Abstract
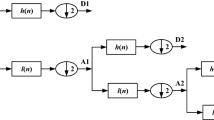
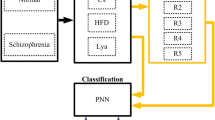
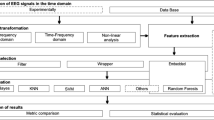
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by neurophysiological dysfunctions that result in disturbances in thinking, perception, and behavior. Early identification of schizophrenia can help prevent potential complications and facilitate effective treatment and management of the condition. This paper proposes a computer aided diagnosis system for the early detection of schizophrenia using 19-channel Electroencephalography (EEG) signals from 28 subjects, leveraging statistical moments of Mel-frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) and ensemble learning. Initially, the EEG signals are passed through a high-pass filter to mitigate noise and remove extraneous data. The feature extraction technique is then employed to extract MFC coefficients from the filtered EEG signals. The dimensionality of these coefficients is reduced by computing their statistical moments, which include the mean, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis, and energy. Subsequently, the Support Vector Machine based Recursive Feature Elimination (SVM-RFE) is applied to identify pertinent features from the statistical moments of the MFC coefficients. These SVM-RFE-based selected features serve as input for three base classifiers: Support Vector Machine, k-Nearest Neighbors, and Logistic Regression. Additionally, an ensemble learning approach, which combines the predictions of the three classifiers through majority voting, is introduced to enhance schizophrenia detection performance and generalize the results of the proposed approach. The study’s findings demonstrate that the ensemble model, combined with SVM-RFE-based selected statistical moments of MFCC, achieves encouraging detection performance, highlighting the potential of machine learning techniques in advancing the diagnostic process of schizophrenia.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The EEG signal dataset used in the research have been acquired from Repository for Open Data (RepOD).
References
Agarwal, M., & Singhal, A. (2023). Fusion of pattern-based and statistical features for schizophrenia detection from eeg signals. Medical Engineering & Physics, 112, 103949.
Ahmed, N., Natarajan, T., & Rao, K. R. (1974). Discrete cosine transform. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 100(1), 90–93.
Ahmedt-Aristizabal, D., Fernando, T., Denman, S., Robinson, J. E., Sridharan, S., Johnston, P. J., Laurens, K. R., & Fookes, C. (2020). Identification of children at risk of schizophrenia via deep learning and eeg responses. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 25(1), 69–76.
Akbari, H., Ghofrani, S., Zakalvand, P., & Sadiq, M. T. (2021). Schizophrenia recognition based on the phase space dynamic of eeg signals and graphical features. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 69, 102917.
Aslan, Z., Akin, M. (2020). Automatic detection of schizophrenia by applying deep learning over spectrogram images of eeg signals. Traitement du Signal,37(2)
Aydemir, E., Dogan, S., Baygin, M., Ooi, C. P., Barua, P. D., Tuncer, T., & Acharya, U. R. (2022). Cgp17pat: Automated schizophrenia detection based on a cyclic group of prime order patterns using eeg signals. In Healthcare (Vol. 10, p. 643). MDPI.
Baygin, M. (2021). An accurate automated schizophrenia detection using tqwt and statistical moment based feature extraction. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 68, 102777.
Berardi, M., Brosch, K., Pfarr, J.-K., Schneider, K., Sültmann, A., Thomas-Odenthal, F., Wroblewski, A., Usemann, P., Philipsen, A., Dannlowski, U., et al. (2023). Relative importance of speech and voice features in the classification of schizophrenia and depression. Translational Psychiatry, 13(1), 298.
Berger, H. (1929). Über das elektroenkephalogramm des menschen. Archiv für Psychiatrie und Nervenkrankheiten, 87(1), 527–570.
Berger, H. (1929). Über das elektroenkephalogramm des menschen. Archiv für Psychiatrie und Nervenkrankheiten, 87(1), 527–570.
Berkson, J. (1944). Application of the logistic function to bio-assay. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 39(227), 357–365.
Bhadra, S., & Kumar, C. J. (2024). Enhancing the efficacy of depression detection system using optimal feature selection from ehr. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 27(2), 222–236.
Buettner, R., Beil, D., Scholtz, S., & Djemai, A. (2020) Development of a machine learning based algorithm to accurately detect schizophrenia based on one-minute eeg recordings. In Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (p. 10). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:210847454
Buettner, R., Hirschmiller, M., Schlosser, K., Rössle, M., Fernandes, M., & Timm, I. J. (2019). High-performance exclusion of schizophrenia using a novel machine learning method on eeg data. In 2019 IEEE International conference on E-health networking, application & services (HealthCom) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Collaborators, G. M. D., et al. (2022). Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. The Lancet Psychiatry, 9(2), 137–150.
Cover, T., & Hart, P. (1967). Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 13(1), 21–27.
Cramer, J. (2002). The origins of logistic regression. Tinbergen Institute, Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers.[SPACE]https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.360300
Davis, S., & Mermelstein, P. (1980). Comparison of parametric representations for monosyllabic word recognition in continuously spoken sentences. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 28(4), 357–366.
de Miras, J. R., Ibáñez-Molina, A. J., Soriano, M. F., & Iglesias-Parro, S. (2023). Schizophrenia classification using machine learning on resting state eeg signal. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 79, 104233.
Desai, K. (2023). Using electroencephalographic signal processing and machine learning binary classification to diagnose schizophrenia. Research Square. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2715657/v1
Dietterich, T. G. (2000). Ensemble methods in machine learning. In International workshop on multiple classifier systems (pp. 1–15). Springer.
Diogo, V. S., Ferreira, H. A., Prata, D., & Initiative, A. D. N. (2022). Early diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease using machine learning: A multi-diagnostic, generalizable approach. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy, 14(1), 107.
Drucker, H. (1997). Improving regressors using boosting techniques. In Icml (Vol. 97, p. e115). Citeseer.
Escabí, M. A. (2005) 10 - biosignal processing. In J. D. Enderle, S. M. Blanchard, & J. D. Bronzino (Eds.), Introduction to biomedical engineering (Second edition) (2nd ed., pp. 549–625). Biomedical Engineering, Academic Press, Boston. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-238662-6.50012-4. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780122386626500124
Fleischmann, A., & De Leo, D. (2014). The world health organization’s report on suicide: A fundamental step in worldwide suicide prevention. The Journal of Crisis Intervention and Suicide Prevention, 35(5), 289–291.
Grattan-Guinness, I. (2005). Joseph fourier, théorie analytique de la chaleur (1822). In Landmark Writings in Western Mathematics 1640-1940 (pp. 354–365). Elsevier.
Green, D. M., Swets, J. A., et al. (1966). Signal detection theory and psychophysics (Vol. 1). Wiley New York.
Guyon, I., Weston, J., Barnhill, S., & Vapnik, V. (2002). Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Machine Learning, 46, 389–422.
Hajian-Tilaki, K. (2013). Receiver operating characteristic (roc) curve analysis for medical diagnostic test evaluation. Caspian Journal of Internal Medicine, 4(2), 627.
Hearst, M. A., Dumais, S. T., Osuna, E., Platt, J., & Scholkopf, B. (1998). Support vector machines. IEEE Intelligent Systems and their applications, 13(4), 18–28.
Institute of health metrics and evaluation (ihme). global health data exchange (ghdx). (2019). http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool?params=gbd-api-2019-permalink/27a7644e8ad28e739382d31e77589dd7. Accessed 18 March 2024.
Jahmunah, V., Oh, S. L., Rajinikanth, V., Ciaccio, E. J., Cheong, K. H., Arunkumar, N., & Acharya, U. R. (2019). Automated detection of schizophrenia using nonlinear signal processing methods. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 100, 101698.
Keeley, B. (2021). The state of the world’s children 2021: On my mind–promoting, protecting and caring for children’s mental health. UNICEF.
Kim, J.-Y., Lee, H. S., & Lee, S.-H. (2020). Eeg source network for the diagnosis of schizophrenia and the identification of subtypes based on symptom severity—a machine learning approach. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 3934.
Ko, D.-W., & Yang, J.-J. (2022). Eeg-based schizophrenia diagnosis through time series image conversion and deep learning. Electronics, 11(14), 2265.
Krishnapriya, B. (2024). Eeg-based identification of schizophrenia using deep learning techniques. In Computational intelligence and Network Systems: First International Conference, CINS 2023, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, October 18-20, 2023, Proceedings (p. 26). Springer Nature.
Kumar, J. S., & Bhuvaneswari, P. (2012). Analysis of electroencephalography (eeg) signals and its categorization-a study. Procedia engineering, 38, 2525–2536.
Kumar, T. S., Rajesh, K. N., Maheswari, S., Kanhangad, V., & Acharya, U. R. (2023). Automated schizophrenia detection using local descriptors with eeg signals. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 117, 105602.
Kumar, T. S., Rajesh, K. N., Maheswari, S., Kanhangad, V., & Acharya, U. R. (2023). Automated schizophrenia detection using local descriptors with eeg signals. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 117, 105602.
Mental health. (2022). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthening-our-response. Accessed 18 Mar 2024.
Mikolas, P., Marxen, M., Riedel, P., Bröckel, K., Martini, J., Huth, F., Berndt, C., Vogelbacher, C., Jansen, A., Kircher, T., et al. (2024). Prediction of estimated risk for bipolar disorder using machine learning and structural mri features. Psychological Medicine, 54(2), 278–288.
Moitra, M., Santomauro, D., Degenhardt, L., Collins, P. Y., Whiteford, H., Vos, T., & Ferrari, A. (2021). Estimating the risk of suicide associated with mental disorders: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 137, 242–249.
Najafzadeh, H., Esmaeili, M., Farhang, S., Sarbaz, Y., & Rasta, S. H. (2021). Automatic classification of schizophrenia patients using resting-state eeg signals. Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine, 44(3), 855–870.
Oh, S. L., Vicnesh, J., Ciaccio, E. J., Yuvaraj, R., & Acharya, U. R. (2019). Deep convolutional neural network model for automated diagnosis of schizophrenia using eeg signals. Applied Sciences, 9(14), 2870.
Olejarczyk, E., & Jernajczyk, W. (2017). EEG in schizophrenia. (2017). https://doi.org/10.18150/repod.0107441
Olejarczyk, E., & Jernajczyk, W. (2017). Graph-based analysis of brain connectivity in schizophrenia. PLoS ONE, 12(11), 1–28.
Richhariya, B., Tanveer, M., Rashid, A. H., Initiative, A. D. N., et al. (2020). Diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease using universum support vector machine based recursive feature elimination (usvm-rfe). Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 59, 101903.
Schizophrenia. (2022). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schizophrenia. Accessed 18 March 2024.
Shams, A. M., & Jabbari, S. (2024). A deep learning approach for diagnosis of schizophrenia disorder via data augmentation based on convolutional neural network and long short-term memory. Biomedical Engineering Letters, 1–13.
Sharma, A., & Verbeke, W. J. (2020). Improving diagnosis of depression with xgboost machine learning model and a large biomarkers dutch dataset (n= 11,081). Frontiers in big Data, 3, 15.
Shen, M., Wen, P., Song, B., & Li, Y. (2024). 3d convolutional neural network for schizophrenia detection using as eeg-based functional brain network. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 89, 105815.
Shoeibi, A., Ghassemi, N., Khodatars, M., Moridian, P., Khosravi, A., Zare, A., Gorriz, J. M., Chale-Chale, A. H., Khadem, A., & Rajendra Acharya, U. (2023). Automatic diagnosis of schizophrenia and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in rs-fmri modality using convolutional autoencoder model and interval type-2 fuzzy regression. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 17(6), 1501–1523.
Singh, T. (2019) Fourier transform. (2019). https://medium.com/@tanveer9812/mfccs-made-easy-7ef383006040. Accessed 10 Feb 2024
Soria, C., Arroyo, Y., Torres, A. M., Redondo, M. Á., Basar, C., & Mateo, J. (2023). Method for classifying schizophrenia patients based on machine learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4375.
Soria, C., Arroyo, Y., Torres, A. M., Redondo, M. Á., Basar, C., & Mateo, J. (2023). Method for classifying schizophrenia patients based on machine learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4375.
Sun, J., Cao, R., Zhou, M., Hussain, W., Wang, B., Xue, J., & Xiang, J. (2021). A hybrid deep neural network for classification of schizophrenia using eeg data. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 4706.
Supakar, R., Satvaya, P., & Chakrabarti, P. (2022). A deep learning based model using rnn-lstm for the detection of schizophrenia from eeg data. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 151, 106225.
Teixeira, F. L., Costa, M. R. e., Abreu, J. P., Cabral, M., Soares, S. P., & Teixeira, J. P. (2023). A narrative review of speech and eeg features for schizophrenia detection: Progress and challenges. Bioengineering,10(4), 493.
Tyagi, A., Singh, V. P., & Gore, M. M. (2021). Improved detection of coronary artery disease using dt-rfe based feature selection and ensemble learning. In International conference on advanced network technologies and intelligent computing (pp. 425–440). Springer.
Tyagi, A., Singh, V. P., & Gore, M. M. (2022). Machine learning approaches for the detection of schizophrenia using structural mri. In International conference on advanced network technologies and intelligent computing (pp. 423–439). Springer.
Tyagi, A., Singh, V. P., & Gore, M. M. (2023). Towards artificial intelligence in mental health: A comprehensive survey on the detection of Schizophrenia. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 82(13), 20343–20405.
Tyagi, A., Singh, V. P., & Gore, M. M. (2023). An efficient automated detection of schizophrenia using k-nn and bag of words features. SN Computer Science, 4(5), 518.
Vyškovskỳ, R., Schwarz, D., Churová, V., & Kašpárek, T. (2022). Structural mri-based schizophrenia classification using autoencoders and 3d convolutional neural networks in combination with various pre-processing techniques. Brain Sciences, 12(5), 615.
Zhang, L. (2019). Eeg signals classification using machine learning for the identification and diagnosis of schizophrenia. In 2019 41st annual international conference of the ieee engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC) (pp. 4521–4524). IEEE.
Zhang, J., Yang, H., Li, W., Li, Y., Qin, J., & He, L. (2022). Automatic schizophrenia detection using multimodality media via a text reading task. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 16, 933049.
Zhang, J., Zhongde, P., Chao, G., Jie, Z., & Donghong, C. (2016). Clinical investigation of speech signal features among patients with Schizophrenia. Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 28(2), 95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author contributions are listed below. Ashima Tyagi: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Investigation, and formal analysis Vibhav Prakash Singh: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, and Supervision Manoj Madhava Gore: Resources, Supervision, and Validation
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not incorporate research involving human subjects or animals conducted by any of the authors.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tyagi, A., Singh, V.P. & Gore, M.M. Detection of Schizophrenia from EEG Signals using Selected Statistical Moments of MFC Coefficients and Ensemble Learning. Neuroinform 22, 499–520 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-024-09684-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-024-09684-4