Abstract
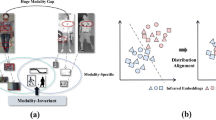
The inherent complexity of visible-infrared person re-identification is characterized by significant intra-class variance and pronounced inter-modal disparities. Existing approaches address these challenges by constructing comprehensive data representations through joint learning of multi-modal samples or cross-modal transformation techniques. However, the lack of a dynamic modulation mechanism limits their ability to adapt modality-specific features effectively, thereby constraining the generalizability of the shared feature space. This limitation results in a shared space that lacks the robustness necessary for effective generalization. To address these issues, we introduce the dual dynamic modality alignment network, a novel framework designed to dynamically calibrate the significance of modality-specific features, optimizing critical data extraction while minimizing reliance on extraneous information. Central to our approach is the class-aware modality hybrid-assisted generator, which conceptualizes the multimodal contrastive representation space as nodes, integrates diverse contrastive representations, and interlinks isolated representations to explore a wider array of contrastive relationships between modalities. Additionally, we propose an auxiliary modal identity center alignment loss that refines feature distribution and reduces divergence between visible and infrared image representations. Extensive evaluation on the SYSU-MM01 and RegDB datasets demonstrates the superior performance of our method, emphasizing its efficacy in creating a more discriminative and balanced shared feature space.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho, Y., Kim, W.J., Hong, S., Yoon, S.-E.: Part-based pseudo label refinement for unsupervised person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7298–7308 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00716
Zhong, S., Bao, Z., Gong, S., Xia, K.: Person reidentification based on pose-invariant feature and B-KNN reranking. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 8(5), 1272–1281 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSS.2021.3063318
Dou, Z., Wang, Z., Li, Y., Wang, S.: Identity-seeking self-supervised representation learning for generalizable person re-identification. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 15801–15812 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.01452
Zheng, Y., Tang, S., Teng, G., Ge, Y., Liu, K., Qin, J., Qi, D., Chen, D.: Online pseudo label generation by hierarchical cluster dynamics for adaptive person re-identification. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 8351–8361 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00826
Nguyen, V.D., Khaldi, K., Nguyen, D., Mantini, P., Shah, S.: Contrastive viewpoint-aware shape learning for long-term person re-identification. In: IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 1030–1038 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV57701.2024.00108
Dai, P., Ji, R., Wang, H., Wu, Q., Huang, Y.: Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training. In: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 677–683 (2018). https://doi.org/10.5555/3304415.3304512
Hao, Y., Wang, N., Li, J., Gao, X.: Hsme: Hypersphere manifold embedding for visible thermal person re-identification. In: Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), vol. 33, pp. 8385–8392 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018385
Lu, Y., Wu, Y., Liu, B., Zhang, T., Li, B., Chu, Q., Yu, N.: Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 13376–13386 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01339
Yang, F., Wang, Z., Xiao, J., Satoh, S.: Mining on heterogeneous manifolds for zero-shot cross-modal image retrieval. In: Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), vol. 34, pp. 12589–12596 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01339
Ye, M., Lan, X., Li, J., Yuen, P.: Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification. In: Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), vol. 33 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33015613
Feng, Y., Yu, J., Chen, F., Ji, Y., Wu, F., Liu, S., Jing, X.-Y.: Visible-infrared person re-identification via cross-modality interaction transformer. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 25, 7647–7659 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2022.3224663
Wu, A., Zheng, W.-S., Gong, S., Lai, J.: RGB-IR person re-identification by cross-modality similarity preservation. Int. J. Comput. Vision 128, 1765–1785 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-019-01290-1
Liao, S., Shao, L.: Graph sampling based deep metric learning for generalizable person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7349–7358 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00721
Wang, G.-A., Zhang, T., Yang, Y., Cheng, J., Chang, J., Liang, X., Hou, Z.-G.: Cross-modality paired-images generation for RGB-infrared person re-identification. In: Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), vol. 34, pp. 12144–12151 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6894
Liu, H., Xia, D., Jiang, W.: Towards homogeneous modality learning and multi-granularity information exploration for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE J. Selected Top. Signal Process. 17(3), 545–559 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3233716
Kong, J., He, Q., Jiang, M., Liu, T.: Dynamic center aggregation loss with mixed modality for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 2003–2007 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2021.3115040
Ling, Y., Zhong, Z., Luo, Z., Li, S., Sebe, N.: Bridge gap in pixel and feature level for cross-modality person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 34(6), 5104–5117 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3338813
Wu, J., Liu, H., Shi, W., Liu, M., Li, W.: Style-agnostic representation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2023.3294002
Zhang, Y., Yan, Y., Lu, Y., Wang, H.: Towards a unified middle modality learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM), pp. 788–796 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3474085.3475250
Wu, A., Zheng, W.-S., Yu, H.-X., Gong, S., Lai, J.: RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 5390–5399 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.575
Sun, H., Liu, J., Zhang, Z., Wang, C., Qu, Y., Xie, Y., Ma, L.: Not all pixels are matched: dense contrastive learning for cross-modality person re-identification. In: ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM), pp. 5333–5341 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3503161.3547970
Yang, M., Huang, Z., Hu, P., Li, T., Lv, J., Peng, X.: Learning with twin noisy labels for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 14288–14297 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01391
Yu, H., Cheng, X., Peng, W., Liu, W., Zhao, G.: Modality unifying network for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 11151–11161 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.01027
Zhang, Y., Wang, H.: Diverse embedding expansion network and low-light cross-modality benchmark for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2153–2162 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00214
Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Zheng, Y., Chuang, Y.-Y., Satoh, S.: Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 618–626 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00071
Choi, S., Lee, S., Kim, Y., Kim, T., Kim, C.: Hi-CMD: Hierarchical cross-modality disentanglement for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10254–10263 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01027
Li, D., Wei, X., Hong, X., Gong, Y.: Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an x modality. In: Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), vol. 34, pp. 4610–4617 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i04.5891
Wei, Z., Yang, X., Wang, N., Gao, X.: Syncretic modality collaborative learning for visible infrared person re-identification. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 225–234 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00029
Cai, X., Liu, L., Zhu, L., Zhang, H.: Dual-modality hard mining triplet-center loss for visible infrared person re-identification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 215, 106772 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.106772
Feng, Y., Chen, F., Yu, J., Ji, Y., Wu, F., Liu, S., Jing, X.-Y.: Homogeneous and heterogeneous relational graph for visible-infrared person re-identification. Pattern Recogn. 158, 110981 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2024.110981
Nguyen, D.T., Hong, H.G., Kim, K.W., Park, K.R.: Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors 17(3), 605 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030605
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Zhong, Z., Zheng, L., Kang, G., Li, S., Yang, Y.: Random erasing data augmentation. Assoc. Adv. Artif. Intell. 34, 13001–13008 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.7000
Ye, M., Shen, J., Lin, G., Xiang, T., Shao, L., Hoi, S.C.H.: Deep learning for person re-identification: a survey and outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(6), 2872–2893 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3054775
Ye, M., Shen, J., J. Crandall, D., Shao, L., Luo, J.: Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 229–247 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58520-4_14
Lu, H., Zou, X., Zhang, P.: Learning progressive modality-shared transformers for effective visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), vol. 37, pp. 1835–1843 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v37i2.25273
Wu, S., Shan, S., Xiao, G., Lew, M.S., Gao, X.: Modality blur and batch alignment learning for twin noisy labels-based visible-infrared person re-identification. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 133, 107990 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2024.107990
Sun, R., Chen, L., Zhang, L., Xie, R., Gao, J.: Robust visible-infrared person re-identification based on polymorphic mask and wavelet graph convolutional network. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 19, 2800–2813 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2024.3354377
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62376041, 62466026), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2021M69236), Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education, the Jilin University (No. 93K172021K01), State Key Lab for Novel Software Technology, the Nanjing University (No. KFKT2024B51), the Scientific Research Foundation of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (No. GJJ2200351).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, S., Li, S., Xie, G. et al. Modality-agnostic learning for robust visible-infrared person re-identification. SIViP 19, 200 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03749-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03749-2