Abstract
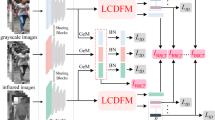
Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification (VI-ReID), which aims to retrieve pedestrian images captured by visible and infrared cameras, presents a significant challenge in intelligent surveillance systems. VI-ReID should not only tackle the modality discrepancies between visible and infrared images, but also address intra-modality discrepancies caused by factors such as image occlusion, lighting changes, and background complexity. In this paper, we propose a novel VI-ReID network (IADGN) that effectively combines an Information Augmentation Aggregation Module (IAAM) with a Dual-Granularity Feature Module (DGFM) to balance the processing of cross-modality and intra-modality discrepancies. First, during the data processing stage, a random grayscale strategy is employed for both visible and infrared images to effectively minimize the interference of color information. Second, to address common intra-modality discrepancies such as occlusion, lighting changes, and background complexity, we design an Information Augmentation Aggregation Module (IAAM) based on a self-attention mechanism. This module accurately focuses on pedestrian features and aggregates them with the original features in a channel-adaptive manner, effectively ignoring the cluttered background and enhancing feature discriminability. Additionally, we propose a Dual-Granularity Feature Module (DGFM) that integrates global and local features, overcoming the limitations of single-granularity feature learning, and significantly enhancing the network’s recognition accuracy. Finally, we propose the Center Distribution Consistency Loss function (CDCL), which reduces modality discrepancies and enhances the modality consistency of feature representation by aligning the inter-class distributions of visible and infrared images. Extensive experimental results on three publicly available datasets-SYSU-MM01, RegDB, and LLCM-demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Hauptmann, A. G.: Person re-identification: past, present and future. arXiv prepr preprint arXiv:1610.02984, (2016)
Wu, A., Zheng, W-S., Yu, H-X., Gong, S., Lai, J.: Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5380–5389 (2017)
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Cui, Z.: Incomplete multimodality-diffused emotion recognition. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 36 (2024)
Wang, Y., Cui, Z., Li, Yng.: Distribution-consistent modal recovering for incomplete multimodal learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 22025–22034 (2023)
Dai, P., Ji, R., Wang, H., Wu, Q., Huang, Y.: Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training. IJCAI 1, 6 (2018)
Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Zheng, Y., Chuang, Y-Y., Satoh, S.: Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 618–626 (2019)
Wang, Guan’an., Zhang, Tianzhu., Cheng, Jian., Liu, Si., Yang, Yang., Hou, Zengguang.: Rgb-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3623–3632 (2019)
Wang, Guan-An., Zhang, Tianzhu, Yang, Yang, Cheng, Jian, Jianlong Chang, Xu., Liang, Zeng-Guang.: Cross-modality paired-images generation for RGB-infrared person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intel. 34, 12144–12151 (2020)
Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., Bengio, Y.: Generative adversarial nets. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 27 (2014)
Ye, M., Lan, X., Li, J., Yuen, P.: Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32 (2018)
Liu, Haijun, Cheng, Jian, Wang, Wen, Yanzhou, Su., Bai, Haiwei: Enhancing the discriminative feature learning for visible-thermal cross-modality person re-identification. Neurocomputing 398, 11–19 (2020)
Zhang, Q., Lai, C., Liu, J., Huang, N., Han, J.: Fmcnet: feature-level modality compensation for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7349–7358 (2022)
Lu, Y., Wu, Y., Liu, B., Zhang, T., Li, B., Chu, Q., Yu, N.: Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13379–13389 (2020)
Gao, Y., Liang, T., Jin, Y., Gu, X., Liu, W., Li, Y., Lang, C.: MSO: multi-feature space joint optimization network for rgb-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 5257–5265 (2021)
Tian, X., Zhang, Z., Lin, S., Qu, Y., Xie, Y., Ma, L.: Farewell to mutual information: variational distillation for cross-modal person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1522–1531 (2021)
Yang, M., Huang, Z., Hu, P., Li, T., Lv, J., Peng, X.: Learning with twin noisy labels for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 14308–14317 (2022)
Ye, M., Shen, J., Crandall, D., Shao, L., Luo, J.: Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XVII 16, pp. 229–247. Springer (2020)
Su, P., Liu, R., Dong, J., Yi, P., Zhou, D.: Scfnet: a spatial-channel features network based on heterocentric sample loss for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3552–3568 (2022)
Ye, Mang, Wang, Zheng, Lan, Xiangyuan, Yuen, Pong C.: Visible thermal person re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking. IJCAI 1, 2 (2018)
Ye, Mang, Shen, Jianbing, Lin, Gaojie, Xiang, Tao, Shao, Ling, Hoi, Steven CH..: Deep learning for person re-identification: a survey and outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intel. 44(6), 2872–2893 (2021)
Wang, X., Girshick, R., Gupta, A., He, K.: Non-local neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7794–7803 (2018)
Zhang, Y., Wang, H.: Diverse embedding expansion network and low-light cross-modality benchmark for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2153–2162 (2023)
Sun, Y., Zheng, L., Yang, Y., Tian, Q., Wang, S.: Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 480–496 (2018)
Hao, Y., Wang, N., Gao, X., Li, J., Wang, X.: Dual-alignment feature embedding for cross-modality person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 57–65 (2019)
Jiang, K., Zhang, T., Liu, X., Qian, B., Zhang, Y., Wu, F.: Cross-modality transformer for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 480–496. Springer (2022)
Zhang, Y., Yan, Y., Lu, Y., Wang, H.: Towards a unified middle modality learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 788–796 (2021)
Cai, Shuang, Yang, Shanmin, Jing, Hu., Xi, Wu.: Dual-granularity feature fusion in visible-infrared person re-identification. IET Image Process. 18(4), 972–980 (2024)
Wu, Q., Dai, P., Chen, J., Lin, C-W., Wu, Y., Huang, F., Zhong, B., Ji, R.: Discover cross-modality nuances for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4330–4339 (2021)
Zhang, L., Du, G., Liu, F., Tu, H., Shu, X.: Global-local multiple granularity learning for cross-modality visible-infrared person reidentification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (2021)
Liu, Haijun, Chai, Yanxia, Tan, Xiaoheng, Li, Dong, Zhou, Xichuan: Strong but simple baseline with dual-granularity triplet loss for visible-thermal person re-identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 28, 653–657 (2021)
Ling, Yongguo, Zhong, Zhun, Luo, Zhiming, Yang, Fengxiang, Cao, Donglin, Lin, Yaojin, Li, Shaozi, Sebe, Nicu: Cross-modality earth mover’s distance for visible thermal person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intel. 37, 1631–1639 (2023)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Guo, Jiangtao, Haishun, Du., Hao, Xinxin, Zhang, Minghao: IGIE-net: cross-modality person re-identification via intermediate modality image generation and discriminative information enhancement. Image Vis. Comput. 147, 105066 (2024)
Vaswani, A.: Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (2017)
Radenović, Filip, Tolias, Giorgos, Chum, Ondřej: Fine-tuning CNN image retrieval with no human annotation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intel. 41(7), 1655–1668 (2018)
Luo, Hao, Jiang, Wei, Youzhi, Gu., Liu, Fuxu, Liao, Xingyu, Lai, Shenqi, Jianyang, Gu.: A strong baseline and batch normalization neck for deep person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 22(10), 2597–2609 (2019)
Liu, Haijun, Tan, Xiaoheng, Zhou, Xichuan: Parameter sharing exploration and hetero-center triplet loss for visible-thermal person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 23, 4414–4425 (2020)
Nguyen, Dat Tien, Hong, Hyung Gil, Kim, Ki Wan, Park, Kang Ryoung: Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors 17(3), 605 (2017)
Hao, X., Zhao, S., Ye, M., Shen, J.: Cross-modality person re-identification via modality confusion and center aggregation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 16403–16412 (2021)
Liu, J., Sun, Y., Zhu, F., Pei, H., Yang, Y., Li, W.: Learning memory-augmented unidirectional metrics for cross-modality person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 19366–19375 (2022)
Hu, Lu., Zou, Xuezhang, Zhang, Pingping: Learning progressive modality-shared transformers for effective visible-infrared person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intel. 37, 1835–1843 (2023)
Park, H., Lee, S., Lee, J., Ham, B.: Learning by aligning: Visible-infrared person re-identification using cross-modal correspondences. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 12046–12055 (2021)
Huang, Nianchang, Liu, Jianan, Luo, Yongjiang, Zhang, Qiang, Han, Jungong: Exploring modality-shared appearance features and modality-invariant relation features for cross-modality person re-identification. Pattern Recogn. 135, 109145 (2023)
Liu, Haojie, Xia, Daoxun, Jiang, Wei: Towards homogeneous modality learning and multi-granularity information exploration for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE J. Select. Top. Signal Process. 17(3), 545–559 (2023)
Zhong, Zhun, Zheng, Liang, Kang, Guoliang, Li, Shaozi, Yang, Yi.: Random erasing data augmentation. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intel. 34, 13001–13008 (2020)
Ye, M., Ruan, W., Du, B., Shou, M. Z.: Channel augmented joint learning for visible-infrared recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13567–13576 (2021)
Van der Maaten, Laurens, Hinton, Geoffrey: Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9(11), 2579 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the the Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province (Grant No. QKHJCZK[2024]063), and in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62266011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, M., Long, H., Kong, G. et al. Combining information augmentation aggregation and dual-granularity feature fusion for visible-infrared person re-identification. SIViP 19, 163 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03800-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-024-03800-2