Abstract
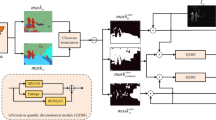
The purpose of infrared and visible image fusion is to synthesize a single image with rich details using the complementary information of the two modal images. Unlike current research methods which primarily focus on the visual quality of the fused images, our method emphasizes the importance of image fusion in enhancing downstream tasks. We propose a dual-modal semantic guidance strategy, which uses a dual-branch semantic segmentation network to guide the fusion network. Specifically, our method utilizes the segmentation results of the infrared and visible images to calculate the mean intersection over union and adjusts the loss function accordingly to guide the fusion network. Additionally, we introduce a novel component called the differential feature complementation module, which strengthen the fusion of complementary information by computing and integrating differential features at the same level of the fusion network. Comparison experiments on the MFNet dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms the performance of existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of fused image quality. Furthermore, segmentation experiments on the MFNet dataset demonstrate that our method effectively improves the performance in the context of the semantic segmentation task. Generalization experiments on the TNO and RoadScene datasets demonstrate that our method also possesses the strong generalization capability.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used in this study were obtained from the publicly accessible websites(https://github.com/Linfeng-Tang/MSRS/).
References
Cao, Y., Guan, D., Huang, W., Yang, J., Cao, Y., Qiao, Y.: Pedestrian detection with unsupervised multispectral feature learning using deep neural networks. Inf. Fus. 46, 206–217 (2019)
Lu, Y., Wu, Y., Liu, B.: Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp.13376–13386 (2020)
Ha, Q., Watanabe, K., Karasawa, T.: MFNet: towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 5108–5115 (2017)
Wang, Z., Cui, Z., Zhu, Y.: Multi-modal medical image fusion by Laplacian pyramid and adaptive sparse representation. Comput. Biol. Med. 123, 103823 (2020)
Liu, Y., Jin, J., Wang, Q., Shen, Y., Dong, X.: Region level based multi-focus image fusion using quaternion wavelet and normalized cut. Signal Process. 97, 9–30 (2014)
Li, H., Wu, X.J., Kittler, J.: MDLatLRR: a novel decomposition method for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 4733–4746 (2020)
Liu, D., Wen, B., Jiao, J., Liu, X., Wang, Z., Huang, T.S.: Connecting image denoising and high-level vision tasks via deep learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 29, 3695–3706 (2020)
Haris, M., Shakhnarovich, G., Ukita, N.: Task-driven super resolution: object detection in low-resolution images. arXiv preprint arXiv. 1803.11316 (2018)
Liu, X., Mei, W., Du, H.: Structure tensor and nonsubsampled shearlet transform based algorithm for CT and MRI image fusion. Neurocomputing 235, 131–139 (2017)
Zhang, Q., Maldague, X.: An adaptive fusion approach for infrared and visible images based on NSCT and compressed sensing. Infrared Phys. Technol. 74, 11–20 (2016)
Wu, M., Ma, Y., Fan, F., Mei, X., Huang, J.: Infrared and visible image fusion via joint convolutional sparse representation. JOSA A 37(7), 1105–1115 (2020)
Liu, Y., Chen, X., Ward, R.K., Wang, Z.J.: Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation. IEEE signal process. Lett. 23(12), 1882–1886 (2016)
Fu, Z., Wang, X., Xu, J., Zhou, N., Zhao, Y.: Infrared and visible images fusion based on RPCA and NSCT. Infrared Phys. Technol. 77, 114–123 (2016)
Mou, J., Gao, W., Song, Z.: Image fusion based on non-negative matrix factorization and infrared feature extraction, In: Proceedings of the International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, pp. 1046–1050 (2013)
Liu, Y., Liu, S., Wang, Z.: A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Information Fus. 24, 147–164 (2015)
Prabhakar, K, R., Srikar, V, S., Babu, R, V.: DeepFuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image pairs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 4714–4722 (2017)
Li, H., Wu, X.J.: DenseFuse: a fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(5), 2614–2623 (2018)
Zhu, Z., Yin, H., Chai, Y., Li, Y., Qi, G.: A novel multi-modality image fusion method based on image decomposition and sparse representation. Inf. Sci. 432, 516–529 (2018)
Zhang, H., Ma, J.: SDNet: a versatile squeeze-and-decomposition network for real-time image fusion. Int. J. Comput. Vision 129(10), 2761–2785 (2021)
Ma, J., Tang, L., Xu, M.: STDFusionNet: an infrared and visible image fusion network based on salient target detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2021.3075747
Tang, L., Yuan, J., Zhang, H., Jiang, X., Ma, J.: PIAFusion: a progressive infrared and visible image fusion network based on illumination aware. Inf. Fus. 83, 79–92 (2022)
Zhu, J., Park, T., Isola, P.: Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2223–2232 (2017)
Guo, Z., Shao, M., Li, S.: Image-to-image translation using an offset-based multi-scale codes GAN encoder. V. Comput. 40(2), 699–715 (2024)
Peng, Y., Meng, Z., Yang, L.: Image-to-image translation for data augmentation on multimodal medical images. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 106(5), 686–696 (2023)
Ma, J., Yu, W., Liang, P., Li, C., Jiang, J.: FusionGAN: a generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fus. 48, 11–26 (2019)
Li, J., Huo, H., Li, C., Wang, R., Feng, Q.: AttentionFGAN: infrared and visible image fusion using attention-based generative adversarial networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 23, 1383–1396 (2020)
Wu, J., Liu, G., Wang X.: GAN-GA: infrared and visible image fusion generative adversarial network based on global awareness. Appl. Intell. 7296-7316 (2024)
Ma, J., Tang, L., Fan, F., Huang, J., Mei, X., Ma, Y.: SwinFusion: cross-domain long-range learning for general image fusion via swin transformer. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sinica 9(7), 1200–1217 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/JAS.2022.105686
Zhao, Z., Bai, H., Zhang, J.: CDDFuse: correlation-driven dual-branch feature decomposition for multi-modality image fusion, In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp.5906–5916 (2023)
Park, S., Vien, A.G., Lee, C.: Cross-modal transformers for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. V. Technol. 34(2), 770–785 (2023)
Changqian, Y., Wang, J., Peng, C., Gao, C., Gang, Y., Sang, N.: BiSeNet: bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision – ECCV 2018: 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, September 8-14, 2018, Proceedings, Part XIII, pp. 334–349. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01261-8_20
Alexander, T.: Hogervorst. Progress in color night vision. Optical Engineering, pp. 1–20 (2012)
Xu, H., Ma, J., Jiang, J.: U2Fusion: a unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3012548
Ma, J., Zhang, H., Shao, Z.: GANMcC: a generative adversarial network with multiclassification constraints for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/tim.2020.3038013
Guihong, Q., Zhang, D., Yan, P.: Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett. 38(7), 313–315 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1049/el:20020212
Han, Y., Cai, Y., Cao, Y., Xiaoming, X.: A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity. Inf. Fus. 14(2), 127–135 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2011.08.002
Eskicioglu, A.M., Fisher, P.S.: Image quality measures and their performance. IEEE Trans. Commun. 43(12), 2959–2965 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1109/26.477498
Funding
The study was funded by the Anhui Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2208085MC60), the Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Provincial Education Department (2023AH050084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WB performed the formulation or evolution of overarching research goals and model structure. ZF performed the creation of models and design of methodology. YD performed the revision of the article. CL provided material support. All authors reviewed the manuscriptt.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, W., Feng, Z., Du, Y. et al. A dual-modal semantic guidance and differential feature complementation fusion method for infrared and visible image. SIViP 19, 150 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03672-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03672-6