Abstract
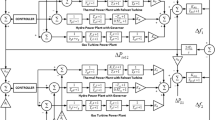
In this paper, application of evolutionary intelligence-based Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) algorithm has been presented to estimate the optimal parameters of Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller for load frequency control (LFC) in multi-source single area power network. The multi-source single area power network which is considered here is comprised of reheat turbine thermal power plant, gas power plant and hydro power plant with the mechanical hydraulic governor. In this paper, the parameters of PID controller for LFC of under study system are optimized using GWO algorithm by considering four important performance indices (instead of considering one or two) namely Integral of Time-weighted Squared Error (ITSE), Integral of Time-weighted Absolute Error (ITAE), Integral of Squared Error (ISE) and Integral of Absolute Error (IAE). The implemented technique has been compared with Genetic Algorithm (GA) technique for 1%, 2% and 5% load disturbances to show the effectiveness and applicability for LFC in multi-source single area power network.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dorigo M, Blum C (2005) Ant colony optimization theory: a survey. Theor Comput Sci 344:243–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2005.05.020
Poli R, Kennedy J, Blackwell T (2007) Particle swarm optimization: an overview. Swarm Intell 1:33–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11721-007-0002-0
Karaboga D, Basturk B (2007) A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J Glob Optim 39:459–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-007-9149-x
Fister I, Yang XS, Brest J (2013) A comprehensive review of firefly algorithms. Swarm Evol Comput 13:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2013.06.001
Bansal JC, Sharma H, Jadon SS, Clerc M (2014) Spider Monkey Optimization algorithm for numerical optimization. Memetic Comput 6:31–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12293-013-0128-0
Yang XS, Deb S (2014) Cuckoo search: recent advances and applications. Neural Comput Appl 24:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1367-1
Mirjalili S (2015) The ant lion optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 83:80–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2015.01.010
Yu JJQ, Li VOK (2015) A social spider algorithm for global optimization. Appl Soft Comput J 30:614–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.02.014
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007
Gupta E, Saxena A (2015) Robust generation control strategy based on Grey Wolf Optimizer. J Electr Syst 11:174–188
Chaman-Motlagh A (2015) Superdefect Photonic Crystal Filter Optimization Using Grey Wolf Optimizer. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett 27:2355–2358. https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2015.2464332
Sulaiman MH, Mustaffa Z, Mohamed MR, Aliman O (2015) Using the gray wolf optimizer for solving optimal reactive power dispatch problem. Appl Soft Comput J 32:286–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.03.041
El-Fergany AA, Hasanien HM (2015) Single and Multi-objective Optimal Power Flow Using Grey Wolf Optimizer and Differential Evolution Algorithms. Electr Power Components Syst 43:1548–1559. https://doi.org/10.1080/15325008.2015.1041625
Song X, Tang L, Zhao S et al (2015) Grey Wolf Optimizer for parameter estimation in surface waves. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 75:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.04.004
Komaki GM, Kayvanfar V (2015) Grey Wolf Optimizer algorithm for the two-stage assembly flow shop scheduling problem with release time. J Comput Sci 8:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2015.03.011
Mirjalili S (2015) How effective is the Grey Wolf optimizer in training multi-layer perceptrons. Appl Intell 43:150–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-014-0645-7
Zhang S, Zhou Y, Li Z, Pan W (2016) Grey Wolf optimizer for unmanned combat aerial vehicle path planning. Adv Eng Softw 99:121–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.05.015
Pradhan M, Roy PK, Pal T (2016) Grey wolf optimization applied to economic load dispatch problems. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 83:325–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2016.04.034
Mirjalili S, Saremi S, Mirjalili SM, Coelho LDS (2016) Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: a novel algorithm for multi-criterion optimization. Expert Syst Appl 47:106–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.039
Jayakumar N, Subramanian S, Ganesan S, Elanchezhian EB (2016) Grey wolf optimization for combined heat and power dispatch with cogeneration systems. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 74:252–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2015.07.031
Nuaekaew K, Artrit P, Pholdee N, Bureerat S (2017) Optimal reactive power dispatch problem using a two-archive multi-objective grey wolf optimizer. Expert Syst Appl 87:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.06.009
Ali M, El-Hameed MA, Farahat MA (2017) Effective parameters’ identification for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell models using grey wolf optimizer. Renew Energy 111:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.04.036
Şimşir Ş, Taşpınar N (2017) Pilot tones design using Grey Wolf Optimizer for OFDM–IDMA system. Phys Commun 25:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phycom.2017.08.010
Zhang S, Zhou Y (2017) Template matching using grey wolf optimizer with lateral inhibition. Optik (Stuttg) 130:1229–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.11.173
Liu H, Wu H, Li Y (2018) Smart wind speed forecasting using EWT decomposition, GWO evolutionary optimization, RELM learning and IEWT reconstruction. Energy Convers Manag 161:266–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.02.006
Gujarathi PK, Shah VA, Lokhande MM (2018) Grey wolf algorithm for multidimensional engine optimization of converted plug-in hybrid electric vehicle. Transp Res Part D Transp Environ 63:632–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2018.06.003
Dehghani M, Seifi A, Riahi-Madvar H (2019) Novel forecasting models for immediate-short-term to long-term influent flow prediction by combining ANFIS and grey wolf optimization. J Hydrol 576:698–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.06.065
Rana KPS, Kumar V, Sehgal N, George S (2019) A Novel [Formula presented] feedback based control scheme using GWO tuned PID controller for efficient MPPT of PEM fuel cell. ISA Trans 93:312–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2019.02.038
Nayak B, Mohapatra A, Mohanty KB (2019) Parameter estimation of single diode PV module based on GWO algorithm. Renew Energy Focus 30:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ref.2019.04.003
Manikandan K (2019) Diagnosis of diabetes diseases using optimized fuzzy rule set by grey wolf optimization. Pattern Recognit Lett 125:432–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.06.005
Shabeerkhan S, Padma A (2020) A novel GWO optimized pruning technique for inexact circuit design. Microprocess Microsyst 73:102975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpro.2019.102975
Kalemci EN, İkizler SB, Dede T, Angın Z (2020) Design of reinforced concrete cantilever retaining wall using Grey wolf optimization algorithm. Structures 23:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2019.09.013
Xianming L, Ping L, Baocun Z et al (2020) Localization of multiple leaks in a fluid pipeline based on ultrasound velocity and improved GWO. Process Saf Environ Prot 137:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.02.006
Ibraheem A, Kumar P, Kothari DP (2005) Recent philosophies of automatic generation control strategies in power systems. IEEE Trans Power Syst 20:346–357
Parmar KPS, Majhi S, Kothari DP (2014) LFC of an interconnected power system with multi-source power generation in deregulated power environment. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 57:277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.11.058
Barisal AK (2015) Comparative performance analysis of teaching learning based optimization for automatic load frequency control of multi-source power systems. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 66:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.10.019
Mohanty B, Panda S, Hota PK (2014) Controller parameters tuning of differential evolution algorithm and its application to load frequency control of multi-source power system. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 54:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2013.06.029
Tan W (2009) Tuning of PID load frequency controller for power systems. Energy Convers Manag 50:1465–1472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2009.02.024
Hassanat A, Almohammadi K, Alkafaween E et al (2019) Choosing mutation and crossover ratios for genetic algorithms-a review with a new dynamic approach. Inf 10:1–36. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10120390
Bhatt P, Roy R, Ghoshal SP (2011) Comparative performance evaluation of SMES-SMES, TCPS-SMES and SSSC-SMES controllers in automatic generation control for a two-area hydro-hydro system. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33:1585–1597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2010.12.015
García S, Fernández A, Luengo J, Herrera F (2010) Advanced nonparametric tests for multiple comparisons in the design of experiments in computational intelligence and data mining: experimental analysis of power. Inf Sci (Ny) 180:2044–2064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2009.12.010
Friedman M (1940) A Comparison of Alternative Tests of Significance for the Problem of m Rankings. Ann Math Stat 11:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177731944
Friedman M (1937) The Use of Ranks to Avoid the Assumption of Normality Implicit in the Analysis of Variance. J Am Stat Assoc 32:675–701. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1937.10503522
Davenport JM (1980) Approximations of the critical region of the friedman statistic. Commun Stat - Theory Methods 9:571–595. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610928008827904
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paliwal, N., Srivastava, L. & Pandit, M. Application of grey wolf optimization algorithm for load frequency control in multi-source single area power system. Evol. Intel. 15, 563–584 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00530-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00530-5