detection. IEEE Wire. Comm. Lett. 12(9), 1603–1607 (2023)
Zhang, T., Wang, S.Y.: Nystrom Kernel algorithm under generalized maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal. Proclet. 27(1), 1535–1539 (2020)
Lin, D.Y., Zhang, Q.Q., Chen, X.F.: Maximum total quaternion generalized correntropy adaptive filtering. IEEE T. Circuits-II. 71(1), 480–484 (2024)
Yu, X.K., Li, J.X.: Adaptive Kalman filtering for recursive both additive noise and multiplicative noise. IEEE T. Aero. Elec. 58(3), 1634–1649 (2022)
Nanda, S., Saxena, K.: Dynamic phasor estimation using \(\ell \)1-norm constraint maximum-Correntropy criterion. IEEE T. Power. Deliver. 39(2), 1075–1087 (2024)
Xu, H.: Adaptive IMM smoothing algorithms for Markov system with mismatched measurement noise covariance matrix. IEEE T. Aero. Elec. 58(3), 1–15 (2024)
Ma, L.L., Chen, J.G.: Interacting multiple model based on quadrature Kalman filtering. Comp. Engi. 37(16), 1–3 (2011)
Liu, S., Liang, Y.: Maneuvering extended object tracking based on constrained expectation maximization. Signal Process. 201(6), 70–77 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by grant for Beilin District Science and Technology Plan Project (GX2231), the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi (2021GY-131), and Yulin Science and Technology Plan Project (CXY-2020-037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bao Liu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing-reviewand editing, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, and Visualization. Ziwei Wu: Soft ware, Validation, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Writing-original draft preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Wu, Z. Maximum correntropy quadrature Kalman filter based interacting multiple model approach for maneuvering target tracking. SIViP 19, 76 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03642-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03642-y