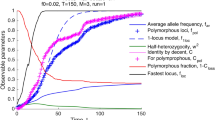
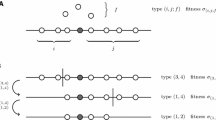
Abstract
Sympatric speciation is still debatable, though some well documented empirical data that support it already exist. Our computer modeling reveals that sympatric speciation is an intrinsic property of the expanding populations with differentiated inbreeding—higher at the edges and lower inside the territory. At the edges of expanding populations, the probability of forming deleterious phenotypes by placing two defective alleles in the corresponding loci is relatively high even with low genetic load. Thus, the winning strategy is to use rather the complementary haplotypes to form zygotes. This strategy leads to a very fast sympatric speciation and specific distribution of recombination activity along the chromosomes—higher at the subtelomeric regions (close to the ends of chromosomes) and lower in the middle of chromosomes, which is also observed in all human chromosomes (excluding Y).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barluenga M, Stolting KN, Salzbulger W, Muschick M, Meyer A (2006) Sympatric speciation in Nicaraguan crater lake cichlid fish. Nature 439:719–723
Bońkowska K, Kula M, Cebrat S, Stauffer D (2007) Inbreeding and outbreeding depressions in the Penna model as a result of crossover frequency. Int J Mod Phys C 18(8), ArXiv q-bio/0702041
Bunje PME, Barluenga M, Meyer A (2007) Sampling genetic diversity in the sympatrically and allopatrically speciating Midas cichlid species complex over a 16 year time series. BMC Evol Biol 7:25–39
Cheung VG, Burdick JT, Hirschmann D, Morley M (2007) Polymorphic variation in human meiotic recombination. Am J Hum Genet 80:526–530
Doebeli M, Dieckmann U (2003) Speciation along environmental gradients. Nature 421:259–264
Ehlers A, Beck S, Forbes SA, Trowsdale J, Volz A, Younger R, Ziegler A (2000) MHC-linked olfactory receptor loci exhibit polymorphism and contribute to extended HLA/OR-haplotypes. Genome Res 10:1968–1978
Feldmesser E, Olender T, Khen M, Yanai I, Ophir R, Lancet D (2006) Widespread ectopic expression of olfactory receptor genes. BMC Genomics 7:121–139
Fernandez N, Cooper J, Sprinks M, AbdElrahman M, Fiszer D, Kurpisz M, Dealtry G (1999) A critical review of the role of the major histocompatibility complex in fertilization, preimplantation development and feto-maternal interactions. Hum Reprod Update 5:234–248
Fukuda N, Yomogida K, Okabe M, Touhara K (2004) Functional characterization of a mouse testicular olfactory receptor and its role in chemosensing and in regulation of sperm motility. J Cell Sci 117:5835–5845
Garver-Apgar CE, Gangestad SW, Thornhill R, Miller RD, Olp JJ (2006) Major histocompatibility complex alleles, sexual responsivity, and unfaithfulness in romantic couples. Psychol Sci 17:830–835
Gendzekhadze K, Norman PJ, Abi-Rached L, Layrisse Z, Parham P (2006) High KIR diversity in Amerindians is maintained using few gene-content haplotypes. Immunogenetics 58:474–480
Glusman G, Yanai I, Rubin I, Lancet D (2001) The complete human olfactory subgenome. Genome Res 11:685–702
Hiby SE, Walker JJ, O’shaughnessy KM, Redman CW, Carrington M, Trowsdale J, Moffett AJ (2004) Combinations of maternal KIR and fetal HLA-C genes influence the risk of preeclampsia and reproductive success. Exp Med 200:957–965
Hoffman JI, Forcada J, Trathan PN, Amos W (2007) Female fur seals show active choice for males that are heterozygous and unrelated. Nature 445:912–915
Jacob S, McClintock MK, Zelano B, Ober C (2002) Paternally inherited HLA alleles are associated with women’s choice of male odor. Nat Genet 30:175–179
Jensen-Seaman MI, Furey TS, Payseur BA, Lu Y, Roskin KM, Chen CF, Thomas MA, Haussler D, Jacob HJ (2004) Comparative recombination rates in the rat, mouse, and human genomes. Genome Res 14:528–538
Jiggins CD (2006) Sympatric speciation: why the controversy? Curr Biol 16:R333–R334
Kong A, Gudbjartsson DF, Sainz J, Jonsdottir GM, Gudjonsson SA, Richardsson B, Sigurdardottir S, Barnard J, Hallbeck B, Masson G, Shlien A, Palsson ST, Frigge ML, Thorgeirsson TE, Gulcher JR, Stefansson K (2002) A high-resolution recombination map of the human genome. Nat Genet 31:241–247
Łaszkiewicz A, Szymczak Sz, Cebrat S (2003) Speciation effect in the Penna aging model. Int J Mod Phys C 14:765–774
Lederberg J, Cavalli LL, Lederberg EM (1952) Sex compatibility in Escherichia coli. Genetics 37:720–730
Luz-Burgoa K, Moss de Oliveira S, Schwämmle V, Sá Martins JS (2006) Thermodynamic behavior of a phase transition in a model for sympatric speciation. Phys Rev E 74:021910
Mayr E (1942) Systematics and the origin of species. Columbia Press, New York
Novick RP (1987) Plasmid incompatibility. Microbiol Rev 51:381–395
Ober C, Weitkamp LR, Cox N, Dytch H, Kostyu D, Elias S (1997) HLA and mate choice in humans. Am J Hum Genet 61:497–504
Ober C, Hyslop T, Elias S, Weitkamp LR, Hauck WW (1998) Human leukocyte antigen matching and fetal loss: results of a 10 year prospective study. Hum Reprod 13:33–38
Payseur BA, Nachman MW (2000) Microsatellite variation and recombination rate in the human genome. Genetics 156:1285–1298
Pękalski A (2007) Simple model of mating preference and extinction. Int J Mod Phys C 18(10) (in press)
Potts WK, Manning CJ, Wakeland EK (1991) Mating patterns in seminatural populations of mice influenced by MHC genotype. Nature 352:619–621
Santos PS, Schinemann JA, Gabardo J, Bicalho Mda G (2005) New evidence that the MHC influences odor perception in humans: a study with 58 Southern Brazilian students. Horm Behav 47:384–388
Schwämmle V, Sousa AO, Moss de Oliveira S (2006) Monte Carlo simulations of parapatric speciation. Eur Phys J B 51:563–570. doi: 10.1140/epjb/e2006-00251-5
Seehausen O (2006) Conservation: losing biodiversity by reverse speciation. Curr Biol 16:R334–R337
Som C, Reyer H-U (2006) Variation in sex ratio and evolutionary rate of hemiclonal Rana esculenta populations. Evol Ecol 20:159–172
Spehr M, Schwane K, Riffell JA, Zimmer RK, Hatt H (2006) Odorant receptors and olfactory-like signaling mechanisms in mammalian sperm. Mol Cell Endocrinol 250:128–136
Stauffer D, Moss de Oliveira S, de Oliveira PMC, Sá Martins JS (2006) Biology, sociology, geology by computational physicists. Elsevier, Amsterdam
The International HapMap Consortium (2003) The international hapmap project. Nature 426:789–796
Trowsdale J (2001) Genetic and functional relationships between MHC and NK receptor genes. Immunity 15:363–374
Wedekind C, Seebeck T, Bettens F, Paepke AJ (1995) MHC-dependent mate preferences in humans. Proc Biol Sci 260:245–249
Yamazaki K, Boyse EA, Mike V, Thaler HT, Mathieson BJ, Abbott J, Boyse J, Zayas ZA, Thomas L (1976) Control of mating preferences in mice by genes in the major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med 144:1324–1335
Yawata M, Yawata N, Draghi M, Little AM, Partheniou F, Parham P (2006) Roles for HLA and KIR polymorphisms in natural killer cell repertoire selection and modulation of effector function. J Exp Med 203:633–645
Younger RM, Amadou C, Bethel G, Ehlers A, Lindahl KF, Forbes S, Horton R, Milne S, Mungall AJ, Trowsdale J, Volz A, Ziegler A, Beck S (2001) Characterization of clustered MHC-linked olfactory receptor genes in human and mouse. Genome Res 11:519–530
Zawierta M, Biecek P, Waga W, Cebrat S (2007) The role of intragenomic recombination rate in the evolution of population’s genetic pool. Theory Biosci. doi:10.1016/j.thbio.2007.02.002
Ziegler A, Dohr G, Uchanska-Ziegler B (2002) Possible roles for products of polymorphic MHC and linked olfactory receptor genes during selection processes in reproduction. Am J Reprod Immunol 48:34–42
Acknowledgments
We thank D. Stauffer, S. Moss de Oliveira and PMC de Oliveira for discussion. The work was supported by ESF/COST, FP6/GIACS and Polish Foundation for Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waga, W., Mackiewicz, D., Zawierta, M. et al. Sympatric speciation as intrinsic property of the expanding population. Theory Biosci. 126, 53–59 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-007-0010-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12064-007-0010-z