Abstract
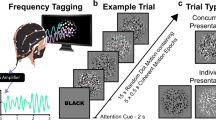
Classification based on EEG data in an RSVP experiment is considered. Although the latency in neural response relative to the stimulus onset time may be more realistically considered to vary across trials due to factors such as subject fatigue and environmental distractions, it is nevertheless assumed to be time-locked to the stimulus in most of the existing work as a means to alleviate the computational complexity. We consider here a more practical scenario that allows variation in response latency and develop a rigorous statistical formulation for modeling the uncertainty within the varying latency coupled with a likelihood ratio test (LRT) for classification. The new model not only improves the EEG classification performance, but also may predict the true stimulus onset time when this information is not precisely available. We test the proposed LRT algorithm on an EEG data set from an image RSVP experiment and show that, by admitting the latency variation, the proposed approach consistently outperforms a method that relies on perfect time-locking (AUC: 0.88 vs 0.86), especially when the stimulus onset time is not precisely available (AUC: 0.84 vs 0.71). Furthermore, the predicted stimulus onset times are highly enriched around the true onset time with p-value \(= 5.2 \times 10^{-44}\).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bigdely-Shamlo, N., Vankov, A., Ramirez, R., Makeig, S. (2008). IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 16(5), 432.
Delorme, A., & Makeig, S. (2004). Journal of neuroscience methods, 134(1), 9.
Eriksen, C., & Spencer, T. (1969). Journal of Experimental Psychology, 79(2p2), 1.
Fawcett, T. (2006). Pattern recognition letters, 27(8), 861.
Felzenszwalb, P., & Huttenlocher, D. (2005). International Journal of Computer Vision, 61(1), 55.
Felzenszwalb, P., Girshick, R., McAllester, D., Ramanan, D. (2010). IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 32(9), 1627.
Fisher, R. (1936). Annals of Human Genetics, 7(2), 179.
Gerson, A., Parra, L., Sajda, P. (2005). Neuroimage, 28(2), 342.
Goupillaud, P., Grossmann, A., Morlet, J. (1984). Geoexploration, 23(1), 85.
Hild, K., Pavel, M., Erdogmus, D., Mathan, S. (2009). In Signals, systems and computers, 2009 conference record of the forty– third IEEE conference on asilomar (pp 51–54).
Luo, A., & Sajda, P. (2009). Comparing neural correlates of visual target detection in serial visual presentations having different temporal correlations. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 3. doi:10.3389/neuro.09.005.2009.
Makeig, S., Bell, A., Jung, T., Sejnowski, T., et al. (1996). In Advances in neural information processing systems pp(145–151).
Meng, J., Merio, L. M., Shamlo, N. B., Makeig, S., Robbins, K., Huang, Y. (2012). PLoS ONE, 7, e44464. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044464.
Niedermeyer, E., & Da Silva, F. (2005). Electroencephalography: basic principles, clinical applications and related fields. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Philiastides, M., Ratcliff, R., Sajda, P. (2006). The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(35), 8965.
Sajda, P., Gerson, A. D., Philiastides, M. G., Parra, L. C. (2007). Single-trial analysis of EEG during rapid visual discrimination: enabling cortically-coupled computer vision.Towards brain-computer interfacing.
Sutton, S., Braren, M., Zubin, J. (1965). E. John, Science, 150(3700), 1187.
VanRullen, R., Busch, N., Drewes, J., Dubois, J. (2011). Frontiers in psychology, 2.
Vidal, J. (1973). Annual Review of Biophysics and Bioengineering, 2(1), 157.
Wolpaw, J., Birbaumer, N., Heetderks, W., McFarland, D., Peckham, P., Schalk, G., Donchin, E., Quatrano, L., Robinson, C., Vaughan, T. (2000). IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering, 8(2), 164.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Army Research Laboratory CANCTA initiative and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities (G12MD007591) from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, J., Meriño, L.M., Robbins, K. et al. Classification of Imperfectly Time-Locked Image RSVP Events with EEG Device. Neuroinform 12, 261–275 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-013-9203-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-013-9203-4