Summary
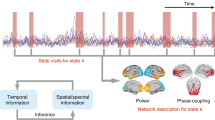
This paper presents superbinding, a concept that represents integrative oscillatory dynamics over the time and space axes. Principle of superposition describes integration over the temporal axis; selectively distributed and selectively coherent oscillatory neural populations describe integration over the spatial axis. Integrative activity is a function of the coherences between spatial locations of the brain; these coherences vary according to the type of sensory and or cognitive event and possibly the consciousness state of the species. Complex percepts and integrative activity in general that is achieved by superbinding supported by the neurons-brain theory may replace the Sherringtonian integrative brain function that is achieved through the single neuron doctrine.
Results of recent experiments related to the percept of the grandmother-face support our concept of super-synergy in the whole brain in order to explain manifestation of Gestalts and Memory-Stages. The strategies of the Grandmother paradigm may open new horizons in search of memories or evolving memories, and possibly provide relevant clinical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles, M.; Prut, Y. (1996) Spatio-temporal firing pattern in the frontal cortex of behaving monkeys. J. Physiology 90: 249–250.
Barlow, H. B.; (1995) The neuron doctrine in perception. In: M. Gazzaniga (ed) The Cognitive Neurosciences, Vol. 1, Cambridge, MIT Press, 1995, pp 415–436.
Başar, E. (1980) EEG-Brain Dynamics: Relation Between EEG and Brain Evoked Potentials, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Başar, E. (1999) Brain Function and Oscillations, II. Integrative Brain Function - Neurophysiology and Cognitive Processes, Springer, Berlin.
Başar, E.; Başar-Eroğlu, C.; Karakaş, S.; Schürmann, M. (1999) Are cognitive processes manifested in event-related gamma, alpha, theta and delta oscillations in the EEG? Neurosci. Lett. 259: 165–168.
Başar, E.; Başar-Eroğlu, C.; Karakaş, S.; Schürmann, M. (2000) Brain oscillations in perception and memory. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 35: 95–124.
Başar, E.; Hai, R.; Lopes da Silva, F. H.; Schürmann, M. (eds) (1997) Brain Alpha Activity — New Aspects and Functional Correlates. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 26: 1–482.
Başar, E.; Özgören, M.; Karakaş, S. (2001) A Brain Theory Based on Neural Assemblies and Superbinding. In: Reuter, H.; Schwab, P.; Kleiber, D., Gniech, G. (eds) Wahrnehmen und Erkennen. PABST Science Publishers, Lengerich, pp 11–24.
Başar, E.; Özgören, M.; Karakaş, S.; Başar-Eroğlu, C. (2002) Super-synergy in Brain oscillations and the grandmother percept. Int. J. Bifurcation and Chaos (submitted).
Berger, H. (1929) Über das Elektroenzephalogramm des Menschen, Bericht, Arch. Psychit. Nervenk 87: 27–570.
Bullock, T. H.; McClune, M. C. (1989) Lateral coherence of the electrocorticogram: a new measure of brain synchrony. EEG and clinical Neurophysiol. 73: 479–498.
Chen, A. C. N.; Herrmann, C. S. (2001) Perception of pain coincides with the spatial expansion of electroencephalographic dynamics in human subjects. Neurosci. Lett. 297: 183–186.
Courtney, S. M.; Ungerleider, L. G.; Keil, K.; Haxby, J. V. (1997) Transient and sustained activity in a distributed neural system for human working memory. Nature 386: 608–611.
Crick, F.; Koch, C. (1998) Consciousness and neuroscience. Cerbral Cortex 8: 97–107.
Doppelmayr, M.; Kbimesch, W.; Schwaiger, J.; Stadler, W.; Röhm, D. (2000) The time locked theta response reflects interindividual diferences in human memory performance. Neuroscience Letters 278: 141–144.
Eckhorn, R.; Bauer, R.; Jordan, R.; Brosch, W.; Kruse, M.; Munk, M.; Reitboeck, H. J. (1988) Coherent oscillations: a mechanism of feature linking in the visual cortex? Biol. Cybern. 60: 121–130.
Engel, A. K.; Fries, P.; Singer, W. (2001) Dynamic predictions: oscillations and synchrony in top-down processing. Nature Rev. Neuroscience 2: 704–716.
Fuster, J. M. (1997) Network Memory. Trends Neurosci. 20: 451–459.
Gray, C. M.; Singer, W. (1989) Stimulus-specific neuronal oscillations in orientation columns of cat visual cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 86: 1698–1702.
Grossberg, S. (1999) The link between brain learning, attention, and consciousness. Conscious Cogn. 8(1): 1–44.
Haenschel, C.; Baldeweg, T.; Croft, R. J.; Whittington, M.; Gruzelier, J. (2000) Gamma and beta frequency oscillations in response to novel auditory stimuli: A comparison of human electroencephalogram (EEG) data with in vitro models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97(13): 7645–7650.
Hebb, D. O. (1949) The organization of behaviour, Wiley, New York.
Karakaş, S.; Erzengin, O. U.; Başar, E. (2000) The genesis of human event-related responses explained through the theory of oscillatory neural assemblies. Neurosci. Lett. 285(1): 45–48.
Kiss, T.; Orban G.; Lengyel M.; Erdi P. (2001) Intrahippocampal gamma and theta rhythm generation in a network model of inhibitory interneurons. Neurocomputing 38–40: 713–719.
Klimesch, W.; Doppelmayr, M.; Pöllhuber, D.; Stadler, W. (2000) Simultaneous desynchronization and synchronization of different alpha responses in the human electroencephalograph: a neglected paradox? Neurosci. Lett. 284: 97–100.
Kocsis, B.; Viana, Di Prisco G.; Vertes, R. P. (2001) Theta synchronization in the limbic system: The role of Gudden’s tegmental nuclei. European J. Neuroscience 13(2): 381–388.
Miltner, W.; Braun, C.; Arnold, M.; Witte, H.; Taub, E. (1999) Coherence of gamma-band EEG activity as a basis for associative learning. Nature 397: 434–436.
Mountcastle, V. B. (1998) Perceptual Neuroscience. The Cerebral Cortex, Harvard University Press.
Pulvermuller, F.; Preissl, H.; Lutzenberger, W.; Birbaumer, N. (1996) Brain rhythms of language: nouns versus verbs. The European Journal of Neuroscience 8: 937–941.
Quiroga, R Q.; Rosso, O. A.; Başar, E. (1999) Wavelet entropy: a measure of order in evoked potentials. Electrenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol. Suppl. 49: 299–303.
Sakowitz, O. W.; Quiroga, R. Q.; Schürmann, M.; Başar, E. (2001) Bisensory stimulation increases gammaresponses over multiple cortical regions. Cognitive Brain Res. 11: 267–279.
Schürmann, M.; Demiralp, T.; Başar, E.; Başar-Eroğlu, C. (2000) Electroencephalogram alpha (8–15) responses to visual stimuli in dat cortex, thalamus, and hippocampus: a distributed alpha network? Neurosci. Lett., 292: 175–178.
Schütt, A.; Başar, E.; Bullock, T. H. (1992) The effects of acetylcholine, dopamine and noradrenaline on the visceral ganglion of Helix pomatia. 1. Ongoing compound field potentials of low frequencies. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 102(1): 159–168.
Sherrington, C. (1948) The Integrative Action of the Nervous System. Cambridge University Press.
Stryker, M. P. (1989) Is grandmother an oscillation? Nature, 338: 297–298.
Tallon-Baudry, C.; Bertrand, O.; Peronnet, F.; Pernier, J. (1998) Induced gamma-band activity during the delay of a visual short-term memory task in humans. J. Neurosci. 18: 4244–4254.
Yordanova, J.; Kolev, V.; Rosso, O. A.; Schürmann, M.; Sakowitz, O. W.; Özgören, M.; Başar, E. (2002) Wavelet entropy analysis of event-related potentials indicates modality-independent theta dominance. Journal of Neuroscience Methods (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Başar, E., Özgören, M., Başar-Eroğlu, C. et al. Superbinding: Spatio-temporal oscillatory dynamics. Theory Biosci. 121, 371–386 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-003-0043-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-003-0043-x