Abstract
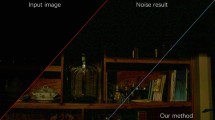
To achieve a visually captivating nocturnal image that closely resembles its natural daytime counterpart, people employ a range of techniques to process the nighttime image. The primary focus lies in achieving rapid and stable unsupervised image enhancement effects specifically tailored for nocturnal scenes, without relying on daytime contrast image. However, existing neural network-based methods for enhancing nighttime image often rely on supervised paired training data, which presents challenges in practical production scenarios. The acquisition of image pairs depicting the same scene and the creation of a large-scale, feature-rich training dataset pose significant difficulties. In this study, we propose a fast pure nighttime image enhancement technique based on preprocessing inspired by the varying light sensitivity exhibited by fish during night fishing. The sensitivity of fish to light varies at different depths, analogous to the concealed richness of effective information within seemingly dark nighttime image, which can be effectively and comprehensively unveiled through preprocessing techniques. Subsequently, we employ an improved dual logarithmic image processing method based on type-II fuzzy sets to fuse the layer information obtained from preprocessing, resulting in enhanced contrast, noise reduction, color enhancement, and improved illumination with superior quality. The extensive experimental and comparative results demonstrate that our method’s robust enhancement and restoration capabilities surpass even those of state-of-the-art supervised methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Hu, Q., Li, G.: Crowd counting study based on low light image enhancement. In: 2023 4th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Application (ICCEA), pp. 792–796 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCEA58433.2023.10135501
Xing, L., Qu, H., Xu, S., Tian, Y.: Clegan: toward low-light image enhancement for uavs via self-similarity exploitation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 61, 1–14 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2023.3279826
Chen, X., Han, P., Huang, Y., Han, Y., Zhong, Y., Li, Z., Yuan, Z., Muntean, G.-M.: A genetic algorithm-based image enhancement approach for autonomous driving at night. In: 2023 IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting (BMSB), pp. 1–6 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/BMSB58369.2023.10211326
Kumari, N., Sharma, P., Kansal, I.: An analytical review on image enhancement techniques. In: 2023 2nd Edition of IEEE Delhi Section Flagship Conference (DELCON), pp. 1–10 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/DELCON57910.2023.10127353
Liang, Z., Ding, X., Jin, J., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Fu, X.: A color cast image enhancement method based on affine transform in poor visible conditions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1–5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2022.3156264
Kim, Y.-T.: Contrast enhancement using brightness preserving bi-histogram equalization. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 43(1), 1–8 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1109/30.580378
Stark, J.A.: Adaptive image contrast enhancement using generalizations of histogram equalization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 9(5), 889–896 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/83.841534
Yuan, Z., Zeng, J., Wei, Z., Jin, L., Zhao, S., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Zhou, G.: Clahe-based low-light image enhancement for robust object detection in overhead power transmission system. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 38(3), 2240–2243 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRD.2023.3269206
Tang, J., Mat Isa, N.A.: Bi-histogram equalization using modified histogram bins. Appl. Soft Comput. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.01.053
Zhu, X., Xiao, X., Tjahjadi, T., Wu, Z., Tang, J.: Image enhancement using fuzzy intensity measure and adaptive clipping histogram equalization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.05922 (2021)
Onyedinma, E., Onyenwe, I., Inyiama, H.: Performance evaluation of histogram equalization and fuzzy image enhancement techniques on low contrast images. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.03957 (2019)
Rahman, Z., Jobson, D.J., Woodell, G.A.: Multi-scale retinex for color image enhancement. In: Proceedings of 3rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, 3, pp. 1003–10063 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.1996.560995
Li, M., Liu, J., Yang, W., Sun, X., Guo, Z.: Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 27(6), 2828–2841 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2810539
Ren, X., Yang, W., Cheng, W.-H., Liu, J.: Lr3m: Robust low-light enhancement via low-rank regularized retinex model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 5862–5876 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2020.2984098
Lin, S., Li, Z., Zheng, F., Zhao, Q., Li, S.: Underwater image enhancement based on adaptive color correction and improved retinex algorithm. IEEE Access 11, 27620–27630 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3258698
Tao, R., Zhou, T., Qiao, J.: Improved retinex for low illumination image enhancement of nighttime traffic. In: 2022 International Conference on Computer Engineering and Artificial Intelligence (ICCEAI), pp. 226–229 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCEAI55464.2022.00055
Fan, J., Li, Y., Liang, B., Ding, Y.: Self-supervised low-light image enhancement based on retinex model. In: 2022 IEEE 10th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), 10, pp. 2138–2141 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ITAIC54216.2022.9836737
Jha, M., Bhandari, A.K.: Camera response based nighttime image enhancement using concurrent reflectance. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71, 1–11 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2022.3165303
Pashaei, E., Pashaei, E.: A fusion approach based on black hole algorithm and particle swarm optimization for image enhancement. Multimedia Tools Appl. 82(1), 297–325 (2023)
Jang, J.H., Bae, Y., Ra, J.B.: Contrast-enhanced fusion of multisensor images using subband-decomposed multiscale retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(8), 3479–3490 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2012.2197014
Liu, S., Zhang, Y.: Detail-preserving underexposed image enhancement via optimal weighted multi-exposure fusion. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 65(3), 303–311 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2019.2893644
Zhang, S., Hou, X.: A novel low light image enhancement method based on multi-attention generative adversarial networks. In: 2022 10th International Conference on Information Systems and Computing Technology (ISCTech), pp. 702–709 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCTech58360.2022.00116
Hari, U., Bevi, A.R.: Self-supervised learning based low light image enhancement using convolutional neural networks. In: 2022 OPJU International Technology Conference on Emerging Technologies for Sustainable Development (OTCON), pp. 1–6 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/OTCON56053.2023.10113961
Wu, K., Huang, J., Ma, Y., Fan, F., Ma, J.: Cycle-retinex: unpaired low-light image enhancement via retinex-inline cyclegan. IEEE Trans. Multimedia (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2023.3278385
Li, C., Guo, C.G., Loy, C.C.: Learning to enhance low-light image via zero-reference deep curve estimation. In: IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2021)
Ma, L., Ma, T., Liu, R., Fan, X., Luo, Z.: Toward fast, flexible, and robust low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5637–5646 (2022)
Fu, Z., Yang, Y., Tu, X., Huang, Y., Ding, X., Ma, K.-K.: Learning a simple low-light image enhancer from paired low-light instances. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 22252–22261 (2023)
Yao, Z., Su, J.-N., Fan, G., Gan, M., Chen, C.L.P.: Gaca: a gradient-aware and contrastive-adaptive learning framework for low-light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 73, 1–14 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2024.3353285
Chi, K., Yuan, Y., Wang, Q.: Trinity-net: gradient-guided swin transformer-based remote sensing image dehazing and beyond. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 61, 1–14 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2023.3285228
Chi, K., Li, J., Jing, W., Li, Q., Wang, Q.: Neural implicit fourier transform for remote sensing shadow removal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 62, 1–10 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2024.3412368
Wang, Q., Chi, K., Jing, W., Yuan, Y.: Recreating brightness from remote sensing shadow appearance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 62, 1–11 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2024.3398576
Zhang, F., Shao, Y., Sun, Y., Zhu, K., Gao, C., Sang, N.: Unsupervised low-light image enhancement via histogram equalization prior. arxiv 2021. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.01766
Jia, W., Yang, J., Liu, Y., Fan, L., Ruan, Q.: Improved fast image enhancement algorithm based on fuzzy set theory. In: 2014 Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics, 2, pp. 173–175 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/IHMSC.2014.144
Kabir, M., Mobin, J., Hassanat, A., Rahman, M.S.: Image contrast enhancement using fuzzy technique with parameter determination using metaheuristics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.12682 (2023)
Kumar, R., Bhandari, A.K.: Fuzzified contrast enhancement for nearly invisible images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 32(5), 2802–2813 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3098763
Wu, M.: An improved fuzzy algorithmic approach applying on medical image to improve the contrast. In: 2020 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), pp. 511–513 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/IWCMC48107.2020.9148497
Luque-Chang, A., Cuevas, E., Chavarin, A., Perez, M.: Agent-based image contrast enhancement algorithm. IEEE Access 11, 6060–6077 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3237086
Subramani, B., Veluchamy, M.: Bilateral tone mapping scheme for color correction and contrast adjustment in nearly invisible medical images. Color Res. Appl. 48(6), 748–760 (2023)
Jourlin, M., Pinoli, J.-C.: A model for logarithmic image processing. J. Microsc. 149(1), 21–35 (1988)
Florea, C., Florea, L.: Parametric logarithmic type image processing for contrast based auto-focus in extreme lighting conditions. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 23(3) (2013)
Akhondi-Asl, A., Hoyte, L., Lockhart, M.E., Warfield, S.K.: A logarithmic opinion pool based staple algorithm for the fusion of segmentations with associated reliability weights. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 33(10), 1997–2009 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2329603
Hu, H., Cao, W., Yuan, J., Yang, J.: A low-illumination image enhancement algorithm based on morphological-retinex (mr) operator. In: 2021 IEEE/ACIS 6th International Conference on Big Data, Cloud Computing, and Data Science (BCD), pp. 66–72 (2021). IEEE
Wei, C., Wang, W., Yang, W., Liu, J.: Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.04560 (2018)
Ma, K., Zeng, K., Wang, Z.: Perceptual quality assessment for multi-exposure image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(11), 3345–3356 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2442920
Hudson, H.M., Larkin, R.S.: Accelerated image reconstruction using ordered subsets of projection data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 13(4), 601–609 (1994)
Parthasarathy, S., Sankaran, P.: An automated multi scale retinex with color restoration for image enhancement. In: 2012 National Conference on Communications (NCC), pp. 1–5 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/NCC.2012.6176791
Ahn, H., Keum, B., Kim, D., Lee, H.S.: Adaptive local tone mapping based on retinex for high dynamic range images. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), pp. 153–156 (2013). IEEE
Guo, X., Li, Y., Ling, H.: Lime: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(2), 982–993 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2639450
Yang, Y., Xiang, T., Guo, S., Lv, X., Liu, H., Liao, X.: Ehnq: subjective and objective quality evaluation of enhanced night-time images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 33(9), 4645–4659 (2023)
Funding
National Key Research and Development Program of China, Grant/Award Numbers: 2023YFB2504703; National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant/Award Number: 52177132
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Project administration, Supervision, Formal analysis, Writing-review and editing S: Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review and editing, Visualization G: Methodology, Software, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Visualization Z: Validation, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Writing-review and editing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no Conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, X., Song, Y., Guan, L. et al. FPNIE: a fast pure nighttime image enhancement method. SIViP 19, 10 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03648-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03648-6