Abstract
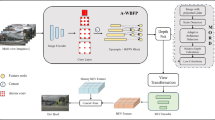
Vehicle detection in high-resolution remote sensing imagery faces challenges such as varying scales, complex backgrounds, and high intra-class variability. We propose an enhanced YOLOv8 framework, incorporating three key advancements: the Adaptive Feature Pyramid Network (AFPN), Omni-Dimensional Convolution (ODConv), and a Slim Neck with Generalized Shuffle Convolution (GSConv). These enhancements improve vehicle detection accuracy, computational efficiency, and visual AI capabilities for applications such as computer animation and virtual worlds. Our model achieves a Mean Average Precision (mAP) of 0.7153, representing a 4.99% improvement over the baseline YOLOv8. Precision and recall increase to 0.9233 and 0.9329, respectively, while box loss is reduced from 1.213 to 1.054. This framework supports real-time surveillance, traffic monitoring, and urban planning. The NEPU-OWOD V2.0 dataset, used for evaluation, includes high-resolution images from multiple regions and seasons, along with diverse annotations and augmentations. Our modular approach allows for separate assessments of each enhancement. The dataset and source code are available for future research and development at (https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13075939).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, K. et al.: Oriented object detection in optical remote sensing images using deep learning: a survey (2023). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2302.10473
Zhang, J. et al.: Fair1m: a benchmark dataset for fine-grained object recognition in high-resolution remote sensing imagery (2021). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2103.05569
Wang, X. et al.: A comprehensive review of yolo architectures in computer vision: from yolov1 to yolov8 and yolo-nas (2023). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2304.00501
Cao, L., Shen, Z., Xu, S.: Efficient forest fire detection based on an improved yolo model. Vis. Intell. 2, 20 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44267-024-00053-y
Cheng, G., et al.: Object detection in optical remote sensing images: a survey and a new benchmark. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 159, 296–307 (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1909.00133
Chen, G., Zhuang, P., Guo, J., Xu, J., Liu, H., Zhang, L.: Omni-dimensional dynamic convolution (2022). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2209.07947
Chen, W. et al.: Castdet: toward open vocabulary aerial object detection with clip-activated student-teacher learning (2023). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2311.11646
Liu, W., Zhang, Y., Hu, Y., Zhou, H.: Efficient meta-learning enabled lightweight multiscale few-shot object detection in remote sensing images (2023)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. 28 (2015). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1506.01497
Dai, L., et al.: A deep learning system for predicting time to progression of diabetic retinopathy. Nat. Med. 30, 584–594 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-023-02702-z
Qian, B. et al.: Drac 2022: a public benchmark for diabetic retinopathy analysis on ultra-wide optical coherence tomography angiography images. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patter.2024.100929
Qin, Y. et al.: Urbanevolver: function-aware urban layout regeneration (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-024-02030-w
Lin, X., et al.: Eapt: Efficient attention pyramid transformer for image processing. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 25, 50–61 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3120873
Zhu, J. et al.: Clustering environment aware learning for active domain adaptation. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2024.3374068
Huang, J. et al.: Speed/accuracy trade-offs for modern convolutional object detectors. pp. 7310–7311 (2017)
Liu, S., Qi, X., Qin, H., Shi, J., Jia, J.: Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. pp. 8759–8768 (2018)
Dai, J., Qi, H., Xiong, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, G., Hu, H., Wei, Y.: Deformable convolutional networks. pp. 764–773 (2017). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1703.06211
Chen, L.-C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, K., Yuille, A.L.: Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation (2017). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.05587
Li, L., Ding, J., Cui, H., Chen, Z., Liao, G.: Litemsnet: a lightweight semantic segmentation network with multi-scale feature extraction for urban streetscape scenes. pp. 1–15 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-024-03569-y
Sheng, B., et al.: Improving video temporal consistency via broad learning system. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 52(7), 6662–6675 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3079311
Li, J., et al.: Automatic detection and classification system of domestic waste via multimodel cascaded convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 18(1), 163–173 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2021.3085669
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Z., He, K., Yuan, B. et al. Enhanced YOLOv8 framework for precision vehicle detection in high-resolution remote sensing images. SIViP 19, 218 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03783-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03783-0