Abstract
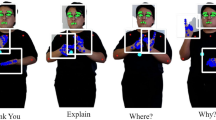
Sign Language Recognition (SLR) involves identifying human actions that convey language, benefiting both deaf-mute individuals and facilitating interactions between humans and computers. SLR models capture linguistic features from upper body movements, which can be depicted as graphical representations. In each video frame, temporal and spatial information is extracted by understanding skeleton graphs and attention mechanism. This graph-based information will encompass both temporal and spatial semantics, enabling comprehension of sign language in videos. In this research, we propose a deep model, termed TeDG, to utilize the potential of graph-based representation using attention mechanisms. The graph is formed by extracting skeleton of the object’s upper body in video frames. Specifically, we employ prompt techniques to extract labels from sign language videos and then apply attention diffusion models and graph skeletons for recognition. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of TeDG compared to existing models on both our new dataset and widely public datasets.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Rastgoo, R., Kiani, K., Escalera, S.: Sign language recognition: a deep survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 164, 113794 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113794
Ho, J., Saharia, C., Chan, W., Fleet, D.J., Norouzi, M., Salimans, T.: Cascaded diffusion models for high fidelity image generation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 23(47), 1–33 (2022)
Dhariwal, P., Nichol, A.: Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis. In: Ranzato, M., Beygelzimer, A., Dauphin, Y., Liang, P.S., Vaughan, J.W. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 34, pp. 8780–8794. Curran Associates, Inc., (2021). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2021/file/49ad23d1ec9fa4bd8d77d02681df5cfa-Paper.pdf
Lugmayr, A., Danelljan, M., Romero, A., Yu, F., Timofte, R., Van Gool, L.: Repaint: Inpainting using denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11461–11471 (2022)
Ghosh, S., Birrell, P.J., De Angelis, D.: Differentiable bayesian inference of sde parameters using a pathwise series expansion of brownian motion. In: Camps-Valls, G., Ruiz, F.J.R., Valera, I. (eds.) Proceedings of The 25th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 151, pp. 10982–10998. PMLR, (2022). https://proceedings.mlr.press/v151/ghosh22a.html
Jalal, A., Liu, L., Dimakis, A.G., Caramanis, C.: Robust compressed sensing using generative models. In: Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M.F., Lin, H. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 33, pp. 713–727. Curran Associates, Inc., (2020). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2020/file/07cb5f86508f146774a2fac4373a8e50-Paper.pdf
Cao, H., Tan, C., Gao, Z., Xu, Y., Chen, G., Heng, P.-A., Li, S.Z.: A survey on generative diffusion models. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2024.3361474
Ngasa, E.E., Jang, M.-A., Tarimo, S.A., Woo, J., Shin, H.B.: Diffusion-based Wasserstein generative adversarial network for blood cell image augmentation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 133, 108221 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2024.108221
You, Z., Zhong, Y., Bao, F., Sun, J., LI, C., Zhu, J.: Diffusion models and semi-supervised learners benefit mutually with few labels. In: Oh, A., Neumann, T., Globerson, A., Saenko, K., Hardt, M., Levine, S. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 36, pp. 43479–43495. Curran Associates, Inc., (2023). https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2023/file/8735753cc18f6baa92d1f069fd8b14a0-Paper-Conference.pdf
Ji, Y., Chen, Z., Xie, E., Hong, L., Liu, X., Liu, Z., Lu, T., Li, Z., Luo, P.: Ddp: Diffusion model for dense visual prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 21741–21752 (2023)
Xiao, Y., Yuan, Q., Jiang, K., He, J., Jin, X., Zhang, L.: Ediffsr: an efficient diffusion probabilistic model for remote sensing image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 62, 1–14 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2023.3341437
Rombach, R., Blattmann, A., Lorenz, D., Esser, P., Ommer, B.: High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10684–10695 (2022)
Huang, W., Deng, Y., Hui, S., Wu, Y., Zhou, S., Wang, J.: Sparse self-attention transformer for image inpainting. Pattern Recognit. 145, 109897 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109897
Chen, B., Zhang, Z., Lu, Y., Chen, F., Lu, G., Zhang, D.: Semantic-interactive graph convolutional network for multilabel image recognition. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybernet.: Syst. 52(8), 4887–4899 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2021.3103842
Li, Q., Peng, X., Qiao, Y., Peng, Q.: Learning label correlations for multi-label image recognition with graph networks. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 138, 378–384 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2020.07.040
Sang, Y., Li, W.: Classification study of Alzheimer’s disease based on self-attention mechanism and dti imaging using gcn. IEEE Access 12, 24387–24395 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3364545
Kuang, W., Zhu, Q., Li, Z.: Multi-label image classification with multi-scale global-local semantic graph network. In: Koutra, D., Plant, C., Gomez Rodriguez, M., Baralis, E., Bonchi, F. (eds.) Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases: Research Track, pp. 53–69. Springer, Cham (2023)
Ding, C., Sun, S., Zhao, J.: Mst-gat: a multimodal spatial-temporal graph attention network for time series anomaly detection. Inf. Fus. 89, 527–536 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2022.08.011
Ciano, G., Rossi, A., Bianchini, M., Scarselli, F.: On inductive-transductive learning with graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(2), 758–769 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3054304
Zhu, H., Koniusz, P.: Transductive few-shot learning with prototype-based label propagation by iterative graph refinement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 23996–24006 (2023)
Weiyao, X., Muqing, W., Min, Z., Ting, X.: Fusion of skeleton and rgb features for rgb-d human action recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 21(17), 19157–19164 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3089705
Zhou, H., Zhou, W., Qi, W., Pu, J., Li, H.: Improving sign language translation with monolingual data by sign back-translation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1316–1325 (2021)
Mohamed, A., Qian, K., Elhoseiny, M., Claudel, C.: Social-stgcnn: A social spatio-temporal graph convolutional neural network for human trajectory prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2020)
Psychogyios, K., Leligou, H.C., Melissari, F., Bourou, S., Anastasakis, Z., Zahariadis, T.: Samstyler: enhancing visual creativity with neural style transfer and segment anything model (sam). IEEE Access 11, 100256–100267 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3315235
Allingham, J.U., Ren, J., Dusenberry, M.W., Gu, X., Cui, Y., Tran, D., Liu, J.Z., Lakshminarayanan, B.: A simple zero-shot prompt weighting technique to improve prompt ensembling in text-image models. In: Krause, A., Brunskill, E., Cho, K., Engelhardt, B., Sabato, S., Scarlett, J. (eds.) Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 202, pp. 547–568. PMLR, (2023). https://proceedings.mlr.press/v202/allingham23a.html
Zha, W., Liu, Y., Wan, Y., Luo, R., Li, D., Yang, S., Xu, Y.: Forecasting monthly gas field production based on the cnn-lstm model. Energy 260, 124889 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.124889
Sherstinsky, A.: Fundamentals of recurrent neural network (rnn) and long short-term memory (lstm) network. Phys. D: Nonlinear Phenom. 404, 132306 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physd.2019.132306
Deng, Q., Söffker, D.: A review of hmm-based approaches of driving behaviors recognition and prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 7(1), 21–31 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIV.2021.3065933
Zhang, Z., Liu, A., Reid, I., Hartley, R., Zhuang, B., Tang, H.: Motion Mamba: Efficient and Long Sequence Motion Generation with Hierarchical and Bidirectional Selective SSM (2024). arXiv:2403.07487
Li, H., Gao, L., Han, R., Wan, L., Feng, W.: Key action and joint ctc-attention based sign language recognition. In: ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 2348–2352 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054316
Zhang, F., Bazarevsky, V., Vakunov, A., Tkachenka, A., Sung, G., Chang, C.-L., Grundmann, M.: MediaPipe Hands: On-device Real-time Hand Tracking (2020). arXiv:2006.10214
Han, J., Deng, S., Lo, D., Zhi, C., Yin, J., Xia, X.: An empirical study of the dependency networks of deep learning libraries. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution (ICSME), pp. 868–878 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSME46990.2020.00116
Zhou, H., Zhou, W., Zhou, Y., Li, H.: Spatial-temporal multi-cue network for sign language recognition and translation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 24, 768–779 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2021.3059098
Suharjito, Thiracitta, N., Gunawan, H.: Sibi sign language recognition using convolutional neural network combined with transfer learning and non-trainable parameters. Proc. Comput. Sci. 179, 72–80 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.12.011
Keskes, O., Noumeir, R.: Vision-based fall detection using st-gcn. IEEE Access 9, 28224–28236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3058219
Park, C., Park, J., Park, S.: Agcn: attention-based graph convolutional networks for drug-drug interaction extraction. Expert Syst. Appl. 159, 113538 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113538
Li, C., Huang, Q., Mao, Y.: Dd-gcn: Directed diffusion graph convolutional network for skeleton-based human action recognition. In: 2023 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 786–791 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICME55011.2023.00140
Wen, Y.-H., Gao, L., Fu, H., Zhang, F.-L., Xia, S., Liu, Y.-J.: Motif-gcns with local and non-local temporal blocks for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 45(2), 2009–2023 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3170511
Wang, J., Luo, Y.: Sa-gcn: structure-aware graph convolutional networks for crowd pose estimation. J. Supercomput. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-023-05055-z
Guo, T., Liu, M., Liu, H., Wang, G., Li, W.: Improving self-supervised action recognition from extremely augmented skeleton sequences. Pattern Recognit. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2024.110333
Xu, K., Ye, F., Zhong, Q., Xie, D.: Topology-Aware Convolutional Neural Network for Efficient Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In: Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI 2022 vol. 36, pp. 2866–2874 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v36i3.20191arXiv:2112.04178
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hoai Nam Vu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing, Visualization, Supervision. Dat Tran-Anh: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Writing - original draft, Writing—review and editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
All the authors involved have agreed to participate in this submitted article.
Consent for publish
All the authors involved in this manuscript give full consent for publication of this submitted article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hoai, N.V., Tran-Anh, D. Diffusion-guided graph convolutional networks for sign language recognition. SIViP 19, 414 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-025-04007-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-025-04007-9