Abstract
The focus of power producers has shifted from conventional energy sources to sustainable energy sources because of the depletion of fossil fuels and carbon emission causing global warming and climate change. Solar cells are the most prominent option to deal with these problems. The precise estimation of solar cell parameters is very much required before their installation to achieve high efficiency. In recent years applications of several optimization algorithms for parameter estimation of the solar cell have been addressed. Recently, intelligent grey wolf optimizer (IGWO), which is an advanced version of grey wolf optimizer (GWO) incorporating a sinusoidal truncated function as a bridging mechanism and opposition based learning has been introduced. The wide applicability of this variant has been examined over different conventional benchmark functions and on some real problems. This fact motivated authors to employ this variant on parameter extraction process. The main motivation behind the implementation of IGWO on solar cell parameter estimation process is the efficiency of this version to deal with complex optimization problems. To estimate the PV cell parameter values, measurement of voltage and current are considered at three important points. These are open circuit point, short circuit point and maximum power point, for two solar cell representative models i.e. single diode model and double diode model. Results of IGWO are compared with the results of other variants of GWO on these two models and for three films (Mono crystalline, poly crystalline and thin film). Results reveal that IGWO produces better results.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PV cell:
-
Photovoltaic cell
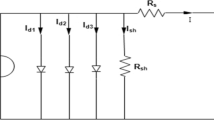
- \(R_{SE}\) :
-
Resistance of series
- \(R_{SH}\) :
-
Resistance of parallel
- \(\psi\) :
-
Ideality factor
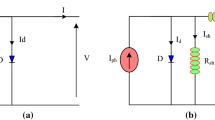
- \(I_{dmc}\) :
-
Generated photocurrent
- \(I_{rsc}\) :
-
Reverse saturation current
- \({\psi _{1}} \ \&\ {\psi _{2}}\) :
-
Ideality factor of first and second diode
- \({I_{rsc_{1}}} \ \&\ {I_{rsc_{2}}}\) :
-
Reverse saturation current of first and second diode
- \(I_{D}\) :
-
Shockley diode equation
- q :
-
Electron charge
- k :
-
Boltzmann constant
- T:
-
Absolute temperature of diode junction (Kelvin)
- \(N_{S}\) :
-
Number of series cells
- \(V_{OC} \ \&\ I_{OC}\) :
-
Voltage and current at open circuit point
- \(V_{SC} \ \&\ I_{SC}\) :
-
Voltage and current at short circuit point
- \(V_{MPP} \ \&\ I_{MPP}\) :
-
Voltage and current at maximum power point
- \(\overrightarrow{K} \ \&\ \overrightarrow{M}\) :
-
Coefficient vector
- \(\overrightarrow{Y}\) :
-
Position vector of grey wolf
- \(r_{1} \ \&\ r_{2}\) :
-
Random numbers
- \(\overrightarrow{c}\) :
-
Control vector
References
El-Naggar KM, AlRashidi MR, AlHajri MF, Al-Othman AK (2012) Simulated annealing algorithm for photovoltaic parameters identification. Sol Energy 86(1):266–274
AlHajri MF, El-Naggar KM, AlRashidi MR, Al-Othman AK (2012) Optimal extraction of solar cell parameters using pattern search. Renew Energy 44:238–245
Ishaque K, Salam Z, Mekhilef S, Shamsudin A (2012) Parameter extraction of solar photovoltaic modules using penalty-based differential evolution. Appl Energy 99:297–308
Askarzadeh A, Rezazadeh A (2013) Extraction of maximum power point in solar cells using bird mating optimizer-based parameters identification approach. Sol Energy 90:123–133
Gong W, Cai Z (2013) Parameter extraction of solar cell models using repaired adaptive differential evolution. Sol Energy 94:209–220
Jiang LL, Douglas LM, Jagdish CP (2013) Parameter estimation of solar cells and modules using an improved adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Appl Energy 112:185–193
Rajasekar N, Neeraja KK, Rini V (2013) Bacterial foraging algorithm based solar PV parameter estimation. Sol Energy 97:255–265
Bagher AM, Mirzaei MAV, Mirhabibi M (2015) Types of solar cells and application. Am J Opt Photon 3(5):94–113
Differences of Solar Cell Modules. https://www.semprius.com/comparing-mono-polycrystalline-and-thin-film-solar-panels/
Arjyadhara P, Ali SM, Jena C (2013) Analysis of solar PV cell performance with changing irradiance and temperature. Int J Eng Comput Sci 2(1):214–220
Bai J, Liu S, Hao Y, Zhang Z, Jiang M, Zhang Yu (2014) Development of a new compound method to extract the five parameters of PV modules. Energy Convers Manage 79:294–303
Joshi AS, Dincer I, Reddy BV (2009) Performance analysis of photovoltaic systems: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 13(8):1884–1897
Ma T, Yang H, Lin L (2013) Performance evaluation of a stand-alone photovoltaic system on an isolated island in Hong Kong. Appl Energy 112:663–672
Ghoneim AA (2006) Design optimization of photovoltaic powered water pumping systems. Energy Convers Manage 47(11–12):1449–1463
Jordehi AR (2016) Parameter estimation of solar photovoltaic (PV) cells: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 61:354–371
Allam D, Yousri DA, Eteiba MB (2016) Parameters extraction of the three diode model for the multi-crystalline solar cell/module using Moth–Flame Optimization Algorithm. Energy Convers Manage 123:535–548
Nishioka K, Sakitani N, Uraoka Y, Fuyuki T (2007) Analysis of multicrystalline silicon solar cells by modified 3-diode equivalent circuit model taking leakage current through periphery into consideration. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 91(13):1222–1227
Ishaque K, Salam Z, Taheri H (2011) Simple, fast and accurate two-diode model for photovoltaic modules. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 95(2):586–594
Appelbaum J, Peled A (2014) Parameters extraction of solar cellsA comparative examination of three methods. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 122:164–173
Oliva D, Cuevas E, Pajares G (2014) Parameter identification of solar cells using artificial bee colony optimization. Energy 72:93–102
Alam DF, Yousri DA, Eteiba MB (2015) Flower pollination algorithm based solar PV parameter estimation. Energy Convers Manage 101:410–422
Chin VJ, Zainal S, Kashif I (2015) Cell modelling and model parameters estimation techniques for photovoltaic simulator application: A review. Appl Energy 154:500–519
Jamadi M, Merrikh-Bayat F, Bigdeli M (2016) Very accurate parameter estimation of single-and double-diode solar cell models using a modified artificial bee colony algorithm. Int J Energy Environ Eng 7(1):13–25
Xiong G, Zhang J, Shi D, He Y (2018) Parameter extraction of solar photovoltaic models using an improved whale optimization algorithm. Energy Convers Manage 174:388–405
Abd Elaziz M, Oliva D (2018) Parameter estimation of solar cells diode models by an improved opposition-based whale optimization algorithm. Energy Convers Manage 171:1843–1859
Biswas PP, P. N S, Guohua W, Gehan AJA (2019) Parameter estimation of solar cells using datasheet information with the application of an adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Renew Energy 132:425–438
Hassanien AE, Rizk-Allah RM, Elhoseny M (2018) A hybrid crow search algorithm based on rough searching scheme for solving engineering optimization problems. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput pp 1–25
Rizk-Allah RM, Hassanien AE, Bhattacharyya S (2018) Chaotic crow search algorithm for fractional optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 71:1161–1175
Rizk-Allah RM, Hassanien AE (2018) New binary bat algorithm for solving 0–1 knapsack problem. Complex Intell Syst 4(1):31–53
Rizk-Allah RM, Hassanien AE, Elhoseny M, Gunasekaran M (2019) A new binary salp swarm algorithm: development and application for optimization tasks. Neural Comput Appl 31(5):1641–1663
Zhang Y, Gong DW, Sun XY, Geng N (2014) Adaptive bare-bones particle swarm optimization algorithm and its convergence analysis. Soft Comput 18(7):1337–1352
Zhang Y, Gong DW, Ding Z (2012) A bare-bones multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm for environmental/economic dispatch. Inf Sci 192:213–227
Zhang Y, Song XF, Gong DW (2017) A return-cost-based binary firefly algorithm for feature selection. Inf Sci 418:561–574
Saxena A, Bhanu PS, Rajesh K, Vikas G (2018) Intelligent Grey Wolf OptimizerDevelopment and application for strategic bidding in uniform price spot energy market. Appl Soft Comput 69:1–13
Villalva MG, Jonas RG, Ernesto RF (2009) Comprehensive approach to modeling and simulation of photovoltaic arrays. IEEE Trans Power Electron 24(5):1198–1208
Soon JJ, Kay-Soon L (2012) Photovoltaic model identification using particle swarm optimization with inverse barrier constraint. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(9):3975–3983
KC200GT High Efficiency Multicrystal Photovoltaic Module Datasheet Kyocera. http://www.kyocerasolar.com/assets/001/5195.pdf
Mirjalili S, Seyed MM, Andrew L (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61
Emary E, Hossam MZ, Aboul EH (2016) Binary grey wolf optimization approaches for feature selection. Neurocomputing 172:371–381
Gupta E, Saxena A (2016) Grey wolf optimizer based regulator design for automatic generation control of interconnected power system. Cogent Eng 3(1):1151612
Saxena A, Shekhawat S. (2017). Ambient air quality classification by grey wolf optimizer based support vector machine. J Environ Public Health
Tizhoosh HR (2005) Opposition-based learning: a new scheme for machine intelligence. In: International conference on computational intelligence for modelling, control and automation and international conference on intelligent agents, web technologies and internet commerce (CIMCA-IAWTIC’06), vol 1, pp 695-701. IEEE
Shekhawat S, Saxena A (2020) Development and applications of an intelligent crow search algorithm based on opposition based learning. ISA Trans 99:210–230
Saxena A (2019) A comprehensive study of chaos embedded bridging mechanisms and crossover operators for grasshopper optimisation algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 132:166–188
Saxena A, Kumar R, Das S (2019) chaotic map enabled grey wolf optimizer. Appl Soft Comput 75:84–105
Dinkar SK, Deep K (2017) Opposition based Laplacian ant lion optimizer. J Comput Sci 23:71–90
Khandelwal A, Bhargava A, Sharma A, Sharma H (2018) Modified grey wolf optimization algorithm for transmission network expansion planning problem. Arab J Sci Eng 43(6):2899–2908
Yang B, Zhang X, Tao Yu, Shu H, Fang Z (2017) Grouped grey wolf optimizer for maximum power point tracking of doubly-fed induction generator based wind turbine. Energy Convers Manage 133:427–443
Madhiarasan M, Deepa SN (2016) Long-term wind speed forecasting using spiking neural network optimized by improved modified grey wolf optimization algorithm. Int J Adv Res 4(7):356–368
Mittal N, Urvinder S, Balwinder SS (2016) Modified grey wolf optimizer for global engineering optimization. Appl Comput Intell Soft Comput 8
Pradhan M, Provas KR, Tandra P (2017) Oppositional based grey wolf optimization algorithm for economic dispatch problem of power system. Ain Shams Eng J 9:2015–2025
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors of the manuscript declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, A., Sharma, A. & Shekhawat, S. Parameter extraction of solar cell using intelligent grey wolf optimizer. Evol. Intel. 15, 167–183 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00499-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00499-1